- Chasqui I
-
Chasqui I Operator  Peru National University of Engineering
Peru National University of EngineeringMission type Scientific Satellite of Earth Orbits Low Earth orbit Launch date 2010 Homepage chasqui.uni.edu.pe Mass 180 grams Chasqui I is a one-kilogram satellite equipped with two cameras, a visible and an infrared, which will take photos of the Earth. Nanotechnology can adapt to this satellite very small size electronic circuits, and cells that capture solar energy and transform it into energy to operate the device.
The Chasqui I is being developed by students at UNI and is part of the satellite project that seeks to acquire the experience and ability in developing satellites. UNI in collaboration with the European Space Agency is already working on Chasqui II satellite and other project is the UNI-KURSK microsatellite developed in collaboration with the University of Kursk (Russia).
General Objectives
Capacities of UNI in satellite technology through the design, analysis, assembly, integration, test, launch and operation of a technology nanosatellite Cubesat. The satellite Chasqui I will take pictures of the earth and transmit it to the ground station.
Specific Objectives
- Establish contacts and support to other universities and / or institutions involved in such projects.
- To deepen the knowledge in information and communications technologies emerging.
- To lead such projects in Latin America.
- To demonstrate and validate new technologies.
Goals
- Design of the project profile.
- Funding.
- Capacity building.
- Implementation of the Laboratory.
- Development of the project.
- Testing integrated.
- Guidelines.
- Operation
Project
 Chasqui I in space
Chasqui I in space
The nanosatellite Chasqui I research project is an effort to secure Peru's first access to space and gives the opportunity to open new application areas specific to its own geographical and social reality. It is also from an academic point of view a tool that facilitates collaboration between the various faculties of the university trains students and teachers with real world experience in satellite, allowing technological advances in the aerospace industry in our country. Develop scale satellites Chasqui I gives way to the various opportunities of access to space with lower costs and development time. For this reason, various universities, companies and government organizations in the world show interest in developing nanosatellites that allow to carry out experiments and scientific missions. The educational benefits of the project can be emphasized in training camp for future engineers and scientists.
 Chasqui I logo
Chasqui I logo
The research project Chasqui I nanosatellite aims to build a miniaturized satellite based on the CubeSat technology, the mass of the satellite will be less than 1 kg and have a volume of up to 1 Lt. The project demonstrates its utility in image capture land, more specifically from the Peruvian region, using a CMOS camera that seeks to distinguish between fertile land and uncultivated areas. To minimize the cost of development and construction, Chasqui I will be constructed using commercial components. However, the very fact of using these components in a space environment present new challenges in relation to tolerance to temperature and radiation and also present increased requirements in areas related to redundancy when designing hardware and software components. Additionally, the Chasqui I will use the amateur radio frequency, making it possible to be accessed by an entire amateur radio community can be located throughout the country, increasing the educational potential of the project. The project also includes the implementation of a ground station that allows monitoring of Chasqui I, as well as monitoring other small satellites of universities.
Peru has a great geographical diversity, which makes it very difficult to constantly monitor the situation of certain events, whether natural or man-made, such as permanent snow melting, deforestation of the Amazon, the protection habitats of endangered species, combating narco-terrorism, surveillance of our borders and territorial sea, the prediction and mitigation of natural disasters, etc.. It is in this context that space technology is presented as an alternative to solve problems of national interest. UNI, with its project Chasqui I are taking the first steps in the process of addressing problems such as crop monitoring and telecommunications areas.
The project Chasqui I, which initially was formative in nature, has evolved into a technological and scientific challenge for all members of the project. It is expected that Chasqui I allowed to plant the foundations for future work in the area of small satellites and, to be increasing their size or number, give rise to satellite projects in different categories, in areas such as: communications, meteorology, remote sensing, earth images, navigation and oceanography.
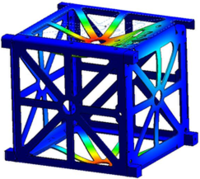
Outline of the Project Development Modules
 Outline of the Project Development Modules
Outline of the Project Development Modules
Project Modules
Mechanical Structure - EMEC
The research group module mechanical structure (EMEC) is responsible for reviewing the state of art, comparative analysis of existing cases to the pico-satellite design and manufacture our own model based on the Standard Cubesat.
Within the pico-satellite will be assembled the following modules: Central Control and Management Information (CCMI), Unit Identification and Attitude Control (DCA), Imaging Management System (SIMA), Unit Power and Thermal Control (PCT) and Communications System (SICOM).
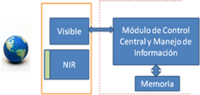
Central Control and Information Management - CCMI
This module manages and monitors information from all subsystems Chasqui I. The module to meet the goals set must have within it a processor (called OBC: On Board Computer), which fulfills the following functions in each module:
- Camera (SIMA): Regulates the satellite image capture and storage in an external memory.
- Attitude (DCA): Order and confirms the stabilization order and spatial orientation.
- Power (PCT): Manages and monitors satellite states of physical variables such as temperature, voltage and current.
- Communication (SICOM) ground station receives orders and sends the information of camera data and pico-satellite states
The data managed are: Data from the camera, Data Maintenance and commands.
Power and Thermal Control - PCT
 Energy Cycle Chasqui I
Energy Cycle Chasqui I
The first subsystem is the Power and is responsible for receiving, processing, storing and distributing power to other subsystems in the Chasqui I. The objective of this subsystem is to ensure electricity supply for Chasqui I give it the energy needed at the right time.
The second subsystem is the Thermal Control and he is responsible for maintaining the temperature of the batteries and other components of the satellite in its operating range, in order to ensure the functioning of Chasqui I. The most critical task of this subsystem is to maintain the batteries to operate within its limit of operation (0 °C to 20 °C.). Through heaters specifically designed and constructed at the National University of Engineering.
Both subsystems are being designed and built at the National Engineering University.
Communication System - SICOM
The TT & C module is responsible to provide a means of communication between the peak itself and the satellite earth station.
Image Acquisition System - SIMA
The main objective of the research group is to obtain photographs of the Earth from Chasqui I. SIMA The module consists of two cameras, a visible range and the other in the near infrared range. Digital information is collected by the Central Control Module and Management Information (CCMI) and then sent to the Earth Station (ESTER).
Additionally, the Group is responsible for processing digital images obtained by the Chasqui I.
System Identification and Attitude Control - SDCA
 System Identification and Attitude Control
System Identification and Attitude Control
The SDCA maintains the pico-satellite stabilization and guidance to a desired direction when necessary. Specifically, we can say that SDCA is responsible for:
- Stabilize the pico-satellite after leaving the deployer through reduction (within 0.1rad / s) and control their angular velocities.
- Maintain a pointing accuracy of 3 degrees for taking pictures of Peru and, if technically possible, having a wide coverage of South America through maneuvers of 30 degrees in roll (roll) and 30 degrees pitch (pitch).
- Maintain a less demanding pointing accuracy (e.g. 20 degrees) to enable up / down data between the pico-satellite and ground station.
The SDCA enables the pico-satellite by using sensors to determine its attitude, calculate the correction required to achieve the desired orientation and execute the necessary maneuvers using the actuators. The attitude determination system will use magnetometers, sun sensors and attitude determination algorithms for estimating positions and angular velocities. Using a GPS and gyroscopes as sensors for determining attitude will also be evaluated. The attitude control system will use electromagnetic coils and permanent magnets as actuators. The electromagnetic coils are especially important for the stabilization of the pico-satellite once it leaves the deployer. The inclusion of the permanent magnet can have a system of active-passive control. More than one control law will be studied for possible implementation. The use of magnetic materials and hysteretic also be evaluated.
Ground Station - ESTER
 Block Diagram - ESTER
Block Diagram - ESTER
This subsystem is not part of the satellite itself, but its existence and operation is necessary to achieve the objectives of Chasqui I. The set of facilities and wireless communication (radio) needed to communicate with the Chasqui I, and any satellite.
The main functions of this module are:
- Follow-up: radioforo hear the beacon or satellite for its position.
- Telemetry: Request state variables (temperature, voltage, etc..) To monitor and validate the satellite orbit calculation.
- Commando: Order to extend the satellite antenna; order reset the system, order the taking and sending photos.
System Orbits - SORS
 Trajectory of Chasqui I
Trajectory of Chasqui I
The module aims to simulate the trajectories of Chasqui I, which is previously calculated differential equations of motion and then solve them in parallel with two programs: Delphi and Matlab.
This simulation is accomplished by taking into consideration the following phases:
- Considering the Earth as an inertial reference system, the quadrupole term of the gravitational potential and using Newton's second law, we obtained the equations of motion are nonlinear equations.
- Using the Runge-Kutta of order 4 with the Delphi program to solve the equations of motion energy remaining constant.
- Phase 2 was repeated with the Matlab program and with this software are carried out trajectory simulations Chasqui I.
Module Integration and Testing - MIP
The module aims to achieve the assembly of components developed by different modules of the project as electronic circuit boards, cameras, batteries, antennas, sensors, and electromagnetic coils.
This goal can be achieved:
- Optimizing surfaces, volumes, masses, finding center of gravity, center of mass.
- Planning and conducting standardized testing requirements.
- Perform field tests planned in the project.
See also
External links
- National University of Engineering Home of this public university located in Lima Peru.
- CTIC - UNI Center for Information & Communication Technologies (CTIC-UNI).
- Project Official Site Chasqui 1 All information relating to the project.
Categories:- Student satellites
- CubeSats
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.