- Chucalissa Indian Village
-
Chucalissa Site
 C.H. Nash Museum at Chucalissa (2009)
C.H. Nash Museum at Chucalissa (2009)Location: 1987 Indian Village Drive, Memphis, Tennessee Coordinates: 35°3′45″N 90°7′44″W / 35.0625°N 90.12889°WCoordinates: 35°3′45″N 90°7′44″W / 35.0625°N 90.12889°W Area: 160 acres (0.65 km2)[1] Governing body: Private NRHP Reference#: 73001830 Significant dates Added to NRHP: May 7, 1973[2] Designated NHL: April 19, 1994[3] Chucalissa Indian Village (40 SY 1) is Mississippian culture archaeological site dating back to the 15th century. The site is located in the city of Memphis in West Tennessee. Chucalissa is a U.S. National Historic Landmark.
Contents
Description
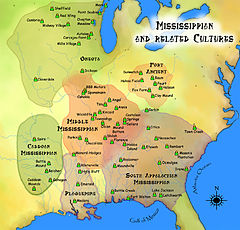
Chucalissa is a Walls Phase mound and plaza complex that was occupied, abandoned and reoccupied several times throughout its history, spanning from 1000 to 1550 CE. It is located on a bluff overlooking the Mississippi River. Other contemporaneous groups in the area include the Parkin Phase, Menard Phase, and the Nodena Phase. It is known for the well preserved architectural, floral, faunal, and human osteological remains excavated there. During the early 1540s the Hernando de Soto Expedition passed through the area, stopping at many villages along the way. It is thought that the Walls phase may be the Province of Quizquiz encountered by de Soto on the banks of the Mississippi River. It is unlikely that Chucalissa itself was visited by the expedition, as it is thought to have been abandoned at the time.[4]
Modern museum
Civilian Conservation Corps workers discovered Native American artifacts on the site in 1938 and archaeological excavations of this Mississippian mound complex were initiated. The facility has been operated by the University of Memphis since 1962.[5]
In 1973 Chucalissa Indian Village was added to the National Register of Historic Places.[2] Later, in 1994, it was declared a National Historic Landmark.[1][3] The museum, named after its founding director, curates an extensive collection of artifacts recovered during a 40-year period of systematic excavations. The site features a Mississippian mound complex, nature trail and arboretum, hands-on archaeology lab, and exhibits that explore the history and life-ways of Native Americans of the historic and prehistoric southeastern United States.
Chucalissa is the site of the Southeast Indian Heritage Festival held annually in October.[6][7]
See also
References
- ^ a b Gerald P. Smith, Charles McNutt, and Mark R. Barnes (January 29, 1993) (PDF), National Register of Historic Places Inventory-Nomination: Chucalissa Site / 40SY1, National Park Service, http://pdfhost.focus.nps.gov/docs/NHLS/Text/73001830.pdf, retrieved 2009-06-22 and Accompanying eight photos, aerial, site, and artifacts, from 1970, 1980, 1987, 1990, and undatedPDF (1.02 MB)
- ^ a b "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places. National Park Service. 2007-01-23. http://nrhp.focus.nps.gov/natreg/docs/All_Data.html.
- ^ a b "Chucalissa Site". National Historic Landmark summary listing. National Park Service. http://tps.cr.nps.gov/nhl/detail.cfm?ResourceId=1390&ResourceType=Site. Retrieved 2008-06-29.
- ^ Charles H. McNutt, ed (1996). Prehistory of the Central Mississippi Valley. University of Alabama Press. pp. 241–253.
- ^ C.H. Nash Museum at Chucalissa website http://www.memphis.edu/chucalissa/ Accessed August 2009
- ^ University of Memphis's press release on the 2008 Southeast Indian Heritage Festival http://www.memphis.edu/releases/oct08/indianheritage.htm Accessed August 2009
- ^ C.H. Nash Museum website "About" page: http://www.memphis.edu/chucalissa/about.htm Accessed August 2009
External links
 Pre-Columbian North America
Pre-Columbian North AmericaArchaeological cultures North American pre-Columbian chronology – Adena – Alachua – Ancient Pueblo (Anasazi) – Baytown – Belle Glade – Buttermilk Creek Complex – Caborn-Welborn – Calf Creek – Caloosahatchee – Clovis – Coles Creek – Deptford – Folsom – Fort Ancient – Fort Walton – Fremont – Glades – Glacial Kame – Hopewell (List of Hopewell sites) – Hohokam – Leon-Jefferson – Mississippian (List of Mississippian sites) – Mogollon – Monongahela – Old Cordilleran – Oneota – Paleo-Arctic – Paleo-Indians – Patayan – Plano – Plaquemine – Poverty Point – Prehistoric Southwest – Red Ocher – Santa Rosa-Swift Creek – St. Johns – Steed-Kisker – Tchefuncte – Tocobaga – Troyville
Archaeological sites Angel Mounds – Bandelier National Monument – The Bluff Point Stoneworks – Cahokia – Chaco Canyon – Casa Grande – Coso Rock Art District – Eaker – Effigy Mounds National Monument – Etowah Indian Mounds – Eva – Folsom Site – Fort Ancient – Fort Center – Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument – Holly Bluff Site – Hopewell Culture National Historical Park – Kincaid Mounds – Kolomoki – Manitou Cliff Dwellings – Marksville – Meadowcroft Rockshelter – Mesa Verde – Moorehead Circle – Moundville – Mummy Cave – Nodena Site – Ocmulgee National Monument – Old Stone Fort – Parkin Park – Pinson Mounds – Portsmouth Earthworks – Poverty Point – Pueblo Bonito – Rock Eagle – Rock Hawk – Salmon Ruins – Serpent Mound – Spiro Mounds – SunWatch – Taos Pueblo – Toltec Mounds – Town Creek Indian Mound – WintervilleMiscellaneous Ballgame – Black drink – Buhl woman – Calumet – Chunkey – Clovis point – Container Revolution – Eastern Agricultural Complex – Eden point – Effigy mound – Falcon dancer – Folsom point – Green Corn Ceremony – Horned Serpent – Kennewick man – Kiva – Metallurgy – Mi'kmaq hieroglyphic writing – Medicine wheel – Mound builders – N.A.G.P.R.A. – Norse colonization of the Americas – Piasa – Pueblo dwellings – Southeastern Ceremonial Complex – Three Sisters agriculture – Thunderbird – Underwater panther
Related: Genetic history · Indigenous Portal of North America · Pre-Columbian era U.S. National Register of Historic Places Topics Lists by states Alabama • Alaska • Arizona • Arkansas • California • Colorado • Connecticut • Delaware • Florida • Georgia • Hawaii • Idaho • Illinois • Indiana • Iowa • Kansas • Kentucky • Louisiana • Maine • Maryland • Massachusetts • Michigan • Minnesota • Mississippi • Missouri • Montana • Nebraska • Nevada • New Hampshire • New Jersey • New Mexico • New York • North Carolina • North Dakota • Ohio • Oklahoma • Oregon • Pennsylvania • Rhode Island • South Carolina • South Dakota • Tennessee • Texas • Utah • Vermont • Virginia • Washington • West Virginia • Wisconsin • WyomingLists by territories Lists by associated states Other  Category:National Register of Historic Places •
Category:National Register of Historic Places •  Portal:National Register of Historic Places
Portal:National Register of Historic PlacesProtected Areas of Tennessee Federal National ParksChickamauga and Chattanooga National Military Park · Fort Donelson National Battlefield · Fort Donelson National Cemetery · Shiloh National Cemetery • Shiloh National Military Park • Stones River National Battlefield • Stones River National CemeteryAppalachian National Scenic Trail • Natchez Trace National Scenic Trail • Overmountain Victory National Historic Trail • Trail of Tears National Historic TrailChickasaw • Cross Creeks • Hatchie • Lake Isom • Lower Hatchie • Reelfoot • Tennessee
Wilderness AreasBald River Gorge • Big Frog • Big Laurel Branch • Citico Creek • Cohutta • Gee Creek • Joyce Kilmer-Slickrock • Little Frog Mountain • Pond Mountain • Sampson Mountain • Unaka Mountain
Natchez Trace Parkway • Obed Wild and Scenic RiverState Big Ridge • Booker T. Washington • Cove Lake • Cumberland Mountain • Justin P. Wilson Cumberland Trail • Davy Crockett Birthplace • Fort Loudoun • Frozen Head • Harrison Bay • Hiwassee/Ocoee • Indian Mountain • Norris Dam • Panther Creek • Pickett • Red Clay • Roan Mountain • Sycamore Shoals • Warriors' Path
Bicentennial Capitol Mall • Bledsoe Creek • Burgess Falls • Cedars Of Lebanon • Cordell Hull Birthplace • David Crockett • Dunbar Cave • Edgar Evins • Fall Creek Falls • Harpeth River • Henry Horton • Johnsonville • Long Hunter • Montgomery Bell • Mousetail Landing • Old Stone Fort • Port Royal • Radnor Lake • Rock Island • Sgt. Alvin C. York • South Cumberland • Standing Stone • Tims Ford
Big Cypress Tree • Big Hill Pond • Chickasaw • Fort Pillow • Meeman-Shelby • N. B. Forrest • Natchez Trace • Paris Landing • Pickwick Landing • Pinson Mounds • Reelfoot Lake • Ross Cross Landing • T.O. Fuller
Bledsoe • Cedars of Lebanon • Chickasaw • Chuck Swan • Franklin • Lewis • Lone Mountain • Martha Sundquist • Natchez Trace • Pickett • Prentice Cooper • Scott • Standing Stone • Stewart
Honey Creek * Piney Falls • Laurel-Snow • North Chickamauga Creek Gorge • Stinging Fork Falls • Virgin Falls
Other OtherTennessee Department of Environment and Conservation (web) - Tennessee Department of Agriculture {web} City of Memphis & Memphis metropolitan area (counties in TN, MS and AR) Memphis topics History | Geography | Government | Economy | Education | Culture | Tourism | Sports | Transportation | Memphians







Memphis districts Memphis
neighborhoodsBelle Meade - Berclair - Binghampton - Capleville - Central Gardens - Chickasaw Gardens - Cooper-Young - Cordova - Douglass - Evergreen - Frayser - General DeWitt Spain Airport - Glenview - Harbor Town - Hickory Hill - High Point Terrace - Hollywood - Hyde Park - Lenox - Medical District - Mud Island - Normal Station - Nutbush - Orange Mound - Parkway Village - Raleigh - Riverside - Sherwood Forest - South Main - Uptown - Victorian Village - Vollintine Hills - Whitehaven - Wolfchase
Memphis
metro area
landmarksTennessee: A. Schwab's - Art Museum of the University of Memphis - AutoZone Stadium - Bartlett Museum - Beale Street - Bellevue Baptist Church - Belz Museum - Botanic Garden - Brooks Museum - Burkle Estate - Central Station - Chickasaw Bluff - Children's Museum - Chucalissa Museum - Cotton Museum - Davies Manor - Dixon Gallery and Gardens - Downtown Trolleys - Elmwood Cemetery - FedExForum - Fire Museum - Fort Assumption - Fort Wright - Graceland - Hernando de Soto Bridge - Liberty Bowl Stadium - Libertyland - Lichterman Nature Center - Lincoln American Tower - Magevney House - Mallory-Neely House - Meeman-Shelby Forest State Park - Memorial Park Cemetery - Memphis Cotton Exchange - Memphis International Airport - Memphis Motorsports Park - Memphis National Cemetery - Memphis Parkway System - Memphis Zoo - Mississippi River - Mississippi River Park - Mud Island Monorail - National Civil Rights Museum - National Ornamental Metal Museum - Oaklawn Garden - Orpheum Theatre - Overton Park - Peabody Hotel - Pink Palace - The Pyramid - Rhodes College - Rock N' Soul Museum - St. Jude Children's Research Hospital - St. Mary's Episcopal Cathedral - Shelby Farms - Stax Museum - Sun Studio - South Main Arts District - Tennessee Brewery - Tipton County Museum - T. O. Fuller State Park - Tom Lee Park - Union Station - University of Memphis - Victorian Village - Wolf River
Mississippi: Arkabutla Lake - Bally's Casino - DeSoto County Museum - DeSoto Civic Center - Gold Strike Casino - Harrah's Casino (formerly Grand Casino) - Holly Springs National Forest - Horseshoe Casino - Mississippi River - Resorts Casino Tunica - Sam's Town Gambling Hall - Tunica Resorts - Tunica Roadhouse Casino - Wall Doxey State Park
Arkansas: Horseshoe Lake - Mississippi River - Southland Greyhound Park - Wapanocca National Wildlife Refuge
Memphis
metro area
suburbsTennessee: Arlington - Bartlett - Brunswick - Capleville - Collierville - Covington - Eads - Ellendale - Fisherville - Germantown - Lakeland - Millington - Somerville - Shelby Forest
Mississippi: Hernando - Holly Springs - Horn Lake - Olive Branch - Senatobia - Southaven - Tunica - Tunica Resorts (former Robinsonville) - Walls
Arkansas: Marion - West Memphis
Metro area counties Categories:- Middle Mississippian culture
- National Historic Landmarks in Tennessee
- Archaeological sites on the National Register of Historic Places in Tennessee
- Museums in Memphis, Tennessee
- Archaeology museums in Tennessee
- Native American museums in Tennessee
- University of Memphis
- University museums in Tennessee
- Civilian Conservation Corps in Tennessee
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.