- Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy
-
Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy 
Author(s) Telford Taylor Language English Publisher Quadrangle Publication date June, 1970 Media type Hardcover
PaperbackPages 224 pages ISBN 0-8129-0210-6 Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy is a book written by Telford Taylor, the Chief Counsel Prosecutor at the Nuremberg Trials.
Contents
Introduction
The book Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy, published in 1970, is an examination of the United States’ conduct of the Vietnam War in comparison to the actions taken by Nazi Germany during the Second World War. Its author, Telford Taylor, was once the Chief Counsel Prosecutor at the war crimes trials of Nazi leaders in Nuremberg, Germany from 1946–1949. In that capacity, Taylor helped to establish the laws by which Nazi war criminals would be tried for their crimes.
Perhaps most interesting about the book is that it was published in 1970, three years before the cease-fire agreement of 1973 and the subsequent withdrawal of United States troops from Vietnam. For this reason, the release of the book would have appeared premature had Taylor not been particularly suited for the undertaking. Furthermore, Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy is not a seething indictment of U.S. policy in Vietnam as the title may suggest, but rather an unbiased perspective of the Vietnam War based on international law.
Synopsis
The book begins with a lengthy history of war crimes beginning with the “knightly chivalry” of the medieval period. These rules were put into place in order to minimize unnecessary cruelties during the course of warfare. The rules protected civilian populations from massacre and the needless spread of disease. Thus, the blanket of immunity that protects soldiers from being held criminally responsible for murder committed during the course of warfare had to be carefully balanced so as to discourage wartime atrocities.
The laws of war remained largely unwritten until U.S. President Abraham Lincoln approved the “Instructions for the Government of Armies of the United States in the Field”, in 1863. Concerning spies, prisoners of war, and the punishment of war crimes, this document comprising 159 articles facilitated the formation of military tribunals and later led to a demand for the formalization of international laws of warfare. Thus, international laws of warfare were codified by means of a series of treaties known as the Hague and Geneva conventions. The most important consequence of these treaties is that all nations, whether signatory or otherwise, were bound by international laws of war.
The Nuremberg Trials, for which Taylor served as a leading figure, gave rise to several developments in regard to international law as applied to warfare. First, it gave international jurisdiction to the prosecution of war crimes; and second, it obligated individuals engaged in warfare to adhere to international laws of conduct over and above those of their respective armies. Of greatest importance with respect to this book however is that the United States as a result of its participation emerged as legally, morally, and politically bound to the principles that resulted from the Nuremberg trials. Thus, Taylor is concerned by how the principles of the Nuremberg trials would apply to the United States’ conduct of the Vietnam War.
When Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy was published, those in favor and opposition to the United States involvement in Vietnam frequently cited the Nuremberg trials in support of their positions. Those in favor of United States involvement argued that North Vietnam attacked South Vietnam in violation of Article 2 of the United Nations Charter; South Vietnam was justified in using force to repel such an attack; and this in turn allowed the United States to join with South Vietnam as provided by Article 51.
Those opposed to the United States involvement in the Vietnam War asserted that both South Vietnam and the United States violated the Geneva Declaration of 1954 by attacking North Vietnam, rearming illegally, preventing the 1956 national elections which were provided for in the Declaration, and subsequently bombing North Vietnam. Such actions would constitute “aggressive warfare” by the standards of Nuremberg. Taylor points out that the definition of “aggressive warfare” is ambiguous, thus severely hindering any attempt to determine which of the belligerent powers involved in the Vietnam War could be deemed the “aggressor.” What’s more, such ambiguities lead to several related questions, such as the legality of refusing to serve in Vietnam. At the time, many conscientious objectors refused to serve in Vietnam on the grounds that their complicity in an illegal war made them, by implication, guilty of crimes against humanity.
 Civilians lie dead after the My Lai Massacre of 1968.
Civilians lie dead after the My Lai Massacre of 1968.
Taylor cites possible war crimes in regard to the Son My incident, which is more commonly known as the My Lai Massacre of 1968 (
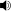 /ˈmiːlaɪ/). It is in this portion of the book that Taylor makes the most convincing comparison of Nuremberg to the Vietnam War. In this section, Taylor quotes two eyewitness accounts, each from a different war. One account, written by a German construction engineer, describes the killing of Jews during the Holocaust by German SS officers in 1942. This account is juxtaposed on the adjacent page by an eyewitness account of the My Lai Massacre. The accounts are eerily similar, yet Taylor explains all of the differences, and in characteristically unbiased fashion shows the difficulty in determining whether or not crimes were committed by the United States.
/ˈmiːlaɪ/). It is in this portion of the book that Taylor makes the most convincing comparison of Nuremberg to the Vietnam War. In this section, Taylor quotes two eyewitness accounts, each from a different war. One account, written by a German construction engineer, describes the killing of Jews during the Holocaust by German SS officers in 1942. This account is juxtaposed on the adjacent page by an eyewitness account of the My Lai Massacre. The accounts are eerily similar, yet Taylor explains all of the differences, and in characteristically unbiased fashion shows the difficulty in determining whether or not crimes were committed by the United States.Taylor also raises domestic problems with regard to the United States’ involvement in the Vietnam War. According to Taylor, it remains to be seen whether the United States Congress or the Executive branch of government held responsibility for officially declaring military action in Vietnam. It is the opinion of Taylor that both the President and the Congress bear responsibility, and that the Vietnam War could only be ended by an act of national will, rather than by judicial means.
Conclusion
Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy, is an unbiased account of the Vietnam War in regard to international law, written by an expert on the subject. It stands not as an accusation, but as an exposition of possible problems faced by the United States as a result of its involvement in the Vietnam War. The Nuremberg Trials are used more or less as a counterpoint, though this in itself shows that Taylor likely opposed the Vietnam War and foresaw its adverse consequences.
Additional works by the author
- Anatomy Of The Nuremberg Trials: A Personal Memoir, Knopf 1992; ISBN 0-394-58355-8
- Breaking Wave, Nautical & Aviation Publication Corporation of America 1991; ISBN 0-933852-95-9
- Courts of terror: Soviet criminal justice and Jewish emigration , Knopf 1976; ISBN 0-394-71758-9
- Grand Inquest: The Story of Congressional Investigations, Da Capo PR 1974; ISBN 0-306-70620-2
- Munich: The Price of Peace, Random House Inc 1980; ISBN 0-394-74482-9
- Perspectives on Justice, Northwestern University Press 1974; ISBN 0-8101-0453-9
- Sword and Swastika: Generals and Nazis in the Third Reich, Peter Smith Publisher 1980; ISBN 0-8446-0934-X
- Two Studies in Constitutional Interpretations, Ohio State University Press 1969; ISBN 0-8142-0122-9
External links concerning the author
- Taylor's presentation of the High Command case on April 1, 1946 at the Nuremberg Trial.
- A short biography from Columbia University.
References
- Nuremberg and Vietnam: An American Tragedy, Times Books 1970; ISBN 0-8129-0210-6
Categories:- 1970 books
- Nuremberg Trials
- Vietnam War books
- Military history of the United States
- International criminal law
- International law literature
- Laws of war
- Conscription in the United States
- Military sociology
- Conscientious objection
- War crimes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

