- Dutasteride
-
Dutasteride 
Systematic (IUPAC) name (5α, 17β)-N-{2,5 bis(trifluoromethyl) phenyl}-3-oxo-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide Clinical data Trade names Avodart AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a603001 Pregnancy cat. X(US) Not to be handled by pregnant women Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 60% Protein binding 99% Metabolism Hepatic (CYP3A4-mediated) Half-life 5 weeks Excretion Fecal Identifiers CAS number 164656-23-9 
ATC code G04CB02 PubChem CID 6918296 DrugBank APRD00385 ChemSpider 5293502 
UNII O0J6XJN02I 
KEGG D03820 
ChEBI CHEBI:521033 
ChEMBL CHEMBL1200969 
Chemical data Formula C27H30F6N2O2 Mol. mass 528.53 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Dutasteride (trade name Avodart by GlaxoSmithKline) is a dual 5-a reductase inhibitor that inhibits conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Dutasteride is FDA approved for treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and is also prescribed off-label for treatment of male pattern baldness (MPB).
Contents
Medical uses
Benign prostatic hyperplasia
Dutasteride is approved for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) (also known as enlarged prostate).
Male pattern baldness
Phase I and II clinical trials for dutasteride as a hair loss drug were undertaken, but called off in late 2002, with reasons for terminatation unknown.
The phase II results indicated that dutasteride at both 0.5 mg and 2.5 mg/day generated a superior hair count to finasteride 5 mg at 12 and 24 weeks.[1]
Phase II study results at 24 weeks:
- Placebo: - 32.3 hairs
- Finasteride 5 mg: + 75.6 hairs
- Dutasteride 0.1 mg: + 78.5 hairs
- Dutasteride 0.5 mg: + 94.6 hairs
- Dutasteride 2.5 mg: + 109.6 hairs
In December 2006, GlaxoSmithKline launched a new phase III, six month study in Korea to test the safety, tolerability and effectiveness of a once-daily dose of dutasteride (0.5 mg) for the treatment of MPB in the vertex region of the scalp (types IIIV, IV and V on the Hamilton-Norwood scale). The study was completed in January 2009.[2][3] Future intentions by GlaxoSmithKline to continue or abandon plans for FDA approval of dutasteride in treatment of male pattern baldness (MPB) remain unknown.
Contraindications
The teratogenic effect (abnormalities of physiological development) from dutasteride is harmful to male children. Women who are pregnant should not handle the capsules, as inadvertent consumption, such as skin contact, could cause birth defects of the male fetus. The adverse effects would be similar to 5-alpha-reductase deficiency, where a developing male child is naturally deficient in 5-alpha reductase type II, and thus unable to synthesize it. As dutasteride blocks the same process, developing males would have a DHT deficiency with its adverse effects as a result of the drug. Men who are taking dutasteride should not donate blood, and due to its long half-life, should also not donate blood for at least 6 months after the cessation of treatment. These precautions are to be taken in order to prevent the potential risk of causing birth defects in a pregnant woman who receives a transfusion with blood that contains dutasteride.[4]
Adverse effects
Clinical trial results
Month 0-6 ( n = 2,167 ) [5]
- Impotence: 4.7%
- Decreased libido: 3%
- Ejaculation disorders: 1.4%
- Breast disorders: 0.5%
Month 7-12 ( n = 1,901 ) [5]
- Impotence: 1.4%
- Decreased libido: 0.3%
- Ejaculation disorders: 0.5%
- Breast disorders: 1.1%
Month 13-18 ( n = 1,725 ) [5]
- Impotence: 1%
- Decreased libido: 0.1%
- Ejaculation disorders: 0.4%
- Breast disorders: 0.8%
Month 19-24 ( n = 1,605 ) [5]
- Impotence: 0.8%
- Decreased libido: 0.3%
- Ejaculation disorders: 0.1%
- Breast disorders: 0.6%
Observed in practice
The FDA has added warning to dutasteride about an increased risk of high-grade prostate cancer.[6] Whilst the potential for positive, negative or neutral changes to the potential risk of developing prostate cancer with dutasteride has not been established, evidence has suggested it may temporarily reduce the growth and prevalence of benign prostate tumors, but could also mask the early detection of prostate cancer. The primary area for concern is for patients who may develop prostate cancer whilst taking dutasteride for benign prostatic hyperplasia, which in turn could delay diagnosis and early treatment of the prostate cancer, thereby potentially increasing the risk of these patients developing high-grade prostate cancer.[7]
Mechanism of action
Dutasteride belongs to a class of drugs called 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors, which block the action of the 5-alpha-reductase enzymes that convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Finasteride, which is also approved for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), in addition to the treatment of male pattern baldness (MPB), belongs to this class of drugs. Dutasteride inhibits both isoforms of 5-alpha reductase, type I and type II, whereas finasteride only inhibits type II. There are no long-term randomized trials comparing the effects of dutasteride and finasteride in patients with BPH. The EPICS trial, a 12-month clinical study done by GlaxoSmithKline, demonstrated treatment with dutasteride and finasteride resulted in similar decreases in prostate volume, with numerically but not statistically significantly greater improvements in symptom scores for the dutasteride group.[8] Finasteride is marketed by Merck under trademark names Proscar (5 mg/day finasteride) for BPH and Propecia (1 mg/day finasteride) for MPB. Published data from controlled clinical trials demonstrated the 5 mg dose of finasteride did not produce better results than the 1 mg dose.[9]
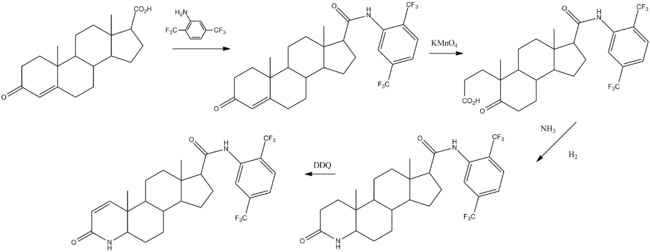
Chemical synthesis
 Avodart (dutasteride) 500 µg capsules
Avodart (dutasteride) 500 µg capsules
Batchelor, K. W.; Frye, S. V.; Dorsey, G. F.; Mook, R. A.; 1996, U.S. Patent 5,565,467.
See also
- Finasteride, related 5-alpha reductase inhibitor.
References
- ^ Olsen EA, Hordinsky M, Whiting D, et al. (Dec 2006). "The importance of dual 5alpha-reductase inhibition in the treatment of MPB: results of a randomized placebo-controlled study of dutasteride versus finasteride". J Am Acad Dermatol. 55 (6): 1014–23. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2006.05.007. PMID 17110217.
- ^ ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00441116
- ^ Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of dutasteride 0.5 mg once daily in male patients with male pattern hair loss: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III study | Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology (JAAD)
- ^ Avodart Information | Drugs.com
- ^ a b c d Avodart Side Effects | Drugs.com
- ^ 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs): Label Change - Increased Risk of Prostate Cancer | U.S. Department of Health & Human Services
- ^ Walsh, PC (2010 Apr 1). "Chemoprevention of prostate cancer.". The New England journal of medicine 362 (13): 1237–8. doi:10.1056/NEJMe1001045. PMID 20357287.
- ^ Managing the progression of lower urinary tract symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia: therapeutic options for the man at risk | UroToday
- ^ Propecia (Finasteride) - See "Increasing the Dose" | Bernstein Medical Center for Hair Restoration
External links
Drugs used in benign prostatic hypertrophy (G04C) 5α-reductase inhibitors Dutasteride • FinasterideAlpha blockers (α1) Herbals Pygeum africanum • Saw palmetto extractOther Categories:- 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors
- GlaxoSmithKline
- Lactams
- Organofluorides
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.