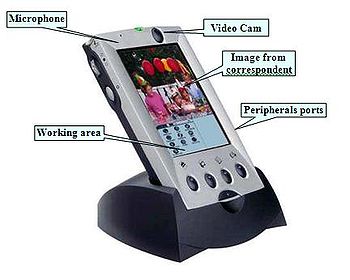
- Multimedia terminal mobile
-
Contents
Introduction
The first integration between mobile phone and Palm (PDA Personal Device Assistant) occurred in 1999, as a result of an Italian–lead project[1] submitted to the action line V1.1 CPA1 "Integrated application platforms and services" 5th Framework Program[2] of the European Community (project number IST1999-11100)[3][4][5][6][7][8]). The project, called MTM (Multimedia Terminal Mobile), was a multimedia platform, including both phone and PDA features; it also integrated the first miniature camera and a unidirectional microphone for video conferencing and commands interpretation through voice recognition. The creator and coordinator of the project, Alessandro Pappa,[9] worked in a team with ten other European partners.[10] It was one of the larger projects accepted by the EC in terms of cost and numbers of project participants. It received a no refundable loan for more than 50% of the investments. The MTM formed the basis of other international projects[11] and started the video broadband communication technology.
Project goals
The major objectives of the MTM project were to:
- Introduce a new generation of communication in the millennium 2000: trough a mobile terminal, making phone calls using the new high bandwidth transmission technology and at the same time being able to see the other person in video conference.
- Create an object capable of connecting to broadband for telephony and for Internet, with WEB navigation emailing, etc. Basically, having the office in your pocket.
The project in brief
The MTM project has created a Hardware platform, and four vertical applications: Easy City Guide, Distance Learning, Telemedicine[12][13][14][15][16][17][18][19] and Speech and Speaker Recognition.[20]
- Easy City Guide is a guided tour with photos and voice assistant serving as a guide to museum and historical sites
- Distance Learning is a set of documents shown on a Specimen layout via the MTM in support of technical staff involved in service and maintenance.
- Telemedicine allows a remote retrieval of three-dimensional CT scans, images rotation and zooming in real time through an operator interface to hospital server and medical equips in speakerphone.
- Speech and Speaker Recognition can recognize the person who asked for a command request through biometric voice recognition. This application is designed for data security and it works transversally to the other applications.
The MTM team introduced the wireless transmission for MTM in 1999, right when the new UMTS[21][22] technology came out. Although there weren't worldwide network infrastructures yet (they were expected to be available not before year 2002[23]) the MTM team used the 802.11[24] connection to verify the operation with the server of CHILI (www.chili-radiology.com/de/). CHILI developed a new generation of teleradiology software, where it is possible to see the three-dimensional CT[25] scan and do remote diagnostics to the patient at once.
Many other services and applications have been studied using the MTM. Only some of these applications and services have been so far developed on other technologies such as Smartphones. Although many large companies had worked years before to develop advanced mobile phone and PDA devices [see Nokia 9000 Communicator], none has reached MTM for integration between telephony, video, computer and broadband transmission. The new communication, audio and visual, set the background for a vast array of possible services, of interest to both professional and personal use.
MTM technical features
Feature Specifications Wireless Transmission UMTS GSM module WCDMAx Loudspeaker Incorporated Video Camera Incorporated Microphone Incorporated with noise filter Data PC Transmission IRDA interface 115 k baud or higher Line Powered 6 VDC High Speed Communications From 150 kbit/s to2 Mbit/s maximum RAM From 16 Mb to 32 Mb Downloadable Application SW Flash memory Graphical SVGA display LCD color touch screen 240x320 pixel Voice recorder controller ~ 5 minutes Internet Email reading and writing, browser RS-232 Data Port Serial communication through a PC interface Operating System Linux Dimension Around 7 x 4,5 x 0.5 inc. Notes
- ^ "List of projects under the 5th Framework Program of the IST Program (Czechoslovakia)". Eumed.cz. http://www.eumed.cz/english/Projects_of_5th_frame_programme.htm. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ "2004_1185_testo_EN" (PDF). http://ec.europa.eu/information_society/activities/health/docs/publications/fp5-ehealth-applications-relating-to-health.pdf. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ [http://www.itu.int/ITU-D/study_groups/SGP_1998-2002/TELECOMMUNICATION DEVELOPMENT BUREAU SG2/Documents/2001/195REV2E.DOC-ITU-D Study Groups
- ^ 2001 – European Health Telematics Observatory – USA[dead link]
- ^ "Slovenia". Istworld. 31 December 2001. http://www.ist-world.org/ProjectDetails.aspx?ProjectId=fe44734892bf491290f344a0e9bc53a0. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ "2001 – Stockholm Challenge – Sweden". Stockholm Challenge. http://www.stockholmchallenge.org/project/data/mtm. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ "Cordis IST (Information Society Technologies) Finance Coordinator – Luxembourg". Europa (web portal). http://cordis.europa.eu/fetch?ACTION=D&CALLER=PROJ_IST&RCN=58347. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ Website – Poland
- ^ Born in Colleferro (RM) in 1961, he worked at the PointerCom 1998 to 2001. See Details
- ^ ,
- 1) PointerCom
- 2) Sirius Communication NV
- 3) Sistemas Expertos SA
- 4) Matla System
- 5) University of Avignon – LIA
- 6) Comune di Roma – Eurolaboratorio
- 7) DKFZ-MBI, Div. Medical and Biological Informatics, German Cancer Research Center
- 8) TZMI, Steinbeis-Transferzentrum Medizinische Informatik
- 9) Universidad Politécnica de Madrid
- 10) Clinica Femenia
- 11) Clinica Nuestra senora del Rosario
- ^ ftp://ftp.cordis.europa.eu/pub/ist/docs/transport-environment/intelligentsystems_for_tourism_en.pdf List of projects on tourism in the 5th Framework Program
- ^ 7.pdf January 2009 The Electronic Library of Mathematics – Mathematical Journals – Germany[dead link]
- ^ "2001 – "Mobile Teleradiology on PDAs and Webpads"- Germany". Mocomed.org. 26 July 2011. http://www.mocomed.org/download-veranstaltungen/2002/schweitzer.htm. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ = C000050221 & _version = 1 & _urlVersion = 0 & _userid = 10 & md5 = 334e13f350999e8e4c1de98fb823abb0 2001 – Article "Mobile teleradiology: all images everywhere" on ScienceDirect – USA
- ^ 01.shtml-V-2001 – Germany – Congress Teleradiology Mobile. (German)[dead link]
- ^ "2001 – Germany – Congress Teleradiology Mobile. (English)" (PDF). http://mbi.dkfz-heidelberg.de/mbi/TR/Papers//01-cars-final.pdf. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ "2001 – Article about Virtual Medical Worlds – Netherlands". Hoise.com. 3 May 2001. http://www.hoise.com/vmw/01/articles/vmw/LV-VM-06-01-23.html. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ A Collaborative Virtual Medical Team for Home Healthcare of Cancer Patients ISBN 978-0-387-26558-2
- ^ Mobile http://www.uniklinikum-giessen.de/kis-ris-pacs/archiv/2001/mi1530.pdf CHILI teleradiology mit: Von der Vision zum praktischen Einsatz (German)
- ^ "XXIV Journ'ees `emes d'Etude sur la Parole, Nancy, 24–27 juin 2002 (French)" (PDF). http://lia.univ-avignon.fr/fich_art/304-MTM-jep2002.pdf. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ page Cordis[dead link]
- ^ ftp://ftp.cordis.europa.eu/pub/ist/docs/ka4/final_release7sept99.pdf Report Cordis – 1999
- ^ ftp://ftp.cordis.europa.eu/pub/ist/docs/ka4/umtstaskforce.pdf Task Force UMTS – 1996
- ^ "result & resnum = 5 & ved 0CB0Q6AEwBA = # v = onepage & q =% mtm 20multimedia% 20terminal% 20Mobile & f = false 2002 – Book "802.11 Demystified" page 199 McHGraw – Hill TELECOM, James LaRocca and Ruth LaRocca – (English)". Books.google.it. http://books.google.it/books?id=mC9JV_w_93oC&pg=PA199&lpg=PA199&dq=mtm+multimedia+terminal+mobile&source=bl&ots=FQQYW8mjiN&sig=FU8zlPkGaUJEACqyZgkCVhVXySE&hl=it&ei=TkpDS4fRBdah_gaSvZHzCA&sa=X&oi=book_result&ct. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
- ^ Česky. "X-ray computed tomography – Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia". En.wikipedia.org. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Computed_tomography. Retrieved 21 October 2011.
((portal | Information technology | Library and information science))
Categories:- Telecommunications
- Mobile Web
- Health
- Science and technology in Italy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.