- App Store (iOS)
-

Screenshot of the desktop App Store in iTunes.Developer(s) Apple Inc. Initial release July 10, 2008 Development status Active Operating system iOS,
Mac OS X Tiger or later
Windows XP or later.Platform iPhone, iPod touch, iPad Type Digital distribution, Software update License Proprietary freeware Website apple.com/itunes The App Store is a digital application distribution platform for iOS developed and maintained by Apple Inc. The service allows users to browse and download applications from the iTunes Store that were developed with the iOS SDK or Mac SDK and published through Apple Inc.. Depending on the application, they are available either for free or at a cost. The applications can be downloaded directly to a target device, or downloaded onto a PC or Mac via iTunes. 30% of revenue from the store go to Apple, and 70% go to the producer of the app.[1] The App Store opened on July 10, 2008 via an update to iTunes. On July 11, the iPhone 3G was launched and came pre-loaded with iOS 2.0.1 with App Store support; new iOS 2.0.1 firmware for iPhone and iPod Touch was also made available via iTunes.[2] As of June 6, 2011, there are at least 425,000 third-party apps officially available on the App Store.[3] As of January 18, 2011, the App Store had over 9.9 billion downloads, which was announced via the company's "10 Billion App Countdown".[4] At 10:26 AM GMT on Saturday, January 22, 2011,[5] the 10 billionth app was downloaded from Apple App Store. At early July 2011, 200 million iOS users have downloaded over 15 billion apps from its App Store.[6] The mean revenue per application is estimated to be US$8,700, although data is not publicly available.[7] As of May 2011, Apple approved its 500,000th app and 37 percent of all apps are free with the average price $3.64.[8] The distribution of price follows a power law distribution (the Zipf–Mandelbrot law). Prices can be freely chosen by sellers at multiple of US$1 minus 1 cent (99c, $1.99, and so on).
After the success of Apple's App Store, and the launch of similar services by its competitors, the term "app store" has been adopted to refer to any similar service for mobile devices.[9][10][11][12] However, Apple applied for a trademark on the term App Store in 2008 [13] [14] which was tentatively approved in 2011 .[15] Later, in June 2011, U.S. District Judge Phyllis Hamilton, who is presiding over Apple's case against Amazon, said she'll "probably" deny Apple's motion that seeks to bar the Web retailer from using the "App Store" name.[16][17][18] Later on July 6th, Apple was denied preliminary injunction against Amazon's Appstore by a federal judge.[19]
The term app has become a popular buzzword; in January 2011, app was awarded the honor of being 2010's "Word of the Year" by the American Dialect Society.[20] Apple does not hold a trademark on, or claim exclusive rights to the term app, which has been used as shorthand for "application" since at least 2002, for example Google Apps (first introduced in 2006).[21]
On October 20, 2010, Apple announced the Mac App Store which was eventually launched on January 7, 2011. It is similar to the one for iOS devices, only it has applications designed for Mac computers.[22] The Mac App Store is only accessible by using Mac OS X Snow Leopard or Mac OS X Lion.
The App Store is accessible from the iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad via an iOS application by the same name. It is also the only way to directly download native applications onto an iOS device without jailbreaking the device. Web applications can be installed on these devices, bypassing the App Store entirely, but they tend to have less functionality. The store is also accessible through iTunes, and then on any operating system for which iTunes is provided (Mac OS X and Windows[23]).
In February 2011, Apple announced its new subscription based service which will allow publishers to set the length and price of a subscription. Previously, new magazine or news releases would be sold on a per release basis. The new service allows publishers to sell their content through their apps allowing users to receive the new content over specified period of time. More interesting is that Apple will allow publishers not only to sell from iTunes where revenue will be shared (70% for the publisher, 30% for Apple), but they are also allowing publishers to distribute their subscriptions directly from their websites where no revenue will be shared with Apple.[24]
Contents
iPhone SDK
Main article: iPhone SDKThe Software Development Kit for iPhone OS was announced at the iPhone Software Roadmap event on March 6, 2008. The SDK allows developers running Mac OS X 10.5.4 or higher on an Intel Mac to create applications using Xcode that will natively run on the iPhone, iPod Touch and iPad. A beta version was released after the event and a final version was released in July 2008 alongside the iPhone 3G.[25] This major Roadmap event (coupled with a large distribution program for 3rd-party developers), later became known as the iPhone Developer Program, which currently offers two distribution tracks for 3rd-party developers: Standard, and Enterprise.[26]
Applications distributed through the standard program can be sold exclusively through the iTunes Store on Mac and Windows, or on the App Store on the iPhone, iPod Touch, and iPad.[26] Developers who publish their applications on the App Store will receive 70% of sales revenue, and will not have to pay any distribution costs for the application. However, an annual fee is required to use the iPhone SDK and upload applications to the store.[25]
Applications developed through the enterprise program, officially the "iOS Enterprise Developer Program" (iDEP), are exclusively for institutional use and do not get published on the App Store. This allows corporations, non-profits and government agencies to develop proprietary "in-house" applications not for public release.[26] The enterprise program was updated September 14, 2010, to allow any organization with a DUNS number to join. Prior to this date, only organizations with 500 or more employees could join the enterprise program.
To run an application on the iPhone, the application needs to be signed. This signed certificate is only granted by Apple after the developer has first developed the software through either the US$99/year Standard package or the US$299/year Enterprise package with the iPhone SDK.[25]
Number of launched applications
On July 10, 2008, Apple CEO Steve Jobs told USA Today that the App Store contained 500 third-party applications for the iPhone and the iPod Touch, and of these 25% were free.[27] These third party applications range from business to game applications, entertainment to educational applications, and many more applications available for free or for sale. On July 11, 2008 the store opened, allowing users to buy applications and transfer them to an iPhone or iPod Touch with the iPhone 2.0 software update, which became available through iTunes on the same day. Ten million applications were downloaded the first weekend.[28]
On January 16, 2009, Apple announced on its website that 500 million applications had been downloaded.[29] The billionth application was downloaded on April 23, 2009.[30]
Unlike the apps that come standard on the iPhone, apps downloaded from the App Store can be removed by the user at a future date.
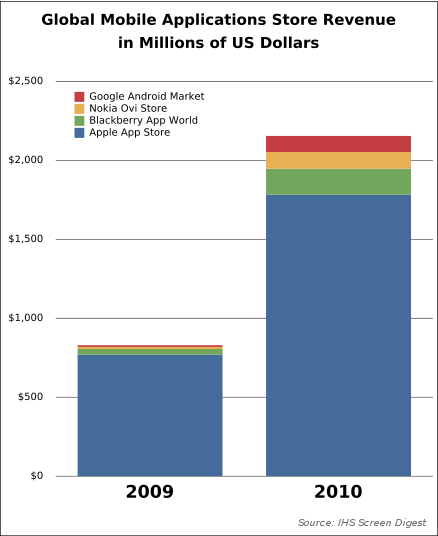
Besides downloading volumes, the App Store's relatively high revenue of US$1782 million in 2010 may be attributed to it having only 28% of free apps, in comparison to Android Market's over 57% of free apps. As a result, both Nokia's Ovi Store and BlackBerry's App World, both of which have only 26% free apps, also pull in higher revenues than Android Market despite having much lower downloading volumes.[31]
Milestones
Date Available apps Downloads to date July 11, 2008[32] 500 0 July 14, 2008[28] 800 10,000,000 September 9, 2008[33] 3,000 55,000,000 October 22, 2008[34] 7,500 200,000,000 January 16, 2009[29] 15,000 500,000,000 March 17, 2009 [35] 25,000 800,000,000 April 23, 2009[30] 35,000 1,000,000,000 June 8, 2009[36] 50,000 1,000,000,000+ July 11, 2009[citation needed] 55,000 1,000,000,000+ July 14, 2009[37] 65,000 1,500,000,000 September 9, 2009 75,000 1,800,000,000 September 28, 2009[38][39] 85,000 2,000,000,000 November 4, 2009[40][41] 100,000 2,000,000,000+ January 5, 2010[42][43] 120,000 3,000,000,000+ March 20, 2010[44] 150,000+ 3,000,000,000+ April 8, 2010[45] 185,000+ 4,000,000,000+ April 29, 2010[46] 200,000+ 4,500,000,000+ June 7, 2010[47] 225,000+ 5,000,000,000+ September 1, 2010[48] 250,000+ 6,500,000,000+ October 20, 2010 300,000+[49] 7,000,000,000[50] Jan 22, 2011[51] 350,000+ 10,000,000,000+ June 6, 2011[3] 425,000+ 14,000,000,000+ July 7, 2011[52] 425,000+ 15,000,000,000+ October 4, 2011 [53] 500,000+ 18,000,000,000+ iPad Applications
The iPad launched in April 2010 with over 3000 applications designed for the iPad. By December 2010, just eight months after the release of the iPad, over 50,000 apps were available for the device.
As of July 2011, 16 months after the iPad launched, there are over 100,000 apps available at the App Store designed specifically for the device.[54]
On the July 7, 2011, Apple announced that over 15 billion apps had been downloaded from the iOS app store.[52] But, micro level information on the number of downloads of each ranked application has not been made available. To help app producers with their marketing effort and help researchers in better understanding the Apple's iOS app store, a recent research study[55] has tried to estimate the model that converts the app rank to daily downloads. Researchers Garg and Telang from Carnegie Mellon University found that the app downloads follow a Pareto distribution and can be estimated using the equations:
iPad_app_downloads = 9,525 * paid_app_rank^(-0.903)
iPhone_app_downloads = 52,511 * paid_app_rank^(-0.944)
NOTE: this claim has not been verified by Apple or any other market research organization.Most popular apps
In April 2009, Apple announced the apps which had the most number of downloads since the store was launched. Among paid apps, Crash Bandicoot Nitro Kart 3D, by Activision Publishing, was ranked first, while Facebook enjoyed the same position among free apps, followed by Google Earth.[56] Other popular apps include Angry Birds and apps made by Ragdoll Studios. Whatsapp is the most popular app for messaging between BB, Android and iPhone. It works similar to the BB messenger.
Application ratings
Apple rates applications worldwide based on their content, and determines what age group each is appropriate for. According to the iPhone OS 3.0 launch event, the iPhone will allow blocking of objectionable apps in the iPhone's settings. The following are the ratings that Apple has detailed:
Rating Description 4+ Contains no objectionable material. 9+ May contain mild or infrequent occurrences of cartoon, fantasy or realistic violence, and infrequent or mild mature, suggestive, or horror-themed content which may not be suitable for children under the age of 9. 12+ May also contain infrequent mild language, frequent or intense cartoon, fantasy or realistic violence, and mild or infrequent mature or suggestive themes, and simulated gambling which may not be suitable for children under the age of 12. 17+ May also contain frequent and intense mature, horror, and suggestive themes; plus strong sexual content, nudity, strong language, alcohol, tobacco, and drugs which may not be suitable for children under the age of 17. Also, if the app accesses the internet it is rated 17+. Consumers must be at least 17 years old to purchase apps with this rating. Whenever an app of this rating is requested for download, a message will appear, verifying if a user is 17 or older, and asking to confirm the purchase for this reason. App approval process
Main article: Approval of iOS appsApplications are subject to approval by Apple, as outlined in the SDK agreement, for basic reliability testing and other analysis. Applications may still be distributed "ad-hoc" if they are rejected, by the author manually submitting a request to Apple to license the application to individual iPhones, although Apple may withdraw the ability for authors to do this at a later date.
Non-disclosure agreements (NDA) have always forbidden developers from publishing the content of their rejection notices, but Apple has now started labeling their rejection letters with Non-Disclosure (NDA) warning THE INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MESSAGE IS UNDER NON-DISCLOSURE. Apple later changed the NDA citing that "it has created too much of a burden on developers" but they did not reverse the decision to forbid publication of rejection notices. Some applications are not available outside the US App Store at the request of the developer. Since so many developers have published rejection emails Apple now most often call submitters to verbally tell them their rejection notice.
In addition, Apple has removed software licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) from the App Store after complaints from one of the program's developers, claiming that the App Store's terms of service are inconsistent with the GPL.[57][58]
Enterprise App Stores
Because Apple's App Store is for consumers, companies are unable to distribute in-house apps on the App Store. Under Apple's iOS Developer Enterprise Program companies can publish in-house apps using an Enterprise App Store[59] with systems such as Apperian EASE[60] or a Mobile Device Management platform such as Sybase Afaria.
Apps published with Apple's iOS Developer Enterprise Program are still subject to Apple's control via the controversial kill switch,[61] where Apple can revoke a publisher's digital certificate and thereby "kill" the app on user devices. However, there is no evidence that this has been done in the enterprise environment.
Similar services for other devices
Competitors also have their own stores for mobile applications. Palm Inc. published an application store similar to the App Store for Palm devices[62] and announced the App Catalog for webOS on the Palm Pre that was released on June 6, 2009. Another platform, Android Market is used in conjunction with Google's Android operating system. Microsoft has released Windows Phone Marketplace, an application store for their Windows Phone platform. Nokia has released The "Ovi Store"[63] (which replaced its earlier "Download!" application, which predated Apple's App Store) for its S60 and S40 based mobile devices. Samsung has created Samsung Apps, primarily to cater for its own Bada OS, but also with support for certain other Samsung devices. RIM also launched its application store BlackBerry App World.[64] The Nintendo DSi is able to connect to an online store called the "DSi Shop", along with Sony's PlayStation Portable (PSP) being able to connect to PlayStation Store to download games, etc. The Nintendo 3DS also has its own application distribution platform, called the Nintendo eShop.
References
- ^ "Analyst: There’s a great future in iPhone apps", Venture Beat, June 11, 2008.
- ^ "Apple Introduces the New iPhone 3G". Apple. 2008-06-09. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2008/06/09iphone.html. Retrieved 2009-09-16.
- ^ a b "Apple Special Event, June 6, 2011". Apple. June 6, 2011. http://www.apple.com/apple-events/wwdc-2011/.
- ^ "10 Billion App Countdown" Apple 2011-01-14.
- ^ 10:26 AM GMT on Saturday, January 22, 2011 setteB.IT 2011-01-22.
- ^ http://techcrunch.com/2011/07/07/apples-app-store-crosses-15b-app-downloads-adds-1b-downloads-in-past-month/?utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+Techcrunch+%28TechCrunch%29
- ^ "Full Analysis of iPhone Economics - it is bad news. And then it gets worse". Communities Dominate Brands. 2010-06-22. http://communities-dominate.blogs.com/brands/2010/06/full-analysis-of-iphone-economics-its-bad-news-and-then-it-gets-worse.html.
- ^ http://news.yahoo.com/s/yblog_technews/20110524/tc_yblog_technews/apple-approves-its-500000th-app-but-do-you-care
- ^ Carew, Sinead (22 April 2009). "In app store war, BlackBerry, Google hold own". Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/technologyNews/idUSTRE53L5DK20090422. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ^ Furchgott, Roy (29 May 2009). "Nokia’s App Store Launches With a Hiccup". The New York Times. http://gadgetwise.blogs.nytimes.com/2009/05/29/nokias-app-store-launches-with-a-hiccup/. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ^ Ganapati, Priya (4 March 2009). "BlackBerry App Store Gets a Name". Wired. http://www.wired.com/gadgetlab/2009/03/blackberry-app/. Retrieved 23 June 2009.
- ^ Shiels, Maggie (2009-07-20). "Technology | Apps 'to be as big as internet'". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/technology/8157043.stm. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ "Apple files for MacRuby, App Store & Finder trademarks". MacNN. 22 July 2008. http://www.macnn.com/blogs/2008/07/22/apple-files-for-macruby-app-store-finder-trademarks.html. Retrieved 27 Aug 2009.
- ^ "Trademark application". United States Patent and Trademark Office. 21 July 2008. http://tarr.uspto.gov/tarr?regser=serial&entry=77%2F525433&action=Request+Status. Retrieved 18 Apr 2011.
- ^ "How Apple Can Trademark 'App Store'". PC Magazine. 1 Apr 2011. http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2382968,00.asp. Retrieved 18 Apr 2011.
- ^ http://news.cnet.com/8301-27076_3-20073524-248/judge-likely-to-deny-apples-appstore-complaint/
- ^ http://www.businessweek.com/news/2011-06-22/apple-bid-to-bar-amazon-appstore-will-likely-be-denied.html
- ^ "Apple may have tough road in Amazon lawsuit". Reuters. 2011-06-22. http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/06/22/us-apple-amazon-idUSTRE75L79Y20110622.
- ^ http://arstechnica.com/apple/news/2011/07/apples-preliminary-injunction-against-amazons-appstore-denied.ars
- ^ "Linguists vote 'app' Word of the Year". The Associated Press. 2011-01-07. Retrieved 2011-01-27.
- ^ http://www.google.co.uk/#q=app+-application&hl=en&lr=&sa=X&rls=com.microsoft:en-us&tbs=cdr:1,cd_min:1/1/1998,cd_max:31/12/2007&fp=1&cad=b
- ^ Apple unveils new MacBook Airs, previews Lion | Beyond Binary - CNET News
- ^ February 2011 "iTunes Download site". http://www.apple.com/itunes/download/accessdate=26 February 2011.
- ^ Thomasch, Paul (15 February 2011). "Apple rolls out subscription service". Toronto: Globe&Mail newspaper. http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/technology/tech-news/apple-rolls-out-subscription-service/article1907736/. Retrieved 15 February 2011.
- ^ a b c Apple Inc. (2008-03-06). "Apple Announces iPhone 2.0 Software Beta". Apple.com. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2008/03/06iphone.html. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ a b c Apple Inc.. "iPhone Developer Program - Enterprise Distribution". Developer.apple.com. http://developer.apple.com/iphone/program/distribute.html. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ "Jobs: App Store launching with 500 iPhone applications, 25% free". Engadget. 2008-07-10. http://www.engadget.com/2008/07/10/jobs-app-store-launching-with-500-iphone-applications-25-free/. Retrieved 2010-06-05.
- ^ a b "iPhone App Store Downloads Top 10 Million in First Weekend". Press Release. Apple Inc.. 2008-07-14. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2008/07/14appstore.html. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ^ a b "iPhone App Store breezes past 500 million downloads". The Register. 2009-01-16. http://www.theregister.co.uk/2009/01/16/half_billion_iphone_apps/. Retrieved 2009-01-24.
- ^ a b "Apple’s Revolutionary App Store Downloads Top One Billion in Just Nine Months". Apple Inc.. 24 April 2009. http://www.apple.com/ca/press/2009_04/app_store.html. Retrieved 3 May 2009.
- ^ "Google Android has double the number of free apps than Apple's App Store". Distimo. 15 July 2009. http://techcrunch.com/2010/07/05/distimo-june-2010/. Retrieved 15 July 2009.
- ^ "iPhone 3G on Sale Tomorrow". Press Release. Apple Inc.. 2008-07-10. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2008/07/10iphone.html. Retrieved 2009-01-17.
- ^ "App Store Downloads Top 100 Million Worldwide". Press Release. Apple Inc.. 2008-09-09. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2008/09/09appstore.html. Retrieved 2008-11-10.
- ^ "Apple Reports Fourth Quarter Results". Press Release. Apple Inc.. 2008-10-21. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2008/10/21results.html. Retrieved 2009-01-17.
- ^ "Apple Opens Up More Ways To Get Paid On The iPhone, Adds Key New Features. Apps Hit 800 Million Downloads.". Press Release. TechCrunch. 2008-10-21. http://techcrunch.com/2009/03/17/phone-apps-hit-800-million-downloads. Retrieved 2009-01-17.
- ^ "TechCrunch.com". TechCrunch. 2009-06-08. http://www.techcrunch.com/2009/06/08/40-million-iphones-and-ipod-touches-and-50000-apps/. Retrieved 2009-06-08.
- ^ June, Laura (2009-07-14). "Apple's App Store crosses the 1.5 billion download mark". Engadget. http://www.engadget.com/2009/07/14/apples-app-store-crosses-the-1-5-billion-download-mark/. Retrieved 2009-07-25.
- ^ "Apple’s App Store Downloads Top Two Billion". Apple Inc.. 2009-09-28. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2009/09/28appstore.html. Retrieved 2009-09-28.
- ^ "Appleinsider.com". Appleinsider. 2009-09-28. http://www.appleinsider.com/articles/09/09/28/apple_announces_app_store_downloads_top_2_billion.html. Retrieved 2009-09-28.
- ^ "Apple Announces Over 100,000 Apps Available on the App Store". Mac Rumors. 2009-11-04. http://www.macrumors.com/2009/11/04/apple-announces-over-100000-apps-available-on-the-app-store/. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ Apple Computer, Inc. (2009-11-04). "Apple Announces Over 100,000 Apps Now Available on the App Store". Apple.com. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2009/11/04appstore.html. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ Apple Announces 3 Billion App Store Downloads - Mac Rumors
- ^ Apple’s App Store Downloads Top Three Billion
- ^ Apple - iPad - Apps for iPad
- ^ Eric Slivka (April 8, 2010). "Apple's iPhone OS 4.0 Media Event: 'Sneak Peek Into the Future'". MacRumors. http://www.macrumors.com/2010/04/08/apples-iphone-os-4-0-media-event-sneak-peek-into-the-future/. Retrieved April 8, 2010.
- ^ Thoughts on Flash
- ^ AppleInsider | Apple says App Store has made developers over billion
- ^ "Apple Special Event, September 1, 2010". Apple. September 1, 2010. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-WIKvtI2Zuw.
- ^ "Jobs Speaks! The complete transcript". Macworld. October 18, 2010. http://www.macworld.com/article/154980/2010/10/jobs_transcript.html. Retrieved June 11, 2011.
- ^ "Apple Special Event, October 20, 2010". Apple. October 20, 2010. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SHllK_hKFxY.
- ^ "Apple's App Store Downloads Top 10 Billion". Apple. January 22, 2011. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2011/01/22appstore.html. Retrieved January 22, 2011.
- ^ a b "Apple’s App Store Downloads Top 15 Billion". Apple. http://www.apple.com/pr/library/2011/07/07Apples-App-Store-Downloads-Top-15-Billion.html.
- ^ "Apple Special Event October 4th 2011, release of the iPhone 4S (scroll to 22 minutes in the presentation)". Apple. http://events.apple.com.edgesuite.net/11piuhbvdlbkvoih10/event/index.html.
- ^ 100,000 iPad Apps Available|
- ^ Estimating App Demand from Publicly Available Data. SSRN. SSRN 1924044.
- ^ Apple's most popular apps ever, announced April 2009 | Mobile Web Go
- ^ Brett Smith, More about the App Store GPL Enforcement, Free Software Foundation blog
- ^ David Murphy (8 January 2011). "Apple Pulls VLC Player from App Store Due to GPL". PCMag.com. PC Magazine. http://www.pcmag.com/article2/0,2817,2375476,00.asp. Retrieved 8 January 2011.
- ^ "Emerging Tech: Alternatives to Apple App Store, For Enterprises". cio.com. 2011-11-19. http://www.cio.com/article/638175/Emerging_Tech_Alternatives_to_Apple_App_Store_For_Enterprises.
- ^ "Enterprise App Services Environment". apperian.com. http://www.apperian.com/ease.
- ^ "Apple iPhone Kill Switch: Can CIOs Trust Apple?". cio.com. 2011-11-15. http://advice.cio.com/tom_kaneshige/14415/apple_iphone_kill_switch_can_cios_trust_apple.
- ^ "The Palm Software Store has gone mobile". Appstore.pocketgear.com. 2009-01-31. http://appstore.pocketgear.com/palm/. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ "Ovi Store". Store.ovi.com. http://store.ovi.com/. Retrieved 2009-12-02.
- ^ "RIM store crowned BlackBerry App World". CNet. 2009-03-04. http://news.cnet.com/8301-17938_105-10188400-1.html. Retrieved 2009-03-08.
External links
- The App Store on iTunes (requires iTunes)
- App Store Downloads (iTunes not needed)
- Official website on Apple.com
- Official iPhone developer site
iOS-based products Hardware Software Cocoa Touch · Core Animation · Core Location · iTunes · iOS (version history) · Notification Center · SDK · Siri · VoiceOver · WebKitApps Services Other iPhone Generations Features iBooks · iBookstore · iCloud · iTunes Store · iMovie · iMessage · iPod (Music) · Mail · Maps · Safari (versions) · Siri · Spotlight · SpringBoard · Newsstand · Find My Friends · App Store · Game Center · iAd · Push Notifications · Cards · FaceTime · Notification Center · YouTubeSupporting
SoftwareRetired Accessories iPod Models Accessories Software Other Italics indicate discontinued products. See also: iOS-based products.Online distribution platforms Books Amazon Kindle · Barnes & Noble Nook · PocketBook Reader · Sony Reader · iBookstore · List of digital library projects · FanFiction.Net · Wattpad · FictionPressDocuments Google Docs · Box.net · Docstoc · Scribd · Calameo · Issuu · WePapers · pastebins (Pastebay) · Blogger · Bloglines · TypePad · WordPress.com · LiveJournal · Docs.comMusic Online music store · 7digital · Amazon MP3 · Amie Street · Bandcamp · Bandit.fm · Beatport · BigPond Music · BuyMusic · CD Baby · Classical Archives · Deezer · Ditto music · Djshop · eMusic · GoMusic · Grooveshark · Guvera · imeem · iMesh · iTunes Store · Jamendo · Juno Records · Kazaa · Last.fm · Magnatune · Mog · MusicStation · Napster · Nimbit · Pandora · PlayNow · Puretracks · Rdio · Rhapsody · RouteNote · Sellaband · Spotify · Songza · Sony Entertainment Network · SoundCloud · Streamwaves · Ubetoo · Vodafone Music · we7 · Walmart Music · WiMP · Zune MarketplaceVideo 56.com · Amazon Instant Video · AOL Video · BBC iPlayer · BigPond Movies · blip.tv · Blockbuster · Break.com · Brightcove · Crackle · Dailymotion · FEARnet · Hulu · iTunes Store · Joost · LoveFilm · megavideo · Metacafe · MUZU TV · Netflix · The NewsMarket · PlayNow · PlayStation Store · Popcornflix · RTÉ player · RuTube · Sony Entertainment Network · ThePlatform · Tudou · TVCatchup · V Cast · Veoh · Vimeo · Voddler · Vudu · Youku · YouTube · Zattoo · Zune MarketplaceGames and
softwareBigPond GamesArena · Desura · Direct2Drive · DotEmu · Gaikai · GamersGate · GameAgent · GameShadow · GameTap · GFW Marketplace · Good Old Games · Green Man Gaming · Impulse · Jumboplay · Metaboli · Microsoft Store · OnLive · Origin · RealArcade · Steam · Stardock Central · Triton · WildTangent · Windows Marketplace · ZylomDesura · Ubuntu Software CenterNintendo Wi-Fi Connection · Nintendo eShop · PlayStation Store · Wii Shop Channel · Xbox Live Marketplace · ZeeboNet 3GAndroid Market · App Catalog · App Store · App World · Cydia · DSi Shop · Get It Now · GetJar · Handango · N-Gage · Ovi Store · PlayNow · PlayStation Store for PSP · Samsung Apps · Windows Marketplace for Mobile · Windows Phone Marketplace · Amazon AppstoreBing Entertainment · Kongregate · Chrome Web Store · MSN Games · Pogo.com · Gaikai · WildTangent · Yahoo! Games · ZylomRelated
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.