- Mutual funds in India
-
The first introduction of a mutual fund in India occurred in 1963, when the Government of India launched Unit Trust of India (UTI). Until 1987, UTI enjoyed a monopoly in the Indian mutual fund market. Then a host of other government-controlled Indian financial companies came up with their own funds. These included State Bank of India, Canara Bank, and Punjab National Bank. This market was made open to private players in 1993, as a result of the historic constitutional amendments brought forward by the then Congress-led government under the existing regime of Liberalization, Privatization and Globalization (LPG). The first private sector fund to operate in India was Kothari Pioneer, which later merged with Franklin Templeton.
Current Scenario
The major fund houses which have operated in India include:
Fortis
Birla Sunlife
Bank of Baroda
HDFC
ING Vysya
ICICI Prudential
SBI Mutual Fund
Tata
Kotak Mahindra
Unit Trust of India
Reliance
IDFC
Franklin Templeton
Sundaram Mutual Fund
Religare Mutual Fund
Principal Mutual FundMutual funds are an under tapped market in India
Despite being available in the market for over two decades now with assets under management equaling Rs 7,81,71,152 Lakhs (as of 28 February 2010) (Source: Association of Mutual Funds, India), less than 10% of Indian households have invested in mutual funds. A recent report on Mutual Fund Investments in India published by research and analytics firm, Boston Analytics, suggests investors are holding back from putting their money into mutual funds due to their perceived high risk and a lack of information on how mutual funds work. This report is based on a survey of approximately 10,000 respondents in 15 Indian cities and towns as of March 2010. There are 43 Mutual Funds recently[citation needed].
The primary reason for not investing appears to be correlated with city size. Among respondents with a high savings rate, close to 40% of those who live in metros and Tier I cities considered such investments to be very risky, whereas 33% of those in Tier II cities said they did not how or where to invest in such assets.
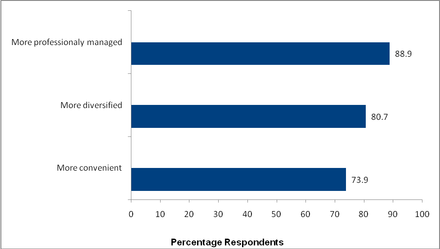
On the other hand, among those who invested, close to nine out of ten respondents did so because they felt these assets were more professionally managed than other asset classes. Exhibit 2 lists some of the influencing factors for investing in mutual funds. Interestingly, while non-investors cite “risk” as one of the primary reasons they do not invest in mutual funds, those who do invest consider that they are “professionally managed” and “more diverse” most often as their reasons to invest in mutual funds versus other investments.
Resources
1. Boston Analytics
2. Association of Mutual Funds India
3. IndiamartCategories:- Mutual funds of India
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.