- Clebsch graph
-
Clebsch graph 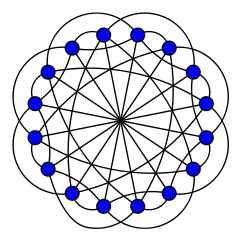
Named after Alfred Clebsch Vertices 16 Edges 40 Radius 2 Diameter 2 Girth 4 Automorphisms 1920 Chromatic number 4[1] Chromatic index 5 Properties Strongly regular
Hamiltonian
Triangle-free
Cayley graph
Vertex-transitive
Edge-transitive
Distance-transitive.v · mathematical field of graph theory, the Clebsch graph[1][2] is an undirected graph with 16 vertices and 40 edges. It is named after Alfred Clebsch, a German mathematician who discovered it in 1868. It is also known as the Greenwood–Gleason graph after the work of Robert M. Greenwood and Andrew M. Gleason (1955), who used it to evaluate the Ramsey number R(3,3,3) = 17.[3][4][5] Contents
Construction
This graph is equivalent to the order-5 folded cube graph. It may be constructed by adding edges between opposite pairs of vertices in a 4-dimensional hypercube graph. (In an n-dimensional hypercube, a pair of vertices are opposite if the shortest path between them has n edges.) Alternatively, it can be formed from a 5-dimensional hypercube graph by identifying together (or contracting) every opposite pair of vertices.
Another construction, leading to the same graph, is to create a vertex for each element of the finite field GF(16), and connect two vertices by an edge whenever the difference between the corresponding two field elements is a perfect cube.[6]
Properties
The Clebsch graph is a strongly regular graph of degree 5 with parameters (v,k,λ,μ) = (16,5,0,2).[7][8] Its complement is also a strongly regular graph.[1][4]
The graph is hamiltonian, non planar and non eulerian. It is also both 5-vertex-connected and 5-edge-connected.
The subgraph that is induced by the ten non-neighbors of any vertex in the Clebsch graph forms an isomorphic copy of the Petersen graph.
The edges of the complete graph K16 may be partitioned into three disjoint copies of the Clebsch graph. Because the Clebsch graph is a triangle-free graph, this shows that there is a triangle-free three-coloring of the edges of K16; that is, that the Ramsey number R(3,3,3) describing the minimum number of vertices in a complete graph without a triangle-free three-coloring is at least 17. Greenwood & Gleason (1955) used this construction as part of their proof that R(3,3,3) = 17.[5][9]
The Clebsch graph is the Keller graph of dimension two, part of a family of graphs used to find tilings of high-dimensional Euclidean spaces by hypercubes no two of which meet face-to-face.
Algebraic properties
The characteristic polynomial of the Clebsch graph is (x + 3)5(x − 1)10(x − 5). Therefore the Clebsch graph is an integral graph: its spectrum consists entirely of integers.[4] The Clebsch graph is the only graph with this characteristic polynomial, making it a graph determined by its spectrum.
The Clebsch graph is a Cayley graph with an automorphism group of order 1920, isomorphic to the Coxeter group D5. As a Cayley graph, its automorphism group acts transitively on its vertices, making it vertex transitive. In fact, it is arc transitive, hence edge transitive and distance transitive.
Gallery
-
Construction of the Clebsch graph from a hypercube graph.
References
- ^ a b c Weisstein, Eric W.. "Clebsch Graph.". From MathWorld--A Wolfram Web Resource. http://mathworld.wolfram.com/ClebschGraph.html. Retrieved 2009-08-13.
- ^ Brouwer et al. (1989) use name Clebsch graph for a different, but related graph.
- ^ Clebsch, A. (1868), "Ueber die Flächen vierter Ordnung, welche eine Doppelcurve zweiten Grades besitzen", J. für Math. 69: 142–184 .
- ^ a b c The Clebsch Graph on Bill Cherowitzo's home page
- ^ a b Greenwood, R. E.; Gleason, A. M. (1955), "Combinatorial relations and chromatic graphs", Canadian Journal of Mathematics 7: 1–7, doi:10.4153/CJM-1955-001-4, MR0067467 .
- ^ De Clerck, Frank (1997). "Constructions and Characterizations of (Semi)partial Geometries". p. 6. http://cage.ugent.be/~fdc/potenza.ps.
- ^ Godsil, C.D. (1995). "Problems in algebraic combinatorics". Electron. J. Combin. 2: 3. http://www.combinatorics.org/Volume_2/PDFFiles/v2i1f1.pdf. Retrieved 2009-08-13.
- ^ Peter J. Cameron Strongly regular graphs on DesignTheory.org, 2001
- ^ Sun, Hugo S.; Cohen, M. E. (1984), "An easy proof of the Greenwood-Gleason evaluation of the Ramsey number R(3,3,3)", The Fibonacci Quarterly 22 (3): 235–238, MR765316, http://www.fq.math.ca/Scanned/22-3/sun.pdf .
Categories:- Individual graphs
- Regular graphs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Clebsch-Graph — In der Graphentheorie ist der Clebsch Graph ein ungerichteter Graph mit 16 Knoten und 40 Kanten. Er ist benannt nach Alfred Clebsch, der ihn 1868 betrachtete. Die Bezeichnung Greenwood–Gleason Graph wird dazu synonym verwendet.[1] … Deutsch Wikipedia
Clebsch — bezeichnet: Alfred Clebsch (1833 1872), deutscher Mathematiker Clebsch Gordan Koeffizient Clebsch Graph Diese Seite ist eine Begriffsklärung zur Unterscheidung mehrerer mit demselben Wort bezeic … Deutsch Wikipedia
Graphe de Clebsch — Représentation du graphe de Clebsch Nombre de sommets 16 Nombre d arêtes 40 Distribution des degrés 5 régulier Rayon … Wikipédia en Français
Complete coloring — of the Clebsch graph with 8 colors. Every pair of colors appears on at least one edge. No complete coloring with more colors exists: in any 9 coloring some color would appear only at one vertex, and there would not be enough neighboring vertices… … Wikipedia
Ramsey's theorem — This article goes into technical details quite quickly. For a slightly gentler introduction see Ramsey theory. In combinatorics, Ramsey s theorem states that in any colouring of the edges of a sufficiently large complete graph (that is, a simple… … Wikipedia
Gallery of named graphs — Some of the finite structures considered in graph theory have names, sometimes inspired by the graph s topology, and sometimes after their discoverer. A famous example is the Petersen graph, a concrete graph on 10 vertices that appears as a… … Wikipedia
Projet:Mathématiques/Liste des articles de mathématiques — Cette page n est plus mise à jour depuis l arrêt de DumZiBoT. Pour demander sa remise en service, faire une requête sur WP:RBOT Cette page recense les articles relatifs aux mathématiques, qui sont liés aux portails de mathématiques, géométrie ou… … Wikipédia en Français
List of mathematics articles (C) — NOTOC C C closed subgroup C minimal theory C normal subgroup C number C semiring C space C symmetry C* algebra C0 semigroup CA group Cabal (set theory) Cabibbo Kobayashi Maskawa matrix Cabinet projection Cable knot Cabri Geometry Cabtaxi number… … Wikipedia
List of theorems — This is a list of theorems, by Wikipedia page. See also *list of fundamental theorems *list of lemmas *list of conjectures *list of inequalities *list of mathematical proofs *list of misnamed theorems *Existence theorem *Classification of finite… … Wikipedia
List of mathematics articles (T) — NOTOC T T duality T group T group (mathematics) T integration T norm T norm fuzzy logics T schema T square (fractal) T symmetry T table T theory T.C. Mits T1 space Table of bases Table of Clebsch Gordan coefficients Table of divisors Table of Lie … Wikipedia
18+© Academic, 2000-2024- Contact us: Technical Support, Advertising
Dictionaries export, created on PHP, Joomla, Drupal, WordPress, MODx.Share the article and excerpts
Clebsch graph
- Clebsch graph
-
Clebsch graph 
Named after Alfred Clebsch Vertices 16 Edges 40 Radius 2 Diameter 2 Girth 4 Automorphisms 1920 Chromatic number 4[1] Chromatic index 5 Properties Strongly regular
Hamiltonian
Triangle-free
Cayley graph
Vertex-transitive
Edge-transitive
Distance-transitive.





