- Markó–Lam deoxygenation
-
The Markó–Lam deoxygenation is an organic chemistry reaction where the hydroxy functional group in an organic compound is replaced by a hydrogen atom to give an alkyl group.[1][2] The Markó-Lam reaction is a variant of the Bouveault–Blanc reduction[3] and an alternative to the classical Barton–McCombie deoxygenation. It is named for the Belgian chemists Istvan Marko and Kevin Lam.[4]
The main features of the reaction are :
- its short reaction time (between 5 seconds to 5 minutes).
- the use of a stable toluate derivative.
- the use of SmI2/HMPA system or electrolysis instead of the classical and difficult to remove tributyltin hydride.

Contents
Mechanism
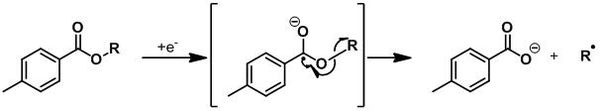
A hydroxyl group is first derivitised into a stable and very often crystalline toluate derivative. The aromatic ester is submitted to a monoelectronical reduction, by the use of SmI2/HMPA[5] or by electrolysis,[6] to yield the a radical-anion which decomposes into the corresponding carboxylate and into the radical of the alkyl part.
This radical could be used for further chemical reactions or can abstract an hydrogen atom to form the deoxygenated product.
Variations
In presence of methanol or isopropanol, the reduction lead to the selective deprotection of the aromatic esters.[7]

In presence of ketones, allylic derivatives lead to the coupling product when treated in Barbier's conditions with samarium diiodide.[8]

Scope
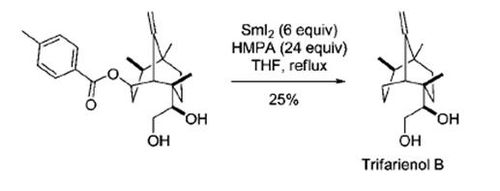
The Markó-Lam reaction was used as a final step in the total synthesis of Trifarienol B:[9]
References
- ^ "Alkane synthesis by deoxygenation". Organic-chemistry.org. http://www.organic-chemistry.org/synthesis/C1H/deoxygenations.shtm. Retrieved 2010-01-01.
- ^ http://www.chem-station.com/odos/2010/06/-marko-lam-deoxygenation.html
- ^ Bouveault, L.; Blanc, G. Bull. Soc. Chim. France, 1904, 31: 666.
- ^ http://www.uclouvain.be/en-207936.html
- ^ Lam, K.; Markó I.E. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2773.
- ^ Lam, K.; Markó I.E. Chem. Comm. 2009, 95.
- ^ Lam, K.; Markó I.E. Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2752.
- ^ Lam, K.; Markó I.E. Tetrahedron. 2009, 65, 10930.
- ^ K.Takahashi, R. Akao, T. Honda, J. Org. Chem., 2009, 74, 3424.
Categories:- Free radical reactions
- Organic redox reactions
- Name reactions
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.