- NATO Operations
-
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization or NATO (
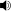 /ˈneɪtoʊ/ nay-toh; French: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique Nord (OTAN)), also called the (North) Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance based on the North Atlantic Treaty which was signed on 4 April 1949.
/ˈneɪtoʊ/ nay-toh; French: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique Nord (OTAN)), also called the (North) Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance based on the North Atlantic Treaty which was signed on 4 April 1949.Although NATO was present throughout the Cold War as the opposite to the Warsaw Pact, joint military exercises were practised but not military operation took place. This came after the Cold War when NATO's influence in a post-Cold War rose to prominence in Bosnia where NATO gradually stepped up their efforts to end the trouble. This culminated with NATO's first air campaign in 1995 which targeted the Army of Republika Srpska whose presence in Bosnia posed a danger to United Nations "safe areas" and ultimately the bombing helped to bring about the Dayton Accords.
The organization now plays a prominent role in Afghanistan after the September 11 attacks in the United States invoked Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty which deemed the attacks to be an external attack on all NATO members under the idea of collective defence. Aside from continuing efforts in Afghanistan NATO has participated in a wide range of roles including relief effort, counter-piracy, enforcing no-fly zones and naval blockades.
Contents
Bosnia (1992-2004)
NATO was prominent in Bosnia during the early 1990s, and gradually its role became larger with some operations escalating, for instance Operation Sky Monitor turned into Operation Deny Flight which gave NATO "all measures necessary" to enforce a more stringent no-fly zone unlike Sky Monitor during which the no-fly zone was violated over 500 times. It took 46 years after NATO's inception in 1949 for the organization first ever military intervention took place in 1995, Operation Deliberate Force which was targeted the Army of Republika Srpska in Bosnia whose presence posed a danger to designated United Nations "safe areas". The air campaign helped bring about the Dayton Accords.
Date Operation Location Type Information 16 July 1992 -
22 November 1992Operation Maritime Monitor International waters off Serbia Naval blockade Naval blockade aimed at enforcing sanctions stipulated in UN Security Council Resolutions 713 and 757. 16 October 1992 -
12 April 1993Operation Sky Monitor
(Resolution 781)Bosnian airspace No-fly zone Established a no-fly zone over the airspace of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Effectiveness of the no-fly zone is debatable as by April 1993 500 violations (by all sides) of the no-fly zone had been recorded. NATO members voted for an "all necessary measures" resolution by the United Nations to allow NATO a mandate to enforce the no-fly zone more stringently. 22 November 1992 - 1993 Operation Maritime Guard
(Resolution 787)International waters in Adriatic Sea Naval blockade Authorized NATO to use force, and included stopping, inspecting, and diverting ships bound for the former Yugoslavia. All ships bound to or coming from the territorial waters of the former Yugoslavia were halted for inspection and verification of their cargoes and destinations. 13 April 1993 -
20 December 1995Operation Deny Flight
(Resolutions 816 and 836)Bosnian airspace No-fly zone Resolution 816 extended the ban to cover flights by all fixed-wing and rotary-wing aircraft over the country, and to use all measures necessary to ensure compliance with the ban. Resolution 836 authorized the use of force by UNPROFOR in the protection of specially designated UN "safe areas". 15 June 1993 -
2 October 1996Operation Sharp Guard
(Numerous resolutions)Yugoslavia Naval blockade A widespread naval blockade aimed at all former Yugoslavia. 30 August -
20 September 1995Operation Deliberate Force Bosnia and Herzegovina Air campaign Involving approximately 400 aircraft, Deliberate Force targeted at the Army of Republika Srpska whose presence in Bosnia posed a danger to United Nations "safe areas". 20 December 1995 -
20 December 1996Operation Joint Endeavour Bosnia and Herzegovina Peacekeeping force NATO-led Implementation Force(IFOR) peacekeeping force was established which was a force tasked with enforcing the peace under the Dayton Accords. 21 December 1996 -
19 June 1998Operation Joint Guard Bosnia and Herzegovina Peacekeeping force NATO-led Stabilisation Force(SFOR) peacekeeping force which replaced the IFOR which was a force tasked with enforcing peace under the Dayton Accords. 20 June 1998 -
2 December 2004Operation Joint Forge Bosnia and Herzegovina Peacekeeping force A continuation of Operation Joint Guard. 2 December 2004 -
PresentEUFOR Althea Bosnia and Herzegovina Peacekeeping force NATO-led European Union Force Althea(EUFOR Althea) peacekeeping force which replaced the SFOR which is a force tasked in enforcing peace under the Dayton Accords. Serbia and Kosovo (1999)
 Operation Allied Force was a controversial air campaign aimed at pushing Serbia into submission to force Slobadan Milosevic to accept a peace agreement
Operation Allied Force was a controversial air campaign aimed at pushing Serbia into submission to force Slobadan Milosevic to accept a peace agreement
Date Operation Location Type Information 24 March 1999 -
10 June 1999Operation Allied Force Kosovo and Serbia Air campaign A sustained air campaign targeting infrastructure in Serbia and Serbian forces in Kosovo with the ulterior aim of getting the 'Serbs out [of Kosovo], peacekeepers in, refugees back' in the eyes of one NATO spokesman. The bombing lasted for nearly 3 months before all sides accepted the Kumanovo Treaty which ended the Kosovo War and the deployment of KFOR. The legitimacy of the NATO air campaign has been questioned as too was the number of civilian casualties in the operation. 12 June 1999 -
PresentKFOR Kosovo Peacekeeping force A NATO-led Kosovo Force(KFOR) international peacekeeping force responsible for establishing a secure environment in Kosovo to enforce Resolution 1244. International Security Assistance Force - Afghanistan (2001-present)
The September 11 attacks in the United States, a NATO member, invoked Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty. It remains the only time since NATO's inception that an attack from an external party or state has been deemed an attack on all NATO members.
On 20 December 2001, UN Security Council Resolution 1386 unanimously approved the International Security Assistance Force, a multi-national NATO-led coalition with the aim of enforcing peace in Afghanistan.
2001-present
 NATO became involved in the growing problem of piracy off the coast of Africa with Operation Ocean Shield in 2009
NATO became involved in the growing problem of piracy off the coast of Africa with Operation Ocean Shield in 2009
 Tomahawk missiles being launched on the first night of engagement in Libya and which NATO codenamed Operation Unified Protector
Tomahawk missiles being launched on the first night of engagement in Libya and which NATO codenamed Operation Unified Protector
Date Operation Location Type Information 8 October 2005 -
9 February 2006[1]Pakistan Earthquake relief Pakistan Relief effort - Airlift NATO took on another new responsibility in the post-Cold War era by providing aid in the wake of 2005 Kashmir Earthquake in Pakistan. NATO accepted a request from the Pakistani government for assistance and in total 3,500 tons of relief supplies were delivered to Pakistan whilst also sending medical teams and engineers. 17 August 2009 -
presentOperation Ocean Shield
(Resolution 1838 and 1950)Red Sea, Gulf of Aden, Indian Ocean Counter-piracy (Piracy in Somalia) In October 2008, NATO announced they would send NATO warships to counter the rising problem of piracy off the coast of Africa.[2] In August 2009, the mission was upgraded to Operation Ocean Shield which was a concerted effort to eradicate piracy and the operation continues to this day with piracy still at large amid calls for greater powers from NATO to combat the problem[3] 27 March 2011 -
PresentOperation Unified Protector
(Resolution 1973)Libya No-fly zone
Air campaignThe Arab Spring spread to Libya by March 2011 with objection to Muammar Gaddafi crushed amid reports Libyan Air Force pilots have been ordered to bomb protesters, two pilots refused to carry out this order and defected landing their fighter jets in Malta.[4] UN SC Resolution 1973 gave NATO a mandate to enforce a no-fly zone and granted "all necessary measures" to protect civilians. References
- ^ "Pakistan earthquake relief operation". NATO. http://www.nato.int/issues/pakistan_earthquake/index.html. "The mission came to an end, on schedule, on 1 February 2006."
- ^ "Nato to target Somalia's pirates". BBC. 2008-10-09. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/7661927.stm. Retrieved 2011-05-28.
- ^ "Nato frustrated amid Somali piracy deluge". BBC. 2010-10-23. http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/world-11609724. Retrieved 2011-05-28.
- ^ "Two Libyan fighter pilots defect, fly to Malta". Reuters. 2011-02-21. http://www.reuters.com/article/2011/02/21/us-libya-protests-malta-idUSTRE71K52R20110221.
North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) History - North Atlantic Treaty
- Summit
- Operations
- Enlargement

Structure Members Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


