- New Cross Gate railway station
-
Not to be confused with New Cross railway station.
New Cross Gate 


Station entrance on New Cross Road
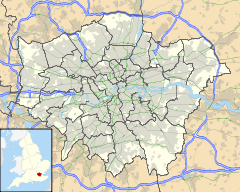
Location of New Cross Gate in Greater LondonLocation New Cross Local authority London Borough of Lewisham Managed by London Overground Owner Network Rail Station code NXG Number of platforms 5 Fare zone 2 Interchange New Cross [1] London Underground annual entry and exit 2004  2.935 million[2]
2.935 million[2]2005  2.997 million[2]
2.997 million[2]2006  3.375 million[2]
3.375 million[2]2007  before closure 3.563 million[2]
before closure 3.563 million[2]National Rail annual entry and exit 2004-05  2.330 million[3]
2.330 million[3]2005-06  2.353 million[3]
2.353 million[3]2006-07  2.338 million[3]
2.338 million[3]2007-08  2.088 million[3]
2.088 million[3]2008-09  1.833 million[3]
1.833 million[3]2009-10  1.839 million[3]
1.839 million[3]5 June 1839 Opened List of stations Underground · National Rail External links Departures • Layout Facilities • Buses Coordinates: 51°28′32″N 0°02′25″W / 51.4755°N 0.0402°W
New Cross Gate station is a railway station in New Cross, London, on the Brighton Main Line. It is about 600 metres west of New Cross station. It is in Travelcard Zone 2, on the East London Line. The station is operated by London Overground.[4]
Contents
History
England's railway boom of the 1830s led to two competing companies driving lines through the area. The first, the London and Croydon Railway (L&CR) established a station on the New Cross Road close to Hatcham in 1839. The second railway line in the area, the South Eastern Railway (SER) established a station near Amersham Way in the heart of New Cross in 1849. Both companies called their stations "New Cross", but the earlier station became "New Cross Gate" when they both came under the common ownership of the Southern Railway on 1 January 1923.
During the 19th century, New Cross (Gate) became an important junction where the Brighton Main Line to London Bridge station diverged from the South London Line, the East London Line, and the Bricklayers Arms Line.
London and Croydon Railway Station
The original station was officially opened 1 June 1839 by the London and Croydon Railway.[5] and became fully operational on 5 June 1839.[6] It was intended to become the main freight depot and locomotive workshop for the company. In July 1841 the line (but not the station) was also used by the London and Brighton Railway, and between 1842 and 1849 the SER. The Croydon and Brighton companies merged to form the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway (LB&SCR), in July 1846. Between February and May 1847 the station at New Cross was the northern terminus of the atmospheric propulsion system introduced by the L&CR,[7] but in the latter month the system was abandoned by the new company. On 1 October 1847 the new company closed their New Cross station, replacing it with another at Cold Blow Lane 0.25 miles to the north, in an attempt to secure passengers from the planned North Kent Line of the SER.[8]
London Brighton and South Coast Railway Station
The Cold Blow station was not a success and was subject to much local criticism so on 1 May 1849 the LB&SCR rebuilt and re-opened New Cross on the original site.[9] It was also rebuilt in 1858 to allow for the quadrupling of the Brighton Main Line. Further rebuilding was undertaken in 1869 when the East London Railway opened a new line from New Cross to Whitechapel and Liverpool Street.
The station was electrified using the overhead system in 1920, but this was soon afterwards replaced by the Southern Railway by the third rail system used by the London and South Western Railway.
East London Railway
The East London Railway (ELR) was a consortium of existing railway companies sharing a cross London route. Passenger services along the line were operated by the LB&SCR between Croydon and Liverpool Street, and from 1884 by the Metropolitan District Railway from New Cross (Gate) to Shoreditch. The LB&SCR services along the East London line ceased 31 March 1913,[10] when the line was electrified using the fourth rail system and thereafter all passenger services were operated by the Metropolitan Railway. A separate ELR station was built alongside the existing station for the East London Line services but this was closed in 1886 and the trains were diverted to the adjacent LB&SCR station. The ELR station was then demolished and the site used for sidings.
In 1933 the Metropolitan railway was taken over by the London Passenger Transport Board who operated services from the station as part of the London Transport Metropolitan Line. London Transport was superseded by Transport for London who's London Underground services stopped serving the Station on 22 December 2007 as the East London Line was scheduled to be converted into a National Rail line which reopened as part of the London Overground network on 27 April 2010.
Freight yard
The London and Croydon planned to use New Cross as the London terminal for its freight traffic, as the station had good access to the Grand Surrey Canal. It therefore built extensive sidings for this purpose.[11] After 1849 the principal freight handling facility in the area was moved to Willow Walk on the Bricklayers Arms site, but the sidings continued to be used for the storage of carriages. An Ordnance Survey map for 1871 shows a substantial carriage shed on the west side of the main line, north of the station, but this was no longer present on the 1894 map. It had been replaced by a combined carriage and locomotive shed on the east side of the line in 1894, but this also closed in 1906.[12]
Cross-London freight services were operated to the yard by the Great Eastern Railway, which maintained its own good depot on the site from the 1870s.[13] These services were continued by the London and North Eastern Railway from 1923, and after 1948 by the Eastern Region of British Railways. They ceased to operate in 1962.
Locomotive depot and repair workshops
The L&CR also opened a motive power depot and a locomotive repair facility at this station in 1839, the former of which appears to have been particularly accident prone. The original building, which was one of the earliest examples of a roundhouse, burned down in 1844.[14] A replacement was built in 1845, together with another straight shed by the LB&SCR in 1848, which was blown down in a gale in October 1863.[15] Two further buildings were constructed by the LB&SCR in 1863 and 1869. By 1882 the second (1845) Croydon shed was derelict and in that year was replaced by the new shed, which was rebuilt with a new roof by the Southern Railway (SR) prior to 1929.[16]
The various running sheds began to be run down during the 1930s as part of a re-organisation scheme involving new developments at Norwood Junction, however the onset of war meant that they were not formally closed until 1947 and still used for stabling locomotive until 1951. They were demolished 1957, together with the repair workshops, and replaced by sidings for the storage of electric multiple units.[16]
The locomotive workshops established by the L&CR continued to undertake minor repairs on locomotives in the London area for the LB&SCR, and SR, and also briefly for British Railways. They were closed in 1949.[17]
London Overground
The East London Line closed on 22 December 2007 and reopened on 27 April 2010, becoming part of the new London Overground system. The service was also closed between 1995 and 1998 due to repair work on the East London Line's tunnel under the River Thames. The East London line extension included a flyover north of New Cross Gate allowing trains to run through to West Croydon, plus the construction of a train servicing facility nearby. Platform 1 and adjacent track (southbound) were refurbished, with the line continuing under New Cross Road, before merging with the existing southbound slow line. LO services did terminate here until 23 May 2010 when services were extended south.[18]
Services
All times below are correct as of the December 2010 timetables.
London Overground
East London Line
Mondays to Saturdays there is a service every 5–10 minutes throughout the day, while on Sundays before 13:00 there is a service every 5–9 minutes, changing to every 7–8 minutes until the end of service after that.[19] Current off peak frequency is:
- 8 Northbound to Highbury & Islington
- 4 Southbound to West Croydon
- 4 Southbound to Crystal Palace
Southern
Southern run trains south to Caterham, London Victoria (on the South London Line) and West Croydon; and north to London Bridge. The next station to the south is Brockley.
The current off-peak frequency is:[20]
- 6 Northbound to London Bridge
- 2 Southbound to London Victoria via Clapham Junction
- 2 Southbound to Horsham fast to Norwood Junction Mon-Sat Daytimes only (Southern)
- 2 Southbound to Caterham (Southern)
Note: Trains from London Bridge to Sutton have been withdrawn. Caterham trains now call at Penge West and Anerley.
Platform layout:
Platform 1 is used by London overground trains to West Croydon (4tph) and Crystal Palace (4tph)
Platform 2 is used by Southern trains to Caterham (2tph) and London Victoria (2tph)
Platform 3 is used by Southern trains to Horsham (2tph)
Platform 4 is used by Southern trains to London Bridge (2tph)
Platform 5 is used by both Southern and London Overground trains to London Bridge (4tph) (southern) and to Highbury and Islington (8tph) (London Overground)
Transport links
The bus routes below all serve the station:
London Buses Stop N New Cross/Jerningham Road 343, N343
Stop M New Cross Gate Station 21, 136, 321 436
Stop O New Cross Gate Station 21, 53, 136, 172, 177, 321, 436, 453Lines
Preceding station  National Rail
National RailFollowing station London Bridge Southern
Brighton Main Line StoppingBrockley Southern
Brighton Main Line FastNorwood Junction Preceding station 
 London Overground
London OvergroundFollowing station Surrey Quaystowards Highbury & IslingtonEast London Line towards Crystal Palace or West CroydonFormer services Preceding station  London Underground
London UndergroundFollowing station towards ShoreditchEast London line Terminus References
- ^ "Out of Station Interchanges" (Microsoft Excel). Transport for London. May 2011. http://www.whatdotheyknow.com/request/67647/response/172834/attach/3/OSI%20Report%20May2011FR%20V2%2017012011.xls. Retrieved 7 August 2011.
- ^ a b c d "Customer metrics: entries and exits". London Underground performance update. Transport for London. 2003-2010. http://www.tfl.gov.uk/tfl/corporate/modesoftransport/tube/performance/default.asp?onload=entryexit. Retrieved 8 May 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f "Station usage". Rail statistics. Office of Rail Regulation. 30 April 2010. http://www.rail-reg.gov.uk/server/show/nav.1529. Retrieved 17 January 2011. Please note: Some methodology may vary year on year.
- ^ http://www.tfl.gov.uk/corporate/projectsandschemes/15359.aspx
- ^ Turner, J.T. Howard (1977). London Brighton and South Coast Railway 1. Origins and Formation. London: Batsford. pp. 63–4. ISBN 0-7134-0275-X.
- ^ Gray, Adrian (1977). The London to Brighton line 1841-1877. Blandford Forum: The Oakwood Press. pp. 120.
- ^ Turner, J.T. Howard (1978). London Brighton and South Coast Railway 2. Establishment and Growth. London: Batsford. pp. 6–7. ISBN 0-7134-1198-8.
- ^ Gray2 (1977), p.35.
- ^ Gray (1977), pp.35-7
- ^ Turner, J.T. Howard (1979). London Brighton and South Coast Railway 3. Completion and Maturity. London: Batsford. pp. 200. ISBN 0-7134-1389-1.
- ^ Turner, (1977), pp.56-7.
- ^ Griffiths, Roger; Smith, Paul (1999). The Directory of British Engine Sheds: 1. Oxford Publishing Co.. pp. 95. ISBN 0-86093-5420-6.
- ^ Connolly, Philip (1980). British Railways Pre-Grouping Atlas and Gazzetteer (fifth ed.). Ian Allan. pp. 39. ISBN 0-71100320-3.
- ^ Hawkins, Chris, and Reeve, George (1979). An historical survey of Southern Sheds. Oxford Publishing Co.. pp. 52–3. ISBN 0-86093-020-3.
- ^ Turner, (1978) pp.278-9.
- ^ a b Griffiths & Smith (1979), p.95
- ^ Hawkins and Reeve (1979), p.52
- ^ BBC London:The new East London Line opens to the public Accessed 27 April 2010
- ^ http://www.tfl.gov.uk/assets/downloads/highburyislington-timetable.pdf
- ^ Southern: Timetables Go to tables 28 & 31 Accessed 23 April 2010
External links
- Train times and station information for New Cross Gate railway station from National Rail
Railway stations in the United Kingdom • Railway station categories A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z
Transport in London Companies and
organisationsBuses · Coaches · Crossrail (under construction) · Cycle Hire · Dial-a-Ride · Docklands Light Railway · London Overground · London Underground · London Rail · River · Source London · Streets · Taxis · TramlinkBus operatorsAbellio · Arriva London · Arriva East Herts & Essex · Arriva Southern Counties · CT Plus · First London · Go-Ahead London · London Sovereign · London United · Metrobus · Metroline · Quality Line · Stagecoach London · UnoTrain operatorsc2c · Chiltern Railways · East Coast · East Midlands Trains · Eurostar · First Capital Connect · First Great Western · First Hull Trains · First ScotRail (Sleeper) · Gatwick Express · Grand Central · Heathrow Connect · Heathrow Express · London Midland · London Overground · National Express East Anglia · South West Trains · Southeastern · Southern · Stansted Express · Virgin TrainsOtherAirports MainOtherMajor stations OtherClapham Junction · East Croydon · Heathrow Stations · Stratford · Wimbledon · Surbiton · All stations by fare zoneRoads MotorwaysRing roadsChargingOlympic Transport Emirates Air Line (cable car) (under construction) · Southeastern Olympic JavelinTicketing  Category ·
Category ·  CommonsCategories:
CommonsCategories:- Stations in London fare zone 2
- Railway stations served by London Overground
- Railway stations in Lewisham
- Former London, Brighton and South Coast Railway stations
- Railway stations opened in 1839
- Railway stations closed in 1847
- Railway stations opened in 1849
- DfT Category C1 stations
- Railway workshops in Great Britain
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.