- Ranjana alphabet
-
Rañjanā 
Type Abugida Languages Nepal Bhasa
Sanskrit
TibetanTime period c. 1100–present Parent systems Child systems Soyombo Sister systems Prachalit
LitumolNote: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. The Rañjanā script (syn: Kutila, Lantsa[1]) is an abugida writing system which developed in the 11th century.[2] It is primarily used for writing Nepal Bhasa but is also used in monasteries of India, Tibet, coastline China, Mongolia, and Japan.[2] It is usually written from left to right but the Kutakshar form is written from top to bottom.[2] It is considered to be the standard Nepali calligraphic script.
Contents
Development
Rañjanā is a Brahmic script and shows similarities to the Devanagari script of northern India and Nepal.[1] The script is also used in most of the Mahayana and Vajrayana monasteries.[3] Along with the Prachalit script, it is considered as one of the scripts of Nepal.[4] It is the formal script of Nepal duly registered in the United Nation while applying for the free Nation. Therefore, it is vital script to all Nepalese as well.
The holy book Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra, lettered in gold ink, written by Bhiksu Ananda of Kapitanagar and dating back to the Nepal Sambat year 345 (1215 A.D.), illustrates the glorious history of the script.[5]
Alphabet
 Mantra in Rañjanā script, on the ceiling of a Buddhist temple in Tianjin, China.
Mantra in Rañjanā script, on the ceiling of a Buddhist temple in Tianjin, China.
 Rañjanā "Oṃ" syllables surrounding the implements of the Four Heavenly Kings. Jing'an Temple, Shanghai, China.
Rañjanā "Oṃ" syllables surrounding the implements of the Four Heavenly Kings. Jing'an Temple, Shanghai, China.
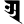 a अ
a अ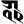 i इ
i इ u उ
u उ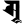 ṛ ऋ
ṛ ऋ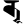 ḷ ऌ
ḷ ऌ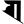 e ए
e ए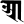 o ओ
o ओ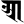 ā आ
ā आ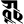 ī ई
ī ई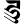 ū ऊ
ū ऊ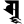 ṝ ॠ
ṝ ॠ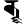 ḹ ॡ
ḹ ॡ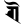 ai ऐ
ai ऐ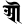 au औ
au औ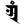 aṃ अं
aṃ अं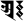 aḥ अः
aḥ अः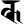 k क
k क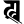 kh ख
kh ख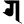 g ग
g ग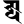 gh घ
gh घ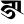 ṅ ङ
ṅ ङ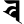 c च
c च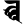 ch छ
ch छ j ज
j ज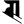 jh झ
jh झ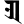 ñ ञ
ñ ञ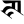 ṭ ट
ṭ ट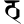 ṭh ठ
ṭh ठ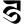 ḍ ड
ḍ ड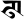 ḍh ढ
ḍh ढ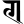 ṇ ण
ṇ ण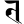 t त
t त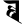 th थ
th थ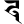 d द
d द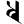 dh ध
dh ध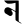 n न
n न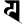 p प
p प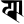 ph फ
ph फ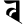 b ब
b ब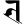 bh भ
bh भ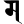 m म
m म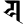 y य
y य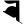 r र
r र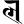 l ल
l ल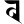 v व
v व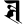 ś श
ś श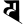 ṣ ष
ṣ ष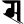 s स
s स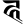 h ह
h ह kṣ क्ष
kṣ क्ष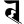 tr त्र
tr त्र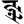 jñ ज्ञ
jñ ज्ञNumerals
 0 ०
0 ०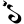 1 १
1 १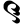 2 २
2 २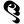 3 ३
3 ३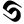 4 ४
4 ४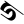 5 ५
5 ५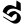 6 ६
6 ६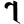 7 ७
7 ७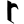 8 ८
8 ८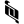 9 ९
9 ९Use
The Rañjanā script is used primarily to write Nepal Bhasa, though sometimes also used to write Sanskrit. In Mahayana and Vajrayana Buddhist traditions, it is famously used to write various mantras including the "Oṃ maṇipadme hūṃ" mantra of Avalokiteśvara, the mantra of Tara: "Om tare tuttare ture svaha", and the mantra of Manjushri: "Om ara pa cana dhi."[6][7][8] The script is also used in Hindu scriptures.[9]
In Chinese Buddhism and other East Asian Buddhism, the standard Sanskrit script for mantras and dharanis was not the Rañjanā script, but rather the earlier Siddhaṃ script which was widely propagated in China during the Tang Dynasty.[10] However, in late imperial China, the influence of Tibetan Buddhism popularized the Rañjanā script as well, and so this script is also found throughout East Asia, but is not as standard as Siddhaṃ.[11]
Lanydza
 Nyingma Tibetan Buddhist temple with decorative use of the Lanydza variant of Rañjanā.
Nyingma Tibetan Buddhist temple with decorative use of the Lanydza variant of Rañjanā.
When Rañjanā was introduced to Tibet, it was referred to as Lanydza (Tib. ལཉྫ་), which simply derives from the Sanskrit word Rañja.[10] This script varies slightly from the standard Rañjanā. In Tibet, the Lanydza variant is used to write original texts of Sanskrit.[12] Examples of such texts include the Mañjusrinama-samgiti, the Diamond Sūtra (Skt. Vajracchedikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra), and the Aṣṭasāhasrikā Prajñāpāramitā Sūtra. The Lanydza script is also found in manuscripts and printed editions of some Sanskrit-Tibetan lexicons like the Mahāvyutpatti.
However the most frequent use for this script today is on the title pages of Tibetan texts, where the Sanskrit title is often written in Lanydza, followed by a transliteration and translation in the Tibetan script. The script is also used decoratively on temple walls, on the outside of prayer wheels, and in the drawing of mandalas.
Numerous alternative spellings of the term Lanydza exist, including the following:
- Lanja
- Landzha
- Lantsa
- Lantsha
- Lentsa
- Lendza
Recent developments
After falling into disuse in the mid-20th century, the script has recently seen dramatically increased use. It is used by many local governments such as those of Kathmandu Metropolitan City, Lalitpur Sub-Metropolitan City, Bhaktapur Municipality, Thimi Municipality, Kirtipur Municipality, Banepa Municipality, in signboards, letterpads, and such. Regular programs are held in the Kathmandu Valley to promote the script and training classes are held to preserve the language. The script is being endorsed by the Nepal Bhasa movement and is used for headings in newspapers and websites.
A Nepalese-German project is trying to conserve the manuscripts of Rañjanā script.[13]
A Unicode block for the script has also been proposed by Evertype.[14]
See also
- Newa people
- Newa scripts
- Nepal Bhasa
- Brahmi Script
External links
- Ranjana script
- Newari/Ranjana script page on Omniglot
- Proposal for encoding Newari in Unicode
- Ranjana script
- Akṣara List of the Manuscript of Aṣṭasāhasrikāprajñāpāramitā, ca. the 11-12th Centuries, Collection of Sanskrit Mss. Formerly Preserved in the China Ethnic Library
- Akṣara List of the Sanskrit Inscriptions of Feilai peak, Hangzhou, China ( 1282-1292 CE)
- Lantsha script
References
- ^ a b Omniglot
- ^ a b c Jwajalapa
- ^ Nepal Lipi: The Nepalese Scripts
- ^ Asian art
- ^ Nagarjuna Institute: Buddhist Sites of Nepal - Hiraynavarna Mahavihara
- ^ Teachings og Buddha
- ^ Dharma Haven
- ^ Ranjana font
- ^ Asian art
- ^ a b Chattopadhayaya, Alaka (1999). Atisa and Tibet: Life and Works of Dipamkara Srijnana: p. 201
- ^ Jiang, Wu (2008). Enlightenment in Dispute: The Reinvention of Chan Buddhism in Seventeenth-Century China: p. 146
- ^ Ranjana script and Nepal Bhasa (Newari) language
- ^ Ranjana Script
- ^ Everton
Topics of Newar Music Cuisine Ailaa • Baji • Chataamari • Yomari • Chwelaa • Jaa • Kachilaa • Lakhamari • Sanyaa • Sanyaakhunya • ThwonFestival Rituals Language Deities Castes Misc Religion Categories:- Newar
- Brahmic scripts
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


