- Climate of the Nordic countries
-
The climate of the Nordic countries make up a region in Northern Europe, consisting of Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden and their associated territories which include the Faroe Islands, Greenland and Åland. Stockholm, Sweden has on average the warmest summer of the Nordic countries with high temperatures of 23 °C (73 °F) in July, Copenhagen and Oslo have 22 °C (72 °F).
Contents
Seasonal conditions
Winter
In Denmark, January temperatures average between −2 °C (28 °F) and 4 °C (39 °F).[1] Denmark's coldest month, however, is February, where the mean temperature is 0 °C (32 °F).[2] The amount of hours of sunlight per day does increase during the month of February for Denmark, where they get seven to eight hours a day.[3] Iceland winters are generally mild considering how high its latitude is. The coastal lowlands of Iceland have average January temperatures of about 0 °C (32 °F), while the highlands of central Iceland generally stay below −10 °C (14 °F). The lowest winter temperatures in Iceland are usually somewhere between −25 °C (−13 °F) and −30 °C (−22 °F), although the lowest temperature ever recorded on Iceland was −39.7 °C (−39 °F).[4] In Norway, the coastal regions have mild winters, while further inland winter is much colder. During midwinter, southern areas of Norway only get five to six hours of sunlight a day, while the north gets little to none.[5] In January, the average temperature in Norway is somewhere in between −6 °C (21 °F) and 3 °C (37 °F).[1] Like neighboring Norway, Sweden averages −6 °C (21 °F) to 1 °C (34 °F) in the month of January.[1] Swedish areas north of the Arctic Circle rarely see the sun rise, due to the natural phenomenon of the polar night.[6] In January and February, temperatures in this area can drop to −15 °C (5 °F).[1] In February, Northern Sweden sees about four to six hours of sunlight a day.[3]
Spring
In Iceland, spring brings warmer and milder temperatures. In the month of May, the average temperature is somewhere between 4 °C (39 °F) and 10 °C (50 °F).[7]
Summer
Denmark's warmest month is July, where the mean temperature is 17 °C (63 °F).[2] In Iceland, occasionally thunderstorms occur in the south in late summertime, due to warm air being deflected to northern latitudes from warm air masses in other parts of Europe. Also, cold air. originating from Canada, warms rapidly over the ocean, forming thunderclouds. Thunderstorms, however, are very rare in Iceland, and there are less than five of them per year.[4] In June, Iceland's average daily temperatures range from 8 °C (46 °F) to 16 °C (61 °F).[8] Summer conditions vary in Norway depending on location. The Norwegian coast has cooler summers than areas further inland. Due to its northern location, there is almost no darkness in June and July in the north, reaching as far south as Trondheim.[5] In summer, the average temperature in the Northern areas are somewhere between 8 °C (46 °F) and 16 °C (61 °F), while further South it is usually 13 °C (55 °F) to 22 °C (72 °F).[8][9] In Sweden, summers experiences more rainfall than other seasons. Swedish areas north of the Arctic Circle rarely see the sun set during the months of June and July, due to the natural phenomenon Midnight sun.[6] Northern parts of Sweden have summer temperatures in the 8 °C (46 °F) to 16 °C (61 °F) range, while furtherther south, the temperature is closer to 13 °C (55 °F) and 22 °C (72 °F).[8][9] During summer in Greenland, ice sheets breaking up trigger what is known as "glacial motion" or "glacial earthquakes".[10]
Global warming
Main article: Global warmingEffects
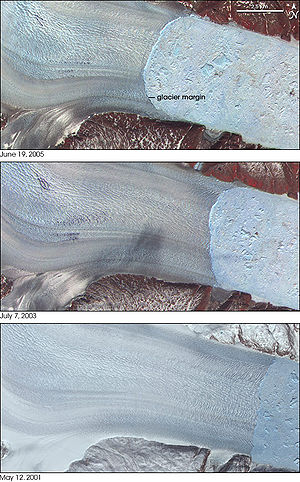
Main article: Effects of global warmingGreenland is one of the areas in both the Nordic region and the world most affected by climate change. A July 2006 study completed by "The Journal of Climate", determined that Greenland was the single largest contributor to global sea-level rise.[10] The temperatures from the year 2000 to the present have caused several very large glaciers that had long been stable, to begin to melt away. Three glaciers that have been researched: Jakobshavn Isbræ, Helheim and Kangerdlugssuaq Glaciers, jointly drain more than 16% of the Greenland Ice Sheet. Satellite images and aerial photographs from the 1950s and 1970s show that the front of the glacier had remained in the same place for decades. In 2001, the ice sheet began retreating rapidly, retreating 7.2 km (4.5 mi) between 2001 and 2005. It has also accelerated from 20 m (66 ft) to 32 m (105 ft) a day.[11] Western Greenland's Jakobshavn Isbræ is generally considered the fastest moving glacier in the world, and has been moving continuously at speeds of over 24 m (79 ft) a day with a stable terminus since at least 1950. The glacier's ice tongue began to break apart in 2000, leading to almost complete disintegration in 2003, while the retreat rate doubled to over 30 m (98 ft) per day.[12] In the summer of 2005, the island of Uunartoq Qeqertoq was discovered off the eastern central coast of Greenland. Prior to 2005, many people assumed that Uunartoq Qeqertoq was actually a peninsula off of Liverpool Land, however, the melting ice shelves revealed that it was only connected to the mainland by glacial ice.[13]
Predicted effects
Scientists estimate that should the current rate of climate change continue, Greenland's ice sheet, which contains 630,000 cubic miles (2,600,000 km3) of ice, could melt and cause global sea level to rise by 23 ft (7.0 m). Some climate experts have estimated that Greenland could be losing 80 cubic miles (330 km3) of ice each year.[10]
The 2008 Environmental Performance Index ranked countries based on the environmental performance of the country's policies. On the list, Norway was ranked 2nd, Sweden was 3rd, 4th was Finland, Iceland was ranked as 11th, and Denmark came in 26th.[14]
See also
- Climate
- Climate change
- Climate of Iceland
- Climate of Norway
- Climate of the Arctic
- Climatology
- Meteorology
References
- ^ a b c d Terri Mapes. "Scandinavia in January - Monthly Events Calendar". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/scandinaviamonthbymonth/p/january.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ^ a b Terri Mapes. "Weather in Denmark: Temperatures, Weather & Climate". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/denmar1/ss/weatherdenmark.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- ^ a b Terri Mapes. "Scandinavia in February - Monthly Events Calendar". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/scandinaviamonthbymonth/p/february.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ^ a b Ólafur Ingólfsson. "The dynamic climate of Iceland". University of Iceland. http://www3.hi.is/~oi/climate_in_iceland.htm. Retrieved 2007-06-07.
- ^ a b Terri Mapes. "Weather in Norway: Temperatures, Weather & Climate". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/norwa1/ss/weathernorway.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- ^ a b Terri Mapes. "Weather in Sweden: Temperatures, Weather & Climate". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/swede1/ss/weathersweden.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- ^ Terri Mapes. "Scandinavia in May - Monthly Events Calendar". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/scandinaviamonthbymonth/p/may.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ^ a b c Terri Mapes. "Scandinavia in June - Monthly Events Calendar". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/scandinaviamonthbymonth/p/june.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ^ a b Terri Mapes. "Scandinavia in July - Monthly Events Calendar". http://goscandinavia.about.com/od/scandinaviamonthbymonth/p/july.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-26.
- ^ a b c "The Warming of Greenland". New York Times. 2007-01-16. http://www.nytimes.com/2007/01/16/science/earth/16gree.html?_r=1&oref=slogin. Retrieved 2008-04-07.
- ^ Emily Saarman (2005-11-14). "Rapidly accelerating glaciers may increase how fast the sea level rises". UC Santa Cruz Currents. http://currents.ucsc.edu/05-06/11-14/glacier.asp. Retrieved 2007-12-28.
- ^ Krishna Ramanujan (2004-12-01). "Fastest Glacier in Greenland Doubles Speed". NASA. http://www.nasa.gov/vision/earth/lookingatearth/jakobshavn.html. Retrieved 2007-12-28.
- ^ Michael McCarthy (2007-04-24). "An island made by global warming". The Independent (London). http://www.independent.co.uk/environment/climate-change/an-island-made-by-global-warming-445966.html. Retrieved 2007-04-24.
- ^ Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy / Center for International Earth Science Information Network at Columbia University. "Environmental Performance Index 2008". http://epi.yale.edu/Home. Retrieved 2008-01-25.
Climate of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territoriesOther entities - European Union
- Sovereign Military Order of Malta
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.