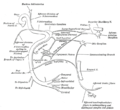
- Otic ganglion
-
Nerve: Otic ganglion 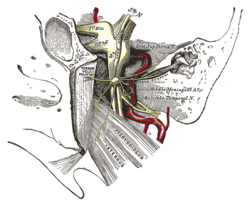
The otic ganglion and its branches. 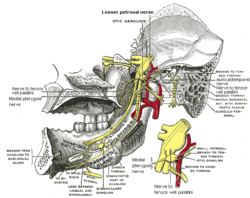
Mandibular division of trifacial nerve, seen from the middle line. The small figure is an enlarged view of the otic ganglion. Latin ganglion oticum Gray's subject #200 897 Innervates parotid gland From lesser petrosal nerve The otic ganglion is a small, oval shaped, flattened parasympathetic ganglion of a reddish-gray color, located immediately below the foramen ovale in the infratemporal fossa. It gives innervation to the parotid gland for salivation.
It is one of four parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck. (The others are the submandibular ganglion, pterygopalatine ganglion, and ciliary ganglion).
It is occasionally absent.[1]
Contents
Filaments
Filaments that pass through the ganglion without synapsing:
- Nerve to tensor tympani (coming from the trigeminal nerve motor nucleus)
- Nerve to tensor veli palatini (coming from the trigeminal nerve motor nucleus)
- Nerve to levator veli palatini (coming from facial nerve thought to run through the chorda tympani)
Branches of communication
Its sympathetic postganglionic fibers consists of a filament from the plexus surrounding the middle meningeal artery.
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres reach it from the glossopharyngeal nerve (and possibly also from the facial nerve) via the lesser petrosal nerve continued from the tympanic plexus. Postganglionic parasympathetic fibres from the ganglion pass with the sympathetic fibres mainly in the auriculotemporal nerve (a branch of CN V3 -- the Mandibular branch of the Trigeminal Nerve) to supply the parotid gland. All postsynaptic parasympathetics will use some branch of the Trigeminal Nerve to get from one of four parasympatheic ganglia (Otic, Ciliary, Submandibular, and Peteryopalatine) to their destination in either smooth muscle or glandular tissue (secretomotor).
A slender filament (sphenoidal) ascends from it to the nerve of the Pterygoid canal, and a small branch connects it with the chorda tympani.
It is connected by two or three short filaments with the nerve to the Pterygoideus internus, from which it may obtain a motor, and possibly a sensory root.
Distribution
Its branches of distribution are: a filament to the Tensor tympani, and one to the Tensor veli palatini.
The former passes backward, lateral to the auditory tube; the latter arises from the ganglion, near the origin of the nerve to the Pterygoideus internus, and is directed forward.
The fibers of these nerves are, however, mainly derived from the nerve to the Pterygoideus internus.
Additional images
References
- ^ Roitman R, Talmi YP, Finkelstein Y, Sadov R, Zohar Y (1990). "Anatomic study of the otic ganglion in humans". Head Neck 12 (6): 503–6. doi:10.1002/hed.2880120610. PMID 2258290.
- Shimizu T (1994). "Distribution and pathway of the cerebrovascular nerve fibers from the otic ganglion in the rat: anterograde tracing study". J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 49 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1016/0165-1838(94)90019-1. PMID 7525688.
External links
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (V, IX)
- Otic+ganglion at eMedicine Dictionary
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Nerves of head and neck: the cranial nerves and nuclei (TA A14.2.01, GA 9.855) olfactory (AON->I) optic (LGN->II) oculomotor
(ON, EWN->III)trochlear (TN->IV) no significant branchestrigeminal
(PSN, TSN, MN, TMN->V)abducens (AN->VI) no significant branchesfacial (FMN, SN, SSN->VII) near origininside
facial canalvestibulocochlear
(VN, CN->VIII)glossopharyngeal
(NA, ISN, SN->IX)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossatympanic (tympanic plexus, lesser petrosal, otic ganglion) • stylopharyngeal branch • pharyngeal branches • tonsillar branches • lingual branches • carotid sinusvagus
(NA, DNVN, SN->X)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossaaccessory (NA, SAN->XI) hypoglossal (HN->XII) The cranial nerves: trigeminal nerve ophthalmic
(V1)frontal: supratrochlear · supraorbital (lateral branch, medial branch)
nasociliary: long ciliary · infratrochlear · posterior ethmoidal · anterior ethmoidal (external nasal, internal nasal) · sensory root of ciliary ganglion (ciliary ganglion)
lacrimalmaxillary
(V2)in meningeszygomatic (zygomaticotemporal, zygomaticofacial) · pterygopalatine (pterygopalatine ganglion see below for details) · posterior superior alveolaron facemandibular
(V3)in meningesanteriorposteriorauriculotemporal (otic ganglion) · lingual (submandibular ganglion) · inferior alveolar (mylohyoid, mental)Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.