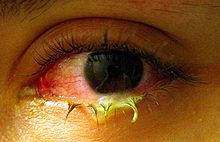
- Pus
-
For other uses, see Pus (disambiguation).
 An abscess is an enclosed collection of pus
An abscess is an enclosed collection of pus
 Duodenoscopy image of hepatopancreatic ampulla with pus extruding from it, indicative of cholangitis
Duodenoscopy image of hepatopancreatic ampulla with pus extruding from it, indicative of cholangitis
Pus is a viscous exudate, typically whitish-yellow, yellow, or yellow-brown, formed at the site of inflammatory during infection.[1] An accumulation of pus in an enclosed tissue space is known as an abscess, whereas a visible collection of pus within or beneath the epidermis is known as a pustule or pimple.
Pus consists of a thin, protein-rich fluid, known as liquor puris, and dead leukocyte of the body's immune response (mostly neutrophils). During infection, macrophages release cytokines which trigger neutrophils to seek the site of infection by chemotaxis. There, the neutrophils engulf and destroy the bacteria and the bacteria resist the immune response by releasing toxins called leukocidins.[2]. As the neutrophils die of from toxins and old age, they are destroyed by macrophages, forming the viscous pus.
Bacteria that cause pus are called suppurative, pyogenic[3][2], or purulent. If the agent also creates mucus, it is called mucopurulent. Purulent infections can be treated with an antiseptic.
Despite normally being of a whitish-yellow hue, changes in the color of pus can be observed under certain circumstances. Pus is sometimes green because of the presence of myeloperoxidase, an intensely green antibacterial protein produced by some types of white blood cells. Blue-green pus is found in certain infections of Pseudomonas aeruginosa as a result of the pyocyanin bacterial pigment it produces; amoebic abscesses of the liver produce brownish pus. Pus can also have a foul odor.
In almost all cases when there is a collection of pus in the body, the clinician will try to create an opening for it to evacuate - this principle has been distilled into the famous Latin aphorism "Ubi pus, ibi evacua!"
Some common disease processes caused by pyogenic infections are impetigo, osteomyelitis, septic arthritis, and necrotizing fasciitis.[4]
Pyogenic bacteria
A great many species of bacteria may be pyogenic. The most commonly found include:[5]
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Staphylococcus epidermidis
- Streptococcus pyogenes
- Escherichia coli (Bacillus coli communis)
- Streptococcus pneumoniae (Fraenkel's pneumococcus)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae (Friedländer's bacillus)
- Salmonella typhi (Bacillus typhosus)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Actinomyces
- Burkholderia mallei (Glanders bacillus)
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis (tubercle bacillus)
See also
References
- ^ "Pus - Definitions from Dictionary.com". reference.com. http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/Pus. Retrieved 2008-08-18.
- ^ a b Madigan, Michael T. and Martin, John M. Brock Biology of Microorganisms 11th ed. Pearson Prentice Hall. USA. 2006: 734
- ^ "pyogenic" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ "Infections Caused by Common Pyogenic Bacteria", Dermatopathology (Springer Berlin Heidelberg): pp. 83–85, doi:10.1007/3-540-30244-1_12
- ^ Thompson, Alexis; Miles, Alexander (1921). "Pyogenic Bateria". Manual of Surgery. Oxford Medical Publications. http://www.manual-of-surgery.com/content/0013-Pyogenic-Bacteria.html.
Categories:- Body fluids
- Immune system
- Medical terms
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.