- Posterior thoracic nucleus
-
Posterior thoracic nucleus 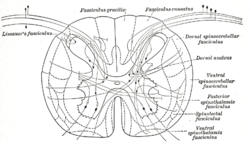
Diagram showing a few of the connections of afferent (sensory) fibers of the posterior root with the efferent fibers from the ventral column and with the various long ascending fasciculi. (Dorsal nucleus labeled at center right.) 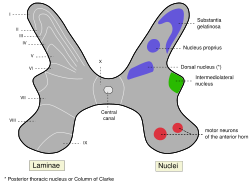
Schematic of spinal cord grey matter showing location of the Dorsal Nucleus Latin nucleus thoracicus posterior, nucleus dorsalis Gray's subject #185 758 Clarke's column (column of Clarke, dorsal nucleus, posterior thoracic nucleus) is a group of interneurons found in Lamina VII, also known as the intermediate zone, of the spinal cord.
Contents
Anatomy
It occupies the medial part of the base of the posterior horn and appears on the transverse section as a well-defined oval area.
It begins below at the level of the second or third lumbar nerve, and reaches its maximum size opposite the twelfth thoracic nerve. Above the level of the ninth thoracic nerve its size diminishes, and the column ends opposite the last cervical or first thoracic nerve.
It is represented, however, in the other regions by scattered cells, which become aggregated to form a cervical nucleus opposite the third cervical nerve, and a sacral nucleus in the middle and lower part of the sacral region.
Nerve cells in Clarke’s column are most abundant between the lower thoracic and upper lumbar segments. Cell bodies are of medium size and oval- or pyriform-shape.
Function
Clarke’s column is a major relay center for unconscious proprioception. Sensory information from muscle spindles and tendon organs is carried by axons of larger neurons in posterior root ganglia, which synapse onto neurons in the spinal cord including cells in Clarke’s column. From Clarke’s column, information continues rostrally until it reaches the cerebellar cortex. This relay pathway is generally known as the dorsal spinocerebellar tract.
Eponym
It is named for Jacob Augustus Lockhart Clarke.[1][2]
References
External links
- http://isc.temple.edu/neuroanatomy/lab/atlas/L3/
- http://www.neuroanatomy.wisc.edu/sc97/text/p3/Pathway.htm
Anatomy of torso (primarily): the spinal cord (TA 14.1.02, GA 9.749) External, dorsal Posterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcusGrey matter/
Rexed laminaeI–VI: Posterior hornI: Marginal nucleus · II: Substantia gelatinosa of Rolando · III+IV: Nucleus proprius · Spinal lamina V · Spinal lamina VIVII: Lateral hornIntermediolateral nucleus · Posterior thoracic nucleusVIII–IX: Anterior hornX: OtherWhite matter somatic/
ascending
(blue)Posterior/PCML: touch: Gracile · Cuneate
Lateral: proprioception: Spinocerebellar (Dorsal, Ventral) · pain/temp: Spinothalamic (Lateral, Anterior) · Posterolateral (Lissauer) · Spinotectal
Spinoreticular tract · Spino-olivary tractmotor/
descending
(red)Lateral: Corticospinal (Lateral) · Ep (Rubrospinal, Olivospinal)
Anterior: Corticospinal (Anterior) · Ep (Vestibulospinal, Reticulospinal, Tectospinal)bothExternal, ventral Anterior median fissure · Anterolateral sulcusExternal, general Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
