- List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System
-
Objects in the
Solar SystemCategories - Round objects
- Moons
- Minor planets
In 2006, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) defined a planet as a body in orbit around the Sun that was large enough to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium and to have cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit.[1] An object in hydrostatic equilibrium is one that is large enough for its gravity to have overcome its internal rigidity, and so relax into a rounded (ellipsoidal) shape. The practical meaning of "cleared the neighborhood" is that a planet is comparatively massive enough for its gravitation to control the orbits of all objects in its vicinity. By the IAU's definition, there are eight planets in the Solar System. Those objects in orbit around the Sun that have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium but have not cleared their neighborhoods are classified as dwarf planets, and the remainder are termed small Solar System bodies. In addition, the Sun itself and 19 known natural satellites are also massive enough to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium.[2] All known objects in the Solar System with a hydrostatic shape are listed below, with a sample of the largest objects whose shape has yet to be accurately determined. The Sun's orbital characteristics are listed in relation to the Galactic Center. All other objects are listed in order of their distance from the Sun.
Contents
Sun
The Sun is a G-type main-sequence star. It contains almost 99.9 percent of all the mass in the Solar System.[3]
Sun[4] 
Astronomical symbol[q] 
Mean distance
from Galactic Centerkm
light years~2.5×1017
~26,000Mean radius km
:E[f]696,000
109Surface area km2
:E[f]6.0877×1012
11,990Volume km3
:E[f]1.4122×1018
1,300,000Mass kg
:E[f]1.9891×1030
332,946Density g/cm3 1.409 Equatorial gravity m/s2 274.0 Escape velocity km/s 617.7 Rotation period days[g] 25.38 Orbital period about Galactic Center[5] million years 225–250 Mean orbital speed[5] km/s ~220 Axial tilt[i] to the ecliptic deg. 7.25 Axial tilt[i] to the galactic plane deg. 67.23 Mean surface temperature K 5,778 Mean coronal temperature[6] K 1–2×106 Photospheric composition H, He, O, C, Fe, S Planets
Key *
terrestrial planet°
gas giantPlanets both are large enough to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium and have cleared their neighborhoods of similar objects. There are four terrestrial planets and four gas giants in the Solar System. The latter combined comprise more than 99 percent of the mass in the Solar System excluding that of the Sun.
*Mercury[7] *Venus[8] *Earth[9] *Mars[10] °Jupiter[11] °Saturn[12] °Uranus[13] °Neptune[14] 







Astronomical symbol[q] 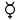


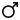
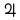
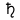

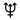
Mean distance
from Sunkm
AU57,909,175
0.38709893108,208,930
0.72333199149,597,890
1.00000011227,936,640
1.52366231778,412,010
5.203363011,426,725,400
9.537070322,870,972,200
19.191263934,498,252,900
30.06896348Equatorial radius km
:E[f]2,439.64
0.38256,051.59
0.94886,378.1
13,397.00
0.5322671,492.68
11.20960,267.14
9.44925,557.25
4.00724,766.36
3.883Surface area km²
:E[f]75,000,000
0.1471460,000,000
0.9010510,000,000
1140,000,000
0.274564,000,000,000
125.544,000,000,000
86.278,100,000,000
15.887,700,000,000
15.10Volume km3
:E[f]6.083×1010
0.0569.28×1011
0.871.083×1012
11.6318×1011
0.1511.431×1015
1,321.38.27×1014
763.596.834×1013
63.0866.254×1013
57.74Mass kg
:E[f]3.302×1023
0.0554.8690×1024
0.8155.9742×1024
16.4191×1023
0.1071.8987×1027
3185.6851×1026
958.6849×1025
141.0244×1026
17Density g/cm3 5.43 5.24 5.515 3.940 1.33 0.70 1.30 1.76 Equatorial gravity m/s2 3.70 8.87 9.81 3.71 23.12 10.44 8.69 11.00 Escape velocity km/s 4.25 10.36 11.18 5.02 59.54 35.49 21.29 23.71 Rotation period[g] days 58.646225 −243.0187[h] 0.99726968 1.02595675 0.41354 0.44401 −0.71833[h] 0.67125 Orbital period[g] years 0.2408467 0.61519726 1.0000174 1.8808476 11.862615 29.447498 84.016846 164.79132 Mean orbital speed km/s 47.8725 35.0214 29.7859 24.1309 13.0697 9.6724 6.8352 5.4778 Eccentricity 0.20563069 0.00677323 0.01671022 0.09341233 0.04839266 0.05415060 0.04716771 0.00858587 Inclination[f] deg. 7.00 3.39 0[9] 1.85 1.31 2.48 0.76 1.77 Axial tilt[i] deg. 0.0 177.3 23.44 25.19 3.12 26.73 97.86 29.58 Mean surface temperature K 440–100 730 287 227 152 [j] 134 [j] 76 [j] 72 [j] Mean air temperature[k] K 288 165 135 76 73 Atmospheric composition He Na+ P+ CO2 N2 N2 O2 CO2 N2 Ar H2 He H2 He H2 He CH4 H2 He CH4 Number of known moons[v] 0 0 1 2 64 62 27 13 Rings? No No No No Yes Yes Yes Yes Planetary discriminant[l][o] 9.1×104 1.35×106 1.7×106 1.8×105 6.25×105 1.9×105 2.9×104 2.4×104 Dwarf planets
Key †
Ceres‡
plutoidDwarf planets are large enough to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium, but have not cleared their neighbourhoods of similar objects. There are currently five objects in this category. Ceres lies in the asteroid belt, between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. The others lie beyond Neptune's orbit and are sub-classified as plutoids. The IAU has recognised these objects as dwarf planets:
†Ceres[15] ‡Pluto[16] ‡Haumea[17] ‡Makemake[18] ‡Eris[19] 




Astronomical symbol[q] 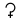
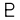
Minor planet number 1 134340 136108 136472 136199 Mean distance
from Sunkm
AU413,700,000
2.7665,906,380,000
39.4826,484,000,000
43.3356,850,000,000
45.79210,210,000,000
67.668Mean radius km
:E[f]471
0.07381,148.07
0.180575
0.1537[20]750+200
−100
0.12[20]1,200
0.19[20]Volume km3
:E[f]4.37×108
0.0005[b]6.33×109
0.0071.3–1.6×109
0.001[y]1.8×109
0.002[b]7.23×109
0.008[b]Surface area km²
:E[f]2,800,000
0.0055[a]17,000,000
0.03336,800,000
0.0133[z]7,000,000
0.015[a]18,000,000
0.0353[a]Mass kg
:E[f]9.5×1020
0.000161.3×1022
0.00224.2 ± 0.1×1021
0.0007[21]4×1021
0.00071.7×1022
0.0028[22]Density g/cm3 2.08 2.0 2.6–3.3[23] 2.0[c] 2.25[c] Equatorial gravity m/s2 0.27[d] 0.60 0.44[d] 0.5[d] ~0.8[d] Escape velocity km/s[e] 0.51 1.23 0.84 0.8 1.37 Rotation period[g] days 0.3781 −6.38718[h] 0.167 ? ? Orbital period[g] years 4.599 247.92065 285.4 309.9 557 Mean orbital speed km/s 17.882 4.7490 4.484[o] 4.4[o] 3.436[n] Eccentricity 0.080 0.24880766 0.18874 0.159 0.44177 Inclination[f] deg. 10.587 17.14175 28.19 28.96 44.187 Axial tilt[i] deg. 4 119.61 ? ? ? Mean surface temperature[w] K 167[24] 40[25] <50[26] 30 30 Atmospheric composition H2O, O2 N2, CH4 N2, CH4.[27] N2, CH4[28] Number of known moons[v] 0 4 2[29] 0[30] 1[31] Planetary discriminant[l][o] 0.33 0.077 0.023 0.02 0.10 Round satellites
Key €
Satellite of Earth₤
Satellite of Jupiter$
Satellite of Saturn₩
Satellite of Uranus₦
Satellite of Neptune¶
Satellite of PlutoSee also: List of moonsThere are 19 natural satellites in the Solar System massive enough to have achieved hydrostatic equilibrium. Another satellite, the Neptunian moon Proteus, is not in hydrostatic equilibrium, but is slightly larger than Mimas, the smallest of the 19 rounded moons.[ab] Satellites are listed first in order from the Sun, and second in order from their parent body.
€Moon[32] ₤Io[33] ₤Europa[34] ₤Ganymede[35] ₤Callisto[36] $Mimas[p] $Enceladus[p] $Tethys[p] $Dione[p] $Rhea[p] 








Astronomical symbol[q] 
Mean distance
from primary:km 384,399 421,600 670,900 1,070,400 1,882,700 185,520 237,948 294,619 377,396 527,108 Mean radius km
:E[f]1,737.1
0.2731,815
0.2861,569
0.2452,634.1
0.4132,410.3
0.378198.30
0.031252.1
0.04533
0.083561.7
0.088764.3
0.12Surface area[a] km²
:E[f]37,930,000
0.07441,910,000
0.08230,900,000
0.06187,000,000
0.14373,000,000
0.143490,000
0.001799,000
0.00164,940,000
0.013,965,000
0.00787,337,000
0.0144Volume[b] km3
:E[f]2.2×1010
0.022.53×1010
0.021.59×1010
0.077.6×1010
0.155.9×1010
0.053.3×107
0.000036.7×107
0.000066.3×108
0.00067.4×108
0.00071.9 ×109
0.0017Mass kg
:E[f]7.3477×1022
0.01238.94×1022
0.0154.80×1022
0.0081.4819×1023
0.0251.0758×1023
0.0183.75×1019
0.0000061.08×1020
0.0000186.174×1020
0.001321.095×1021
0.00032.306×1021
0.0004Density[c] g/cm3 3.3464 3.528 3.01 1.936 1.83 1.15 1.61 0.98 1.48 1.23 Equatorial gravity[d] m/s2 1.622 1.796 1.314 1.428 1.235 0.0636 0.111 0.145 0.231 0.264 Escape velocity[e] km/s 2.38 2.56 2.025 2.741 2.440 0.159 0.239 0.393 0.510 0.635 Rotation period days[g] 27.321582
(sync)[m]1.7691378
(sync)3.551181
(sync)7.154553
(sync)16.68902
(sync)0.942422
(sync)1.370218
(sync)1.887802
(sync)2.736915
(sync)4.518212
(sync)Orbital period about primary days[g] 27.32158 1.769138 3.551181 7.154553 16.68902 0.942422 1.370218 1.887802 2.736915 4.518212 Mean orbital speed[o] km/s 1.022 17.34 13.740 10.880 8.204 14.32 12.63 11.35 10.03 8.48 Eccentricity 0.0549 0.0041 0.009 0.0013 0.0074 0.0202 0.0047 0.02 0.002 0.001 Inclination to primary's equator deg. 18.29–28.58 0.04 0.47 1.85 0.2 1.51 0.02 1.51 0.019 0.345 Axial tilt[i][u] deg. 6.68 0 0 0–0.33[37] 0 0 0 0 0 0 Mean surface temperature[w] K 220 130 102 110[38] 134 64 75 64 87 76 Atmospheric composition H He Na+ K+ Ar SO2[39] O2[40] O2[41] O2 CO2[42] H2O, N2, CO2, CH4[43] Rings? No No No No No No No No No Yes? $Titan[p] $Iapetus[p] ₩Miranda[r] ₩Ariel[r] ₩Umbriel[r] ₩Titania[r] ₩Oberon[r] ₦Triton[44] ¶Charon[16] 








Mean distance
from primary:km 1,221,870 3,560,820 129,390 190,900 266,000 436,300 583,519 354,759 17,536 Mean radius km
:E[f]2,576
0.404735.60
0.115235.8
0.037578.9
0.091584.7
0.092788.9
0.124761.4
0.1191353.4
0.212603.5
0.095Surface area[a] km²
:E[f]83,000,000
0.1636,700,000
0.013700,000
0.00144,211,300
0.0084,296,000
0.0087,820,000
0.0157,285,000
0.01423,018,000
0.0454,580,000
0.009Volume[b] km3
:E[f]7.16×1010
0.0661.67×109
0.00155.5×107
0.000058.1×108
0.00088.4×108
0.00082.06×109
0.00191.85×109
0.00171×1010
0.009589.2×108
0.00085Mass kg
:E[f]1.3452×1023
0.0231.8053×1021
0.00036.59×1019
0.000011.35×1021
0.000221.2×1021
0.00023.5×1021
0.00063.014×1021
0.000462.14×1022
0.003581.52×1021
0.00025Density[c] g/cm3 1.88 1.08 1.20 1.67 1.40 1.72 1.63 2.061 1.65 Equatorial gravity[d] m/s2 1.35 0.22 0.08 0.27 0.23 0.39 0.35 0.78 0.28 Escape velocity[e] km/s 2.64 0.57 0.19 0.56 0.52 0.77 0.73 1.46 0.58 Rotation period days[g] 15.945
(sync)[m]79.322
(sync)1.414
(sync)2.52
(sync)4.144
(sync)8.706
(sync)13.46
(sync)5.877
(sync)6.387
(sync)Orbital period about primary days 15.945 79.322 1.4135 2.520 4.144 8.706 13.46 −5.877[h] 6.387 Mean orbital speed[o] km/s 5.57 3.265 6.657 5.50898 4.66797 3.644 3.152 4.39 0.2 Eccentricity 0.0288 0.0286 0.0013 0.0012 0.005 0.0011 0.0014 0.00002 0.0022 Inclination to primary's equator deg. 0.33 0.34854 15.47 4.2 0.26 0.36 0.34 157 ? Axial tilt[i][u] deg. 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ? Mean surface temperature[w] K 93.7[45] 130 59 58 61 60 61 38 [46] 53 Atmospheric composition N2, CH4[47] N2, CH4[48] Largest dwarf-planet candidates
See also: Small Solar System body and List of dwarf planet candidatesThese trans-Neptunian objects are theoretically large enough to be given dwarf-planet status in the future. A further 30 or so TNOs could eventually be included,[2] and perhaps three other asteroids.[49] Both Quaoar and Orcus have known moons that have allowed the mass of the systems to be calculated. Both candidates are more massive than the 5×1020 kg recommendation of the IAU 2006 draft proposal.[50]
Orcus[51] Ixion[52] Varuna[53] 2005 UQ513[54] Quaoar[55] 2002 TC302[56] 2007 OR10[57] 2007 UK126[58] 2005 QU182[59] Sedna[60] 






Minor-planet number 90482 28978 20000 202421 50000 84522 225088 229762 90377 Semi-major axis km
AU5,896,946,000
39.4195,935,999,000
39.686,451,398,000
43.136,479,089,380
43.316,493,296,000
43.68,264,380,000
55.2410,072,433,340
67.3311,032,000,000
73.7416,991,749,800
113.5878,668,000,000
525.86Mean radius[s] km
:E[f]473
0.0742402
0.063508
0.08460
0.072[aa]422
0.066600
0.094<700
0.11[aa]440
0.07[aa]525
0.08[aa]<950
0.149Surface area[a] km²
:E[f]2,811,462
0.00552,030,775
0.003981,091,000
0.006362,659,044
0.00522,237,870
0.004394,521,600
0.008876,157,522
0.0122,432,849
0.0053,463,606
0.00711,341,150
0.0222Volume[b] km3
:E[f]443,273,768
0.0004272,123,951
0.0002549,135,785
0.0005407,720,083
0.0003314,793,649
0.0002904,320,000
0.00081,436,755,040
0.001356,817,905
0.0002606,131,033
0.00043,591,364,000
0.0033Mass[t] kg
:E[f]6.32×1020[61]
0.00015.4×1020
0.000095.5×1020
0.000098.2×1020
0.0001(2.1–2.9)×1021[62]
0.00041.8×1021
0.00032.9×1021
0.00057.1×1020
0.00011.2×1021
0.00027.2×1021
0.0012Density[t] g/cm3 1.5±0.3[61] 2.0 0.9992[63] 2.0 >2.8[62] 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 Equatorial gravity[d] m/s2 0.27 0.22 0.14 0.26 0.24 0.34 <0.39 0.25 0.29 <0.5 Escape velocity[e] km/s 0.50 0.42 0.38 0.49 0.45 0.63 <0.74 0.46 0.55 <1.0 Rotation period[g] days ? ? 0.13216[63] ? ? ? ? ? ? 0.42[64] Orbital period[g] years 247.492 249.95 283.20 285.12 287.97 410.62 552.52 633.28 1,210.53 12,059.06 Mean orbital speed km/s 4.68 4.66 4.53 4.52 4.52 3.93 3.63 3.25 2.79 1.04 Eccentricity 0.22552 0.242 0.051 0.145 0.038 0.292 0.5 0.490 0.675 0.855 Inclination[f] deg. 22.5 19.6 17.2 25.69 8 35 30.7 23.37 14.03 11.93 Mean surface temperature[w] K ~42 ~43 ~43 ~41 ~41 ~38 ~30 ~32 ~25 ~12 Number of known moons 1[65] 0 0 0 1[66] 0 0 0 0 0 Planetary discriminant[l][o] 0.003 0.0027 0.0027 0.003 0.0015 0.335 0.18[x] 0.036[x] 0.007[x] ?[x] Absolute magnitude (H) 2.30 3.20 3.70 3.40 2.71 3.8 1.7 3.40 3.40 1.58 See also
Notes
Unless otherwise cited:[ac]
- ^ The planetary discriminant for the planets is taken from material published by Stephen Soter.[67] Planetary discriminants for Ceres, Pluto and Eris taken from Soter, 2006. Planetary discriminants of all other bodies calculated from the Kuiper belt mass estimate given by Lorenzo Iorio.[68]
- ^ Saturn satellite info taken from NASA Saturnian Satellite Fact Sheet.[69]
- ^ Astronomical symbols for all listed objects except Ceres taken from NASA Solar System Exploration.[70] Symbol for Ceres was taken from material published by James L. Hilton.[71] The Moon is the only natural satellite with an astronomical symbol, and Pluto and Ceres the only dwarf planets.
- ^ Uranus satellite info taken from NASA Uranian Satellite Fact Sheet.[72]
- ^ Radii for plutoid candidates taken from material published by John Stansberry et al.[20]
- ^ Axial tilts for most satellites assumed to be zero in accordance with the Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac: "In the absence of other information, the axis of rotation is assumed to be normal to the mean orbital plane."[73]
- ^ Natural satellite numbers taken from material published by Scott S. Sheppard.[74]
Manual calculations (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ Surface area A derived from the radius using
 , assuming sphericity.
, assuming sphericity. - ^ Volume V derived from the radius using
 , assuming sphericity.
, assuming sphericity. - ^ Density derived from the mass divided by the volume.
- ^ Surface gravity derived from the mass m, the gravitational constant g and the radius r: g*m/r2 .
- ^ Escape velocity derived from the mass m, the gravitational constant g and the radius r: sqrt((2*g*m)/r).
- ^ Orbital speed is calculated using the mean orbital radius and the orbital period, assuming a circular orbit.
- ^ Assuming Pluto's density of 2.0
- ^ Calculated using the formula
 where Teff =54.8 K at 52 AU, pν is the geometrical albedo, q=0.8 is the phase integral, and r is the distance from the Sun in AU. This formula is a simplified version of that in section 2.2 of Stansberry, et al., 2007,[20] where emissivity and beaming parameter were assumed equal unity, and π was replaced with 4 accounting for the difference between circle and sphere. All parameters mentioned above were taken from the same paper.
where Teff =54.8 K at 52 AU, pν is the geometrical albedo, q=0.8 is the phase integral, and r is the distance from the Sun in AU. This formula is a simplified version of that in section 2.2 of Stansberry, et al., 2007,[20] where emissivity and beaming parameter were assumed equal unity, and π was replaced with 4 accounting for the difference between circle and sphere. All parameters mentioned above were taken from the same paper. - ^ Calculated using the formula
 , where H is the absolute magnitude, p is the geometric albedo and D is the diameter in km, and assuming an albedo of 0.15, as per Dan Bruton.[75]
, where H is the absolute magnitude, p is the geometric albedo and D is the diameter in km, and assuming an albedo of 0.15, as per Dan Bruton.[75]
Individual calculations
- ^ Derived from density
- ^ Surface area was calculated using the formula for an scalene ellipsoid:
 where
where  is the modular angle, or angular eccentricity;
is the modular angle, or angular eccentricity;  and
and  ,
,  are the incomplete elliptic integrals of the first and second kind, respectively. The values 980 km, 759 km, and 498 km were used for a, b, and c respectively.
are the incomplete elliptic integrals of the first and second kind, respectively. The values 980 km, 759 km, and 498 km were used for a, b, and c respectively.
Other notes
- ^ Relative to Earth
- ^ sidereal
- ^ retrograde
- ^ The inclination of the body's equator from its orbit.
- ^ At pressure of 1 bar
- ^ At sea level
- ^ The ratio between the mass of the object and those in its immediate neighborhood. Used to distinguish between a planet and a dwarf planet.
- ^ This object's rotation is synchronous with its orbital period, meaning that it only ever shows one face to its primary.
- ^ Objects' planetary discriminants based on their similar orbits to Eris. Sedna's population is currently too little-known for a planetary discriminant to be determined.
- ^ Proteus average diameter: 210 km;[44] Mimas average diameter: 199 km[69]
- ^ "Unless otherwise cited" means that the information contained in the citation is applicable to an entire line or column of a chart, unless another citation specifically notes otherwise.
References
- ^ "IAU 2006 General Assembly: Result of the IAU Resolution votes" (Press release). International Astronomical Union (News Release – IAU0603). 2006-08-24. http://www.iau.org/public_press/news/release/iau0603/. Retrieved 2007-12-31. (orig link)
- ^ a b Mike Brown. "The Dwarf Planets". CalTech. http://www.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/dwarfplanets/. Retrieved 2008-09-25.
- ^ M Woolfson (2000). "The origin and evolution of the solar system". Astronomy & Geophysics 41 (1): 1.12. doi:10.1046/j.1468-4004.2000.00012.x.
- ^ NASA Solar System exploration Sun factsheet and NASA Sun factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ a b Stacy Leong (2002). "Period of the Sun's Orbit around the Galaxy (Cosmic Year)". In Glenn Elert (ed.). The Physics Factbook (self-published). http://hypertextbook.com/facts/2002/StacyLeong.shtml. Retrieved 2008-06-26.
- ^ Markus J. Aschwanden (2007). "The Sun". In Lucy Ann McFadden, Paul R. Weissman, Torrence V. Johnsson. Encyclopedia of the Solar System. Academic Press. p. 80.
- ^ NASA Mercury Fact Sheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ NASA Venus Factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ a b NASA Earth factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ NASA Mars Factsheet and NASA Mars Solar System Exploration Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ NASA Jupiter factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ NASA Saturn factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Saturn Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ NASA Uranus factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Uranus Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ NASA Neptune factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Neptune Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA Asteroid Factsheet". NASA. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/factsheet/asteroidfact.html. Retrieved 2008-11-17.
- ^ a b NASA Pluto factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Pluto Factsheet Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ (i)D. L. Rabinowitz, K. M. Barkume, M. E. Brown, H. G. Roe, M. Schwartz, S. W. Tourtellotte, C. A. Trujillo (2006). "Photometric Observations Constraining the Size, Shape, and Albedo of 2003 EL61, a Rapidly Rotating, Pluto-Sized Object in the Kuiper Belt". The Astrophysical Journal 639 (2): 1238–1251. arXiv:astro-ph/0509401. Bibcode 2006ApJ...639.1238R. doi:10.1086/499575.
(ii)"Jet Propulsion Laboratory Small-Body Database Browser: 136108 Haumea". NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (2008-05-10 last obs). http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=136108. Retrieved 2008-11-13. (unless otherwise cited) - ^ (i)Marc W. Buie (2008-04-05). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 136472". SwRI (Space Science Department). http://www.boulder.swri.edu/~buie/kbo/astrom/136472.html. Retrieved 2008-07-13.
(ii)"NASA Small Bodies Database Browser: 136472 Makemake (2005 FY9)". NASA JPL. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=136472. Retrieved 2008-10-03. (unless otherwise cited) - ^ "NASA Small Body Database Browser: Eris". NASA JPL. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=Eris. Retrieved 2008-11-13. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ a b c d e J. Stansberry, W. Grundy, M. Brown, et al. (2007). "Physical Properties of Kuiper Belt and Centaur Objects: Constraints from Spitzer Space Telescope". The Solar System beyond Neptune (University of Arizona Press). arXiv:astro-ph/0702538. Bibcode 2008ssbn.book..161S.
- ^ M. E. Brown, A. H. Bouchez, D. L. Rabinowitz, R. Sari, C. A. Trujillo, M. A. van Dam, R. Campbell, J. Chin, S. Hartman, E. Johansson, R. Lafon, D. LeMignant, P. Stomski, D. Summers, P. L. Wizinowich (October 2005). "Keck Observatory laser guide star adaptive optics discovery and characterization of a satellite to large Kuiper belt object 2003 EL61". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 632 (L45): L45. Bibcode 2005ApJ...632L..45B. doi:10.1086/497641.
- ^ Michael E. Brown and Emily L. Schaller (2007). "The Mass of Dwarf Planet Eris". Science 316 (1585): 1585. Bibcode 2007Sci...316.1585B. doi:10.1126/science.1139415. PMID 17569855. http://www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/abstract/316/5831/1585.
- ^ D. L. Rabinowitz, K. M. Barkume, M. E. Brown, H. G. Roe, M. Schwartz, S. W. Tourtellotte, C. A. Trujillo (2006). "Photometric Observations Constraining the Size, Shape, and Albedo of 2003 EL61, a Rapidly Rotating, Pluto-Sized Object in the Kuiper Belt". The Astrophysical Journal 639 (2): 1238–1251. arXiv:astro-ph/0509401. Bibcode 2006ApJ...639.1238R. doi:10.1086/499575.
- ^ O. Saint-Pé; N. Combes, F. Rigaut (1993). "Ceres surface properties by high-resolution imaging from Earth". Icarus 105 (2): 271–281. Bibcode 1993Icar..105..271S. doi:10.1006/icar.1993.1125.
- ^ T. Ker (2006). "Astronomers: Pluto colder than expected". Space.com (via CNN.com). http://www.cnn.com/2006/TECH/space/01/03/pluto.temp/index.html. Retrieved on 2006-03-05.
- ^ Chadwick A. Trujillo, Michael E. Brown, Kristina Barkume, Emily Shaller, David L. Rabinowitz (February 2007). "The Surface of 2003 EL61 in the Near Infrared". The Astrophysical Journal 655 (2): 1172–1178. arXiv:astro-ph/0601618. Bibcode 2007ApJ...655.1172T. doi:10.1086/509861.
- ^ Mike Brown, K. M. Barksume, G. L. Blake, E. L. Schaller, D. L. Rabinowitz, H. G. Roe and C. A. Trujillo (2007). "Methane and Ethane on the Bright Kuiper Belt Object 2005 FY9". The Astronomical Journal 133 (1): 284–289. Bibcode 2007AJ....133..284B. doi:10.1086/509734.
- ^ J. Licandro, W. M. Grundy, N. Pinilla-Alonso, P. Leisy (2006). "Visible spectroscopy of 2003 UB313: evidence for N2 ice on the surface of the largest TNO" (PDF). Astronomy and Astrophysics 458 (1): L5–L8. arXiv:astro-ph/0608044. Bibcode 2006A&A...458L...5L. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20066028. http://www.aanda.org/index.php?option=article&access=standard&Itemid=129&url=/articles/aa/pdf/2006/40/aa6028-06.pdf.
- ^ D. Ragozzine, M. E. Brown, C. A. Trujillo, E. L. Schaller. "Orbits and Masses of the 2003 EL61 Satellite System". AAS DPS conference 2008. http://www.abstractsonline.com/viewer/viewAbstract.asp?CKey={421E1C09-F75A-4ED0-916C-8C0DDB81754D}&MKey={35A8F7D5-A145-4C52-8514-0B0340308E94}&AKey={AAF9AABA-B0FF-4235-8AEC-74F22FC76386}&SKey={545CAD5F-068B-4FFC-A6E2-1F2A0C6ED978}. Retrieved 2008-10-17.
- ^ Brown, M. E. et al. (2006). "Satellites of the Largest Kuiper Belt Objects" (PDF). The Astrophysical Journal 639: L43. arXiv:astro-ph/0510029. Bibcode 2006ApJ...639L..43B. doi:10.1086/501524. http://web.gps.caltech.edu/~mbrown/papers/ps/gab.pdf. Retrieved 2011-10-19.
- ^ M. E. Brown, M. A. van Dam, A. H. Bouchez, D. LeMignant, C. A. Trujillo, R. Campbell, J. Chin, Conrad A., S. Hartman, E. Johansson, R. Lafon, D. L. Rabinowitz, P. Stomski, D. Summers, P. L. Wizinowich (2006). "Satellites of the largest Kuiper belt objects". The Astrophysical Journal 639 (1): L43–L46. arXiv:astro-ph/0510029. Bibcode 2006ApJ...639L..43B. doi:10.1086/501524.
- ^ NASA Moon factsheet and NASA Solar System Exploration Moon Factsheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA Io Factsheet". NASA. http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/io/fact.html#stats. Retrieved 2008-11-16. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA Europa Factsheet". NASA. http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/europa/. Retrieved 2008-11-16. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA Ganymede Factsheet". NASA. http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/ganymede/fact.html. Retrieved 2008-11-16. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA Callisto Factsheet". NASA. http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/callisto/. Retrieved 2008-11-16. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ Bruce G. Bills (2005). "Free and forced obliquities of the Galilean satellites of Jupiter". Icarus 175 (1): 233–247. Bibcode 2005Icar..175..233B. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2004.10.028.
- ^ GS Orton; G.R. Spencer, L.D. Travis, et al. (1996). "Galileo Photopolarimeter-radiometer observations of Jupiter and the Galilean Satellites". Science 274 (5286): 389–391. Bibcode 1996Sci...274..389O. doi:10.1126/science.274.5286.389.
- ^ JC Pearl, et al. (1979). "Identification of gaseous SO2 and new upper limits for other gases on Io". Nature 288 (5725): 755. Bibcode 1979Natur.280..755P. doi:10.1038/280755a0.
- ^ D.T. Hall et al.; Detection of an oxygen atmosphere on Jupiter's moon Europa, Nature, Vol. 373 1995, 677–679 (accessed 2006-15-04)
- ^ DT Hall, PD Feldman, MA McGrath, et al. (1998). "The Far-Ultraviolet Oxygen Airglow of Europa and Ganymede". The Astrophysical Journal 499 (1): 475–481. Bibcode 1998ApJ...499..475H. doi:10.1086/305604. Retrieved on 2008-11-17.
- ^ Liang, Mao-Chang (2005). "Atmosphere of Callisto" (PDF). Journal of Geophysics Research 110 (E02003): E02003. Bibcode 2005JGRE..11002003L. doi:10.1029/2004JE002322. http://yly-mac.gps.caltech.edu/ReprintsYLY/N164Liang_Callisto%2005/Liang_callisto_05.pdf. Retrieved on 2008-11-17.
- ^ JH Waite, et al. (2006). "Cassini Ion and Neutral Mass Spectrometer: Enceladus Plume Composition and Structure". Science 311 (5766): 1419–1422. Bibcode 2006Sci...311.1419W. doi:10.1126/science.1121290. PMID 16527970. Retrieved on 2008-11-17.
- ^ a b Triton info taken from NASA Neptunian Satellite Fact Sheet NASA Retrieved on 2009-01-18 (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ C. A. Hasenkopf (2007). "Optical Properties of Titan Haze Laboratory Analogs Using Cavity Ring Down Spectroscopy". Workshop on Planetary Atmospheres. http://64.233.183.104/search?q=cache:H1UhAFtLEpEJ:www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/patm2007/pdf/9034.pdf+titan+anti-greenhouse-effect+2006+OR+2007&hl=en&ct=clnk&cd=3&gl=uk. Retrieved 2007-10-16.
- ^ Kimberly Tryka, Robert Brown, V. Anicich et al. (August 1993). "Spectroscopic Determination of the Phase Composition and Temperature of Nitrogen Ice on Triton". Science 261 (5122): 751–754. Bibcode 1993Sci...261..751T. doi:10.1126/science.261.5122.751. PMID 17757214.
- ^ H. B. Niemann, et al. (2005). "The abundances of constituents of Titan’s atmosphere from the GCMS instrument on the Huygens probe". Nature 438 (7069): 779–784. Bibcode 2005Natur.438..779N. doi:10.1038/nature04122. PMID 16319830.
- ^ A L Broadfoot, S K Bertaux, J E Dessler et al. (1989-12-15). "Ultraviolet Spectrometer Observations of Neptune and Triton". Science 246 (4936): 1459–1466. Bibcode 1989Sci...246.1459B. doi:10.1126/science.246.4936.1459. PMID 17756000.
- ^ Ron Ekers. "IAU Planet Definition Committee". International Astronomical Union. http://www.iau.org/public_press/news/release/iau0601/newspaper/. Retrieved 2008-10-13.
- ^ O. Gingerich (2006). "The Path to Defining Planets" (PDF). Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and IAU EC Planet Definition Committee chair. http://astro.cas.cz/nuncius/nsiii_03.pdf. Retrieved 2007-03-13.
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 90482 Orcus (2004 DW)". NASA JPL. 2008-02-10 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=Orcus. Retrieved 2008-07-02. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 28978 Ixion (2001 KX76)". NASA JPL. 2007-07-12 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=Ixion. Retrieved 2008-10-04. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 20000 Varuna (2000 WR106)". NASA JPL. 2007-11-17 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=20000. Retrieved 2008-07-02. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2005 UQ513)". 2008-11-29 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2005UQ513. Retrieved 2008-07-31.(unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA JPL Database Browser: 50000 Quaoar". NASA JPL. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=50000. Retrieved 2008-12-19. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 84522 (2002 TC302)". 2007-12-08 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=84522. Retrieved 2009-03-05. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "NASA Small Bodies Database Browser: 2007 OR10". NASA JPL. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2007OR10. Retrieved 2008-12-20. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 229762 (2007 UK126)". 2009-12-20 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=229762. Retrieved 2010-05-02. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: (2005 QU182)". 2008-10-24 last obs. http://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb.cgi?sstr=2005QU182. Retrieved 2008-12-09. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ Marc W. Buie (2007-08-13). "Orbit Fit and Astrometric record for 90377". Deep Ecliptic Survey. http://www.boulder.swri.edu/~buie/kbo/astrom/90377.html. Retrieved 2006-01-17. (unless otherwise cited)
- ^ a b Brown, M.E.; Ragozzine, D.; Stansberry, J.; Fraser, W.C. (2009). "The size, density, and formation of the Orcus-Vanth system in the Kuiper belt". AJ. arXiv:0910.4784. Bibcode 2010AJ....139.2700B. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/139/6/2700.
- ^ a b Brown, M.E.; Fraser, Wesley (2009). "Quaoar: A Rock in the Kuiper Belt". DPS meeting #41. American Astronomical Society. Bibcode 2009DPS....41.6503F. (Backup reference)
- ^ a b David C. Jewitt and Scott S. Sheppard (2002). "Physical Properties of Trans-Neptunian Object (20000) Varuna". The Astronomical Journal 123 (4): 2110–2120. arXiv:astro-ph/0201082. Bibcode 2002AJ....123.2110J. doi:10.1086/339557. http://www.iop.org/EJ/article/1538-3881/123/4/2110/201498.html. Retrieved on 2008-12-19.
- ^ "Case of Sedna's Missing Moon Solved". Harvard Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. 2005. http://www.cfa.harvard.edu/news/2005/pr200510.html. Retrieved 2011-07-05.
- ^ Distant EKO The Kuiper Belt Electronic newsletter, March 2007 Retrieved on 2008-11-17
- ^ "IAUC 8812: Sats OF 2003 AZ_84, (50000), (55637),, (90482); V1281 Sco; V1280 Sco". International Astronomical Union. http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iauc/08800/08812.html. Retrieved 2011-07-05.
- ^ Stephen Soter (2006-08-16). "What is a Planet?". The Astronomical Journal 132 (6): 2513–2519. arXiv:astro-ph/0608359. Bibcode 2006AJ....132.2513S. doi:10.1086/508861.
- ^ Lorenzo Iorio (2007-03). "Dynamical determination of the mass of the Kuiper Belt from motions of the inner planets of the Solar system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 375 (4): 1311–1314. Bibcode 2007MNRAS.tmp...24I. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2006.11384.x.
- ^ a b NASA Saturnian Satellite Fact Sheet NASA Retrieved on 2008-11-17
- ^ "NASA Solar System Exploration: Planet Symbols". NASA. http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/multimedia/display.cfm?IM_ID=167. Retrieved 2009-01-26.
- ^ James L. Hilton. "When did asteroids become minor planets?" (PDF). U.S. Naval Observatory. http://sd-www.jhuapl.edu/weaver_projects/GPD/Contributed_Talks/hilton_gpd_poster.pdf. Retrieved 2008-10-25.
- ^ "NASA Uranian Satellite Fact Sheet". NASA. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/factsheet/uraniansatfact.html. Retrieved 2008-11-17.
- ^ P. Kenneth Seidelmann, ed (1992). Explanatory Supplement to the Astronomical Almanac. University Science Books. p. 384.
- ^ Scott S. Sheppard. "The Jupiter Satellite Page". Carnegie Institution for Science, Department of Terrestrial Magnetism. http://www.dtm.ciw.edu/users/sheppard/satellites. Retrieved 2008-04-02.
- ^ Dan Bruton. "Conversion of Absolute Magnitude to Diameter for Minor Planets". Department of Physics & Astronomy (Stephen F. Austin State University). http://www.physics.sfasu.edu/astro/asteroids/sizemagnitude.html. Retrieved 2009-01-20.
The Solar System  Categories:
Categories:- Lists of Solar System objects
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
