- Diethylaminoethyl cellulose
-
Diethylaminoethyl cellulose (DEAE or DEAE-C) is a positively charged resin used in ion exchange chromatography, a type of column chromatography, used in protein and nucleic acid purification/separation. Gel matrix beads are derivatized with DEAE and lock negatively charged proteins or nucleic acids into the matrix, until released by increasing the salt concentration of the solvent. DE52 has a pKa of 11.5.
DEAE-Dextran (DEAE-D) is also used for transfecting animal cells with foreign DNA. It is added to solution containing DNA meant for transfection. It binds and interacts with negatively charged DNA molecules and via a largely unknown mechanism brings about the uptake of nucleic acids by the cell. This procedure is highly suited for transient transfection used for various molecular biology studies.
Sources
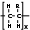
This article about polymer science is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.

