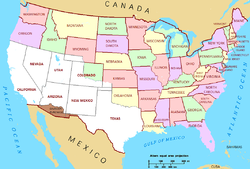
- Southwestern United States
-
 Regional definitions vary from source to source. New Mexico and Arizona (in dark red) are almost always considered the core, modern-day Southwest, while the striped states may or may not be considered to be part of the same region. California is usually excluded from the definition. Texas and Oklahoma (in blue) are considered part of the South by the U.S. Census Bureau, but sometimes grouped with the southwestern states.
Regional definitions vary from source to source. New Mexico and Arizona (in dark red) are almost always considered the core, modern-day Southwest, while the striped states may or may not be considered to be part of the same region. California is usually excluded from the definition. Texas and Oklahoma (in blue) are considered part of the South by the U.S. Census Bureau, but sometimes grouped with the southwestern states. The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. The areas in the United States that were once part of Mexico (white).
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. The areas in the United States that were once part of Mexico (white).
The Southwestern United States (also known as the American Southwest) is a region defined in different ways by different sources. Broad definitions include nearly a quarter of the United States, including Arizona, California, Colorado, Nevada, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas and Utah. Narrowly defined, the "core" Southwest is centered around the Four Corner states, with parts of the other states making up the beginnings and endings of the Southwest. The five main southwestern states; Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Utah, and Nevada are also all considered part of the Mountain West, as well as the southwest. The total population of these states is roughly 19 million people.
Most of it was a part of the Viceroyalty of New Spain, in the Spanish Empire, during the Modern Era. California, Arizona, Nevada, Utah, and parts of New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Oklahoma and Kansas were all part of Mexico before the Mexican-American War. Portions of some of the areas in the "divided" states, and including western parts of Texas, were those in dispute after the Texas Revolution.
Contents
Regional geography
 Big Bend National Park lies along the Rio Grande with the Chihuahuan Desert of West Texas. Here, a view from Sotol Vista.
Big Bend National Park lies along the Rio Grande with the Chihuahuan Desert of West Texas. Here, a view from Sotol Vista.
Geographer Uriah D. W. Meinig defines the core of the Southwest as the portion of New Mexico west of the Llano Estacado and the portion of Arizona east of the Mohave-Sonoran Desert and south of the "canyonlands", and also including the El Paso district of western Texas and the southernmost part of Colorado.[1] He identifies four distinct subregions with this core. He calls the first subregion "Northern New Mexico", and describes it as focused on Albuquerque and Santa Fe. It extends from the San Luis Valley of southern Colorado to south of Socorro and including the Manzano Mountains, with an east-west breadth[2] in the north stretching from the upper Canadian River to the upper San Juan River. Important ethnic groups include Hispanos, Anglo-Americans, and the Puebloan peoples. The area around Albuquerque is sometimes called Central New Mexico. During the Spanish era the term Rio Abajo and Rio Arriba were used for the settled areas around Albuquerque and Santa Fe, respectively.[3] During the 19th century Hispano people expanded north into the San Luis Valley west of the Sangre de Cristo Mountains, and east of the mountains along the Purgatoire River in Colorado. Hispano expansion to the east reached into the Texas Panhandle and, to the west, along the San Juan River and Little Colorado River into Arizona.[4]
"Central Arizona" is a vast metropolitan area spread across one contiguous sprawling oasis, essentially equivalent to the Phoenix metropolitan area. The city of Phoenix is the largest urban center, and located in the approximate center of the area, but it is just one of many urban centers, such as Tempe, Mesa, and many others. None are clearly dominant although the whole can be considered the greater metropolitan area of Phoenix.[5]
Meinig calls the third subregion "El Paso, Tucson, and the Southern Borderlands". While El Paso and Tucson are distinctly different cities they share a similar and somewhat overlapping hinterland between them. El Paso is about 80% Hispano and, with Ciudad Juárez, just half of the largest metropolitan area along the Mexico – United States border. Tucson occupies a large oasis at the western end of the El Paso-Tucson corridor. The region between the two cities is a major transportation trunk with settlements servicing both highway and railway needs. There are also large mining operations, ranches, and agricultural oases. Both El Paso and Tucson have large military installations nearby; Fort Bliss and White Sands Missile Range north of El Paso, and, near Tucson, the Davis-Monthan Air Force Base. About 70 miles (110 km) to the southeast are the research facilities at Fort Huachuca. These military installations form a kind of hinterland around the El Paso-Tucson region, and are served by scientific and residential communities such as Sierra Vista, Las Cruces, and Alamogordo. El Paso's influence extends north into the Mesilla Valley, and southeast along the Rio Grande into the Trans-Pecos region of Texas. The entire region has a large Hispano population. The Native American Tohono O'odham and Yaqui Native Americans continue to preserve cultural traditions and link Tucson with native lands to the west and south.[6]
 The Delicate Arch at Arches National Park.
The Delicate Arch at Arches National Park.
The fourth subregion Meinig calls the "Northern Corridor and Navaholands". A major highway and railway trunk connects Albuquerque and Flagstaff. Just north of the transportation trunk are large blocks of Native American land. Once regarded as a bleak wasteland populated by a dying culture the native cultures, especially the Navajo Nation, have undergone a strong resurgence and are playing an increasingly important role. Other tribes such as the Hopi and Zuni have also experienced a similar resurgence. Several towns and cities serve as contact points between the native peoples and other groups. Notable examples include Farmington, New Mexico, Gallup, Window Rock, Arizona, Flagstaff, Arizona, and, to a lesser degree, Prescott, Arizona. In the Little Colorado River and Mogollon Rim country there is an old and continuing Mormon influence. Many old Mormon settlements have grown rapidly with the arrival of migrants mainly from Texas, the American South, and the Pacific Northwest. Districts around old Mormon villages such as Ramah, New Mexico are often populated by a mix of at least five ethnic groups and culture, such as Mormons, Pueblo Zunis, Navajos, Hispanos, and Texans.[7]
 Four Corners Monument, often considered the heart of the American Southwest.
Four Corners Monument, often considered the heart of the American Southwest.
Many people believe once you hit the High Plains in Eastern Colorado, Eastern New Mexico, and West Texas, you have entered the beginnings of the Southwestern United States. Phoenix, Tucson, and Las Vegas dominate the western most metropolitan areas in the southwest region, while, Albuquerque, Denver, Colorado Springs, and El Paso dominate the eastern most metropolitan areas of the southwest, not including Northern, Central, and Eastern Texas, and Oklahoma, because they are not always considered part of the southwest. Reno and Salt Lake City also dominate the northernmost metropolitan areas of the southwest. Thus the basic spatial structure of the Southwest can be seen as focused on the largest metropolitan areas in each state such as Phoenix, Albuquerque, Denver, Salt Lake City, Las Vegas, and El Paso. This core of the Southwest is directly linked to other regions. The Mojave Desert separates it from Southern California. Several corridors and urban centers in the desert link the two regions, most significantly at Las Vegas, Nevada, where the Arizona and California systems interlock. The Mormon Corridor links the Southwest to the main body of Mormon settlements in Utah. Mormons have colonized areas of Arizona and New Mexico since the 19th century, especially in the San Juan Basin near Farmington and along the Mogollon Rim and Little Colorado River in Arizona. Las Vegas also served as a pivotal point of Mormon Corridor between Utah, northern Arizona, and southern California. These areas link the Southwest with the main concentration of Mormon settlements in Utah and eastern Idaho. The Southwest is linked with the Midwest in northeast New Mexico, into which the grain farming system of Kansas had been extended. The Southwest-Midwest link via the Santa Fe Trail was historically of enormous importance. The Santa Fe Trail went through the midwestern states of Missouri and Kansas, then into the southwestern states of Colorado and New Mexico. The southwest borders the Midwestern United States also. The southwestern state of Colorado borders the Midwest states of Nebraska to the northeast and Kansas to the east. The Southwest is linked to the Northwest in Nevada, Utah, and Colorado. Nevada borders the Northwestern States of Oregon and Idaho to the north. Utah borders the Northwestern States of Wyoming and Idaho also. And, Colorado borders the northwest state of Wyoming. The Southwest also borders the South. New Mexico borders a small portion of Oklahoma to the east. Also, a small portion of Southeastern Colorado borders the state of Oklahoma. West Texas is directly linked with Central and northern Texas, which is often considered part of the American South. El Paso, Amarillo, and Lubbock are almost always considered to be in the southwest region, while Fort Worth, Dallas, and Houston are usually considered to be more a part of the American South. San Antonio, Austin, San Angelo, Abilene, Laredo, Corpus Christi, and Brownsville are in the middle as to what region they belong in. Some may consider these cities to be a part of the Southwest as well, while others usually see them as southern cities. The Southwest is linked to Texas in eastern New Mexico, especially along the Pecos River and on the Llano Estacado, where an early mass influx of Texan farmers was later reinforced by the oil industry. Roswell, New Mexico occupies a border position between Albuquerque and the Texan system. Finally, the Southwest is intimately linked to Mexico, most tightly at El Paso and Ciudad Juarez and secondarily at Tucson and Nogales. Also, the Four Corners of Colorado, Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico is often considered to be the center, or heart, of the American Southwest.[8]
History
Main articles: History of New Mexico, History of Arizona, History of Utah, History of Nevada, History of California, History of Colorado, and History of TexasSee also: OasisamericaWith the European colonization of the Americans, New Spain, later to become Mexico was dominant until the 19th century. With Manifest Destiny, United States gradually gained control over the west. Pro-Confederate Texas and Pro-Union Utah were important at this point, although California rapidly became the main western power. Utahns moved west into Nevada and Northern California, where as Texans moved into New Mexico, Arizona, and Colorado. Parts of New Mexico and Arizona were briefly a Confederate territory, then were transformed into a Union territory, then Union state. Arizona's original government and military were similar to those Texas at the time had. Arizona, in the form of the Gadsden Purchase also has connections to the Republic of Sonora. The Southwestern states take up roughly one third of the United States.
 The Cliff Palace dwellings at Mesa Verde.
The Cliff Palace dwellings at Mesa Verde.
There were a very large population of Native American tribes in the southwestern states, as well as all of America. Some of the larger and more popular tribes of Native Americans in the southwest were the Ute, Navajo, Apache, Comanche, Paiute, Hopi, and the Anasazi. The Ute formally ruled over most of modern day Utah and Colorado, as well as small parts of northern New Mexico. The Navajo had ruled over much of Arizona, New Mexico, and parts of Utah at one point as well. Apache tribes had once ruled over many lands in the southwest. Such as, most of New Mexico, eastern Arizona, and parts of southwest Texas. The Jicarilla tribe of Apache also ruled well into southern and southeastern Colorado as well. The Comanche ruled many lands in the southwest as well. Their historic range consisted of present day eastern New Mexico, southern and southeastern Colorado, northeastern Arizona, and most all of west and northwest Texas. The Paiute people were another very large Nativer American civilization. They controlled most all of present day Nevada, western Utah, and northern Arizona. Some of the oldest evidence of Native Americans in the southwest are from the Hopi and the Anasazi people. The Hopi controlled most all of what is modern day Arizona at one point. On the other hand, the Anasazi (Ancient Pueblo peoples) controlled much of the southwest as well. Their ancient territory consisted of northeastern Arizona, northwestern New Mexico, southeastern Utah, and all of southern Colorado. Some of the more known evidence of the ancient pueblo peoples can be found at Chaco National Park in New Mexico, and Mesa Verde National Park in Colorado.
Origins of the term and historical/cultural variations
The term "Southwest" originally referred to a "major subregion" of the American South, literally being the western frontier of the larger region. This "Old Southwest" of the 19th century included, at varying points in time, Alabama, Mississippi, Tennessee, Kentucky, Arkansas, and Louisiana. After its revolution and statehood, Texas became considered part of this designation. However, as territories and eventual states to the west were added after the Mexican War, the geographical "Southwest" expanded and the relationship of these new acquisitions to the South itself became "increasingly unclear."[9] Today, the generally regarded Southwestern states of Arizona and New Mexico, along with all or parts of Colorado, Utah, Nevada, California, Texas, and Oklahoma, may or may not be considered a region in their own right, as opposed to a general classification divided by an historical and/or cultural fault-line which translates into separate "Southwests". One being the (Interior Southwest) sub-region of the Census Bureau West, and another consisting of states (particularly Texas and Oklahoma) which have traditionally stronger ties to the South.
Texas has long been the focal point of this dichotomy, and is often considered as such to be the "core area" of "the South's Southwest".[10] While the trans-pecos part of the state is generally acknowledged to be part of the "desert Southwest"[11] most of Texas and large parts of Oklahoma are often placed into a sub-region of the South, which some consider Southwestern in the general framework of the original application, meaning the "Western South." This is an area containing the basic elements of Southern history, culture, politics, religion, and linguistic and settlement patterns, yet blended with traits of the frontier West. While this particular Southwest is notably different in many ways from the classic "Old South" or Southeast, these features are strong enough to give it a separate Southwestern identity quite different in nature from that of the Interior Southwestern states to the west.
One of these distinguishing characteristics in Texas is that Native and Spanish American culture never played a central role in the development of this area in relative comparrison to the latter, as the vast majority of settlers were anglo and blacks from the South.[12] Although the present day state of Oklahoma was Indian Territory until the early 20th Century, many of these Native-Americans were from the southeastern United States and became culturally assimilated early on. Combined with that once the territory was open for settlement, it was southeastern pioneers which made up a disporportionate number of these newcomers, all lent to the new state having a different character than other parts of the Southwest which also contained a large Indian population.[13]
The fact that a majority of residents of Texas and Oklahoma -- unlike those in the other Southwestern states -- self-identify as living in the South and considering themselves Southerners, rather than the West and Westerners, also lends to treating these two states as a somewhat distinct and separate entity in terms of regional classification.[14]
Vegetation and terrain
Vegetation of the Southwest generally includes various types of yucca, along with Saguaro Cactus, Barrel Cactus, Prickly Pear Cactus, Desert Spoon, Creosote Bush, Sagebrush, and Greasewood (Chico Brush) to name a few. Although, cacti is thought to only grow in Arizona and New Mexico, many native cacti is grown all throughout Nevada, Utah, Colorado, and West Texas as well. Also, small cacti does grow in Utah and Colorado. These examples (except the Saguaro Cactus), can be seen growing natively and in large numbers more east throughout the Texas Hill Country and South Texas and the Rio Grande Valley. However, none of the vegetation discussed grows natively the further east than the eastern outskirts of San Antonio, Austin, and Fort Worth. Dallas and Houston, for example, share a smiliar terrain with states further east and are often considered to be more of the American South. In the far eastern parts of the southwest, Prairies and Grasslands are found all over. These prairies and grasslands are usually located in Eastern Colorado, Eastern New Mexico, and large areas in West Texas. Steppe is also located all over the high plains areas in Colorado, New Mexico, and Texas. In the mountains of the southwestern states, most have large alpine trees.
Landscape features of the core Southwestern areas usually include mountains, mesas, high broad basins, plateaus, desert lands, and some plains. The High Plains region of the Great Plains are also located in the American Southwest. Eastern Colorado, Eastern New Mexico, and West Texas all have high plains, and rolling land. The entire Southwestern region features semi-arid to arid terrain. The far eastern part of the Southwest in Texas, for example the Texas Hill Country, consists of dry, tall and rugged rocky hills of limestone and granite. South Texas and the Rio Grande Valley is mostly flat with many places consisting of scrub and bare topsoil, much like the deserts further west. Buttes are also located all over the southwestern states. Utah tends to have the most natural buttes, but they do form as far east as some parts of Central Texas.
Wildlife
There is a wide variety of wildlife in the Southwestern United States. Big Horn Sheep, Bobcats, Coyote, Bears, Cottontail rabbit, Mule Deer, White-tailed deer, Gray Fox, Mountain Lion, River Otter, Porcupine, Pronghorn, Raccoon, Mexican Wolf, and Gray Wolf can be found in all states across the southwest. American Bison and Prairie Dogs can be found in the southwest states of Colorado, New Mexico, and Texas. Elk in the southwest are usually only found in Colorado and Utah. White-nosed Coati and Collared Peccary in the southwest are normally found in Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. Also, Armadillos are found in the southwest state of Texas. Snakes are also found all over the southwestern United States. Rattlesnakes are found all throughout every part of the southwest. Also, Coral Snakes can be found in Arizona and New Mexico.
Climate
The Southwestern United States features a semi-arid to arid climate, depending on the location. Much of the southwest is an arid desert climate, but higher elevations in the mountains in each state, with the exception of West Texas, feature alpine climates with very large amounts of snow. The metropolitan areas of Phoenix, Tucson, Las Vegas, and El Paso hardly ever receive any snow at all, as they are strictly desert lands with mountains. However, the metro areas of Reno, Salt Lake City, Denver, and Colorado Springs can receive significant snowfalls. Albuquerque falls at an in between, receiving less snow than other cities, but still receive significant snowfalls in the winter time. Although it snows in this region, the snow in this part of the United States melts rapidly, often before nightfall. This is due mainly to the higher altitude and abundant sunshine in these states.
Nevada and Arizona are both generally arid with desert lands and mountains, and receive large amounts of snow in the higher elevations in and near the mountains. New Mexico, Utah, and Colorado are generally arid, with desert lands and mountains as well. Colorado and New Mexico do have high plains in the far eastern portions of their state. They all receive decent amounts of snow, and large amounts of snow in the high elevations in the mountains. Although some areas in far southwestern and southern New Mexico do not receive much snow at all. West Texas is generally arid as well, but does not receive the same amount of snow that the other southwestern states receive at their high elevations. The terrain of the West Texas region in the southwest is flat rolling land of the plains, which eventually turns into a desert with some hills, and there are significant mountains as well once you reach the Trans-Pecos area.
The term "High Desert" is also synonymous with this region. The High Desert is generally defined as the Mojave Desert (which extends into southern Nevada), and the Great Basin Desert. The Great Basin Desert is defined as the desert lands in Nevada, Western Utah, as well as Southeastern Oregon and Southern Idaho. The High Desert also extends into other parts of the Northwest, such as the Red Desert is Southwestern Wyoming. The High Desert is much different than the general desert lands found in Arizona, in the Sonoran Desert. This area of the desert land generally sits at a very high elevation, much higher than the normal desert land, and can receive very cold temperatures at night in the winter (with the exception of California and southern Nevada), sometimes near zero degrees on very cold nights. The High Desert also receives a decent amount of snowfall in the winter (with the exception of California and southern Nevada), but melts very quickly.
Other areas of the southwest may also be referred to as the "High Desert", such as the Colorado Plateau. The desert lands found in Eastern Utah, Northern Arizona, Colorado, and New Mexico are usually referred to as the high desert. Eastern Utah has a huge mass of desert land, which sits at a high elevation, and is sometimes referred to as the "High Desert" as well. Colorado has scattered desert lands found in southern, southwestern, western, and the northwestern parts of the state. These scattered desert lands are located in and around areas such as, the Roan Plateau, Dinosaur National Monument, Colorado National Monument, Royal Gorge, Cortez, Dove Creek, Canyon of the Ancients National Monument, Four Corners Monument, Montrose, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Pueblo, San Luis Valley, and the Great Sand Dunes. Besides the Chihuahuan Desert lands in southwestern and southern New Mexico, they also have scattered desert lands in the northwestern and northern portions of their state which is referred to as the high desert.
National monuments and parks
 The Grand Canyon.
The Grand Canyon.
 The Great Sand Dunes.
The Great Sand Dunes.
The Southwestern United States have many national monuments and parks located in the region. Some of the more famous monuments and parks in the southwest are the Grand Canyon National Park, Navajo National Monument, Four Corners Monument, Colorado National Monument, Great Sand Dunes National Park, Arches National Park, Red Rock Canyon, Big Bend National Park, and the White Sands National Monument.
In Utah there are also many other monuments and parks such as, Nine Mile Canyon, Mexican Hat, Bryce Canyon National Park, Canyonlands National Park, Capitol Reef National Park, Zion National Park, Arches National Park, Natural Bridges National Monument, Cedar Breaks National Monument, Hovenweep National Monument (also in Colorado), Monument Valley (also in Arizona), Grand Staircase-Escalante National Monument, Rainbow Bridge National Monument, and the Timpanogos Cave National Monument.
Also, in Arizona there is the Agua Fria National Monument, Canyon de Chelly National Monument, Casa Grande Ruins National Monument, Chiricahua National Monument, Ironwood Forest National Monument, Montezuma Castle National Monument, Organ Pipe Cactus National Monument, Petrified Forest National Park, Pipe Spring National Monument, Saguaro National Park, Sonoran Desert National Monument, Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument, Tonto National Monument, Tumacacori National Historical Park, Tuzigoot National Monument, Vermilion Cliffs National Monument, Walnut Canyon National Monument, and the Wupatki National Monument.
In Colorado there is the Arapaho National Recreation Area, Mesa Verde National Park, Black Canyon of the Gunnison National Park, Dinosaur National Monument (small parts also in Utah), Florissant Fossil Beds National Monument, Rocky Mountain National Park, Royal Gorge, Grand Mesa, Garden of the Gods, Blue Mesa Reservoir, Glenwood Canyon, Canyon of the Ancients National Monument, Yucca House National Monument, and Bent's Old Fort National Historic Site.
In New Mexico there is also the Aztec Ruins National Monument, Bandelier National Monument, Capulin Volcano National Monument, Carlsbad Caverns National Park, Chaco Culture National Historical Park, El Malpais National Monument, El Morro National Monument, Gila Cliff Dwellings National Monument, Kasha-Katuwe Tent Rocks National Monument, Pecos National Historical Park, Petroglyph National Monument, and the Salinas Pueblo Missions National Monument.
In the West Texas part of the southwest, there is the Alibates Flint Quarries National Monument, Fort Davis National Historic Site, Guadalupe Mountains National Park, Lake Meredith National Recreation Area, and the Amistad National Recreation Area.
In Nevada there is the Great Basin National Park, Death Valley National Park, and the Lake Mead National Recreation Area.
Ethnicity
 Phoenix, the largest metropolitan area in the Southwest.
Phoenix, the largest metropolitan area in the Southwest.
 Denver, the second largest metropolitan area in the Southwest.
Denver, the second largest metropolitan area in the Southwest.
 Las Vegas, the third largest metropolitan area in the Southwest.
Las Vegas, the third largest metropolitan area in the Southwest.
The Southwest is ethnically varied, with significant Anglo American and Hispanic American populations in addition to more regional African American, Asian American, and Native American populations.
Hispanic Americans (mostly Mexican Americans with large populations of Spanish Americans) can be found in large numbers in every major city in the southwest, such as Phoenix (43%), Tucson (41%), Las Vegas (32%), Reno (22%), Denver (32%), Colorado Springs (16%), El Paso (80%), Albuquerque (45%), and Salt Lake City (19%). San Antonio, Austin, Fort Worth, Dallas, and Houston have large Latino populations as well, but are not always considered part of the Southwest, and are often grouped more with the American South.
Very large Hispanic American populations can also be found in the smaller cities such as, Flagstaff (18%), Yuma (55%), Las Cruces (56%), Santa Fe (48%), Farmington (22%), Roswell (51%), Alamogordo (32%), Pueblo (48%), Greeley (35%), Longmont (25%), Brighton (41%), Carson City (20%), Amarillo (27%), Lubbock (31%), Midland (37%), and Odessa (47%). Many small towns throughout the southwestern states also have significantly large Latino populations.
The largest African American populations in the southwest can be found in Denver (10%), Colorado Springs (7%), Las Vegas (10%), and Phoenix (5%). Dallas, Fort Worth, and Houston all have very large African American populations, although those parts of Texas are not usually considered to be part of the southwestern United States.
The largest Asian American populations in the southwest can be found in Nevada and Utah, with some other significant Asian populations in Denver and Phoenix. The most significant Native Americans populations can be found in New Mexico and Arizona.
Cities and urban areas
The area also contains many of the nation's largest cities and metropolitan areas, despite relatively low population density in rural areas. Phoenix is among the top ten most populous cities in the country, and Reno, Albuquerque, Colorado Springs, and Salt Lake City[15] are some of the fastest-growing cities in America. Also, the region as a whole has witnessed some of the highest population growth in the United States; and according to the U.S. Census bureau, in 2008–2009, Utah was the fastest growing state in America. As of the 2010 Census, Nevada was the fastest growing state in the United States, with an increase of 35.1% in the last ten years. Additionally, Arizona (24.6%), Utah (23.8%), Texas (20.6%), and Colorado (16.9%) were all in the top ten fastest growing states as well.[16]
Largest Cities/Metropolitan Areas
Rank City State Population Metro Population 1 Phoenix Arizona 1,445,632[17] 4,192,887 2 El Paso Texas 649,121[18] 800,647 3 Denver Colorado 600,158[19] 2,552,195 4 Las Vegas Nevada 583,756[20] 1,951,269 5 Albuquerque New Mexico 541,615[21] 869,684 6 Tucson Arizona 520,116[22] 980,263 7 Colorado Springs Colorado 416,427[23] 626,227 8 Reno Nevada 220,598[24] 420,000 9 Salt Lake City Utah 186,440[25] 1,124,197 10 Provo Utah 112,488[26] 526,810 See also
- Water Education Foundation
References
- ^ Meinig, pp. 3–8
- ^ denver co – Google Maps. Maps.google.com (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Meinig, pp. 95–101
- ^ Meinig, pp. 28–29
- ^ Meinig, pp. 103–106
- ^ Meinig, pp. 112–114
- ^ Meinig, pp. 114–119
- ^ Meinig, pp. 123–136
- ^ "Encylopedia of Southern Culture". Charles Reagan Wilson and William Ferris. University of North Carolina Press 1989
- ^ "Encylopedia of Southern Culture". Charles Reagan Wilson and William Ferris. University of North Carolina Press 1989
- ^ "The Southwest Defined. Edited by Joseph Carlton Wilder. University of Arizona Press
- ^ Cultural Regions of the United States. Raymond Gastil. University of Washington Press 1975
- ^ Cultural Regions of the United States. Raymond Gastil. University of Washington Press 1975
- ^ Southern Focus Poll 1992-1999. Odom Institute; Center for the Study of the American South.
- ^ 50 most populous cities in the U.S., Infoplease.com
- ^ http://money.cnn.com/galleries/2010/pf/1012/gallery.fastest_growing_states/index.html
- ^ Phoenix city, Arizona – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Reno city, Nevada – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Denver city, Colorado – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Las Vegas city, Nevada – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Albuquerque city, New Mexico – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Tucson city, Arizona – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Colorado Springs city, Colorado – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Reno city, Nevada – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Salt Lake City city, Utah – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
- ^ Provo city, Utah – Population Finder – American FactFinder. Factfinder.census.gov. Retrieved on 2011-01-27.
Bibliography
- Busby, Mark. The Southwest: The Greenwood Encyclopedia of American Regional Cultures (2004)
- Chávez, John R. The Lost Land: The Chicano Image of the Southwest (Albuquerque, 1984)
- De León, Arnoldo. Mexican Americans in Texas: A Brief History (2nd ed. 1999)
- Garcia, Richard A. "Changing Chicano Historiography," Reviews in American History 34.4 (2006) 521–528 in Project MUSE
- Griffin-Pierce, Trudy. Native Peoples of the Southwest (2000)
- Lamar, Howard, ed. The New Encyclopedia of the American West (Yale U.P., 1998)
- Meinig, Donald W. Southwest: Three Peoples in Geographical Change, 1600–1970, (1971), Oxford University Press, ISBN 0195012887
- Weber, David J. The Mexican Frontier, 1821–1846: The American Southwest Under Mexico (1982)
External links
United States (Outline) History Pre-Columbian era · Colonial era (Thirteen Colonies · Colonial American military history) · American Revolution (War) · Federalist Era · War of 1812 · Territorial acquisitions · Territorial evolution · Mexican–American War · Civil War · Reconstruction era · Indian Wars · Gilded Age · African-American Civil Rights Movement (1896–1954) · Spanish–American War · Imperialism · World War I · Roaring Twenties · Great Depression · World War II (Home front) · Cold War · Korean War · Space Race · African-American Civil Rights Movement (1955–1968) · Feminist Movement · Vietnam War · Post-Cold War (1991–present) · War on Terror (War in Afghanistan · Iraq War) · Timeline of modern American conservatismTopicsDemographic · Discoveries · Economic (Debt Ceiling) · Inventions (before 1890 · 1890–1945 · 1946–1991 · after 1991) · Military · Postal · Technological and industrialFederal
governmentLegislature - Congress
Senate
· Vice President
· President pro tem
House of Representatives
· Speaker
Judiciary - Supreme Court
Federal courts
Courts of appeal
District courtsExecutive - President
Executive Office
Cabinet / Executive departments
Civil service
Independent agencies
Law enforcement
Public policy
Intelligence
Central Intelligence Agency
Defense Intelligence Agency
National Security Agency
Federal Bureau of InvestigationPolitics Divisions · Elections (Electoral College) · Foreign policy · Foreign relations · Ideologies · Local governments · Parties (Democratic Party · Republican Party · Third parties) · Political status of Puerto Rico · Red states and blue states · Scandals · State governments · Uncle SamGeography Cities, towns, and villages · Counties · Extreme points · Islands · Mountains (Peaks · Appalachian · Rocky) · National Park System · Regions (Great Plains · Mid-Atlantic · Midwestern · New England · Northwestern · Southern · Southwestern · Pacific · Western) · Rivers (Colorado · Columbia · Mississippi · Missouri · Ohio · Rio Grande) · States · Territory · Water supply and sanitationEconomy Agriculture · Banking · Communications · Companies · Dollar · Energy · Federal Budget · Federal Reserve System · Financial position · Insurance · Mining · Public debt · Taxation · Tourism · Trade · Transportation · Wall StreetSociety TopicsCrime · Demographics · Education · Family structure · Health care · Health insurance · Incarceration · Languages (American English · Spanish · French) · Media · People · Public holidays · Religion · SportsArchitecture · Art · Cinema · Cuisine · Dance · Fashion · Flag · Folklore · Literature · Music · Philosophy · Radio · Television · TheaterIssuesCategories:- Southwestern United States
- Regions of the Western United States
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.