- Konya
-
For other uses, see Konya (disambiguation).
Konya Konya Collage Location of Konya, Turkey Coordinates: 37°52′N 32°29′E / 37.867°N 32.483°ECoordinates: 37°52′N 32°29′E / 37.867°N 32.483°E Country  Turkey
TurkeyRegion Central Anatolia Province Konya Government - Mayor Tahir Akyürek (AKP) Area - City 39,000 km2 (15,058 sq mi) Elevation 1,200 m (3,937 ft) Population (2010)[1] - Density 50/km2 (129.5/sq mi) - Metro 1,036,027 Time zone EET (UTC+2) - Summer (DST) EEST (UTC+3) Postal code 42XXX Area code(s) (+90) 332 Licence plate 42 Website www.konya.bel.tr Konya (Turkish pronunciation: [ˈkon.ja]) is a city in the Central Anatolia Region of Turkey. The metropolitan area in the entire Konya Province had a population of 1,036,027 as of 2010,[1] making the city seventh most populous in Turkey.
Contents
History
Etymology
Konya, also spelled in some historic English texts as Konia or Koniah, was known in classical antiquity and during the medieval period as Iconium in Latin, and Ἰκόνιον (Ikónion) in Greek. The name Konya is a cognate of icon, as an ancient Greek legend ascribed its name to the "eikon" (image), or the "gorgon's (Medusa's) head", with which Perseus vanquished the native population before founding the city.[2]
Ancient history
Excavations have shown that the region was inhabited during the Late Copper Age, around 3000 BC.[2] The city came under the influence of the Hittites around 1500 BC. These were overtaken by the Sea Peoples around 1200 BC. The Phrygians established their kingdom in central Anatolia in the 8th century BC. Xenophon describes Iconium, as the city was called, as the last city of Phrygia. The region was overwhelmed by Cimmerian invaders c. 690 BC. It was later part of the Persian Empire, until Darius III was defeated by Alexander the Great in 333 BC. Alexander's empire broke up shortly after his death and the town came under the rule of Seleucus I Nicator. During the Hellenistic period the town was ruled by the kings of Pergamon. As Attalus III, the last king of Pergamon, was about to die without an heir, he bequeathed his kingdom to Rome. Under the rule of emperor Claudius, the city's name was changed to Claudioconium, and during the rule of emperor Hadrianus to Colonia Aelia Hadriana.
Saint Paul and Barnabas preached in Iconium during the First Missionary Journey in about 47-48 AD (see Acts 14:1-5 and Acts 14:21), and Paul and Silas probably visited it again during the Second Missionary Journey in about 50 (see Acts 16:2).[3] In Christian legend, it was also the birthplace of Saint Thecla. During the Byzantine Empire the town was destroyed several times by Arab invaders in the 7th-9th centuries.
Seljuk era
The city was conquered by the Seljuk Turks following the Battle of Manzikert in 1071, and from 1097 to 1243 it was the capital of the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate, though very briefly occupied by the Crusaders Godfrey of Bouillon (August 1097) and Frederick Barbarossa (May 18, 1190). The name of the town was changed to Konya by Rukn al-Dīn Mas'ūd in 1134.
Konya reached the height of its wealth and influence as of the second half of the 12th century when Anatolian Seljuk sultans also subdued the Anatolian beyliks to their east, especially that of the Danishmends, thus establishing their rule over virtually all of eastern Anatolia, as well as acquiring several port towns along the Mediterranean (including Alanya) and the Black Sea (including Sinop) and even gaining a momentary foothold in Sudak, Crimea. This golden age lasted until the first decades of the 13th century.
By the 1220s, the city was filled with refugees from the Khwarezmid Empire, fleeing the advance of the Mongol Empire. Sultan Alā al-Dīn Kayqubād bin Kaykā'ūs fortified the town and built a palace on top of the citadel. In 1228 he invited Bahaeddin Veled and his son Mevlana (Rumi), the founder of the Mevlevi order, to settle in Konya.
In 1243, following the Seljuk defeat in the Battle of Köse Dağ, Konya was captured by the Mongols as well. The city remained the capital of the Seljuk sultans, vassalized to the Ilkhanate until the end of the century.
Following the fall of the Anatolian Seljuk Sultanate, Konya was made the capital of a beylik (emirate) in 1307 which lasted until 1322 when the city was captured by the neighbouring Beylik of Karamanoğlu. In 1420, Karamanoğlu fell to the Ottoman Empire and, in 1453, Konya was made the provincial capital of the Ottoman Province of Karaman.
Ottoman era
Under the Ottoman Empire, in the vilayet system established after 1864, Konya was the seat of the Vilayet of Konya.
According to the 1895 census, Konya had a population of nearly forty-five thousand, of which 42,318 were Muslims, 1,566 were Christian Armenians and 899 were Christian Greeks. There were also 21 mosques and 5 Churches in the town.[4] A still-standing Catholic church was built for the Italian railway workers in the 1910s. By 1927, after the Greco-Turkish population exchange accord of 1923, the city's population became almost exclusively Muslim.
Geography
Climate
Konya has a continental climate. Rainfall occurs mostly during the spring and autumn. Under Köppen's climate classification The city has a semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk).[5] Summers temperatures average 30 °C (86 °F). The highest temperature recorded in Konya was 40.6 °C (105 °F) on 30 July 2000. Winters average −4.2 °C (24 °F). The lowest temperature recorded was -25.8 °C (78 °F) on 25 January 1989.
Climate data for Konya Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) 4.6
(40.3)6.7
(44.1)12.0
(53.6)17.4
(63.3)22.3
(72.1)26.9
(80.4)30.3
(86.5)30.3
(86.5)26.3
(79.3)20.0
(68.0)12.5
(54.5)6.2
(43.2)17.96
(64.32)Average low °C (°F) −4.1
(24.6)−3.5
(25.7)−0.1
(31.8)4.5
(40.1)8.6
(47.5)13.0
(55.4)16.3
(61.3)15.9
(60.6)11.4
(52.5)6.3
(43.3)0.7
(33.3)−2.4
(27.7)5.55
(41.99)Precipitation mm (inches) 34.7
(1.366)24.5
(0.965)25.9
(1.02)38.9
(1.531)41.1
(1.618)20.9
(0.823)8.9
(0.35)7.4
(0.291)13.6
(0.535)33.4
(1.315)37.8
(1.488)43.2
(1.701)330.3
(13.004)% humidity 76 72 62 55 53 48 41 39 47 58 70 78 58.3 Avg. rainy days 5 6 5 6 7 5 1 2 2 5 5 7 56 Sunshine hours 96.1 126 189.1 207 266.6 312 347.2 341 288 220.1 150 93 2,636.1 Source no. 1: Devlet Meteoroloji İşleri Genel Müdürlüğü [4] Source no. 2: Hong Kong Observatory [5] Education
There are various elementary and secondary schools in the Konya municipality.
Selçuk University has the largest number of students, 76,080, of any public university in Turkey in the 2008-09 academic year.[6]. It was founded in 1975.
Private colleges in Konya include KTO Karatay and Mevlana universities.[7][8]
Notables
- Ibn Arabi, the Sufi and Islamic philosopher, visited Konya in 1207 at the invitation of the Seljuk governor of that time and married the mother of his disciple Sadreddin Konevi.
- Jalal al-Din Muhammad Rumi, the Persian Sufi poet commonly known as "Mevlâna" and who is the founder of the Sufi Mevlevi order (known for the Whirling Dervishes), spent the last fifty years of his life in Konya. His tomb is located here.
- Hazrat Shah Jalal was born in 1271 in Konya.
- Nasreddin Hodja died in Konya in the 13th century.
- Orkut Büyükkökten, a software engineer who developed the social networking service Orkut, was born in 1975 in Konya [9]
- Ahmet Davutoğlu, Turkish Minister of Foreign Affairs, born 26 February 1959 in Konya.
Notable structures
- Alaeddin Mosque
- Ince Minaret Medrese-- Museum
- Karatay Medrese -- Museum
- Mevlana Museum, formerly the tekke of Mevlana
- Seljuk Tower, the tallest building in Konya
- Alaaddin Hill[10]
Culture
Konya has the reputation of being one of the more religiously conservative metropolitan centers in Turkey. It was once known as the "citadel of Islam" and its inhabitants are still comparatively more devout than those from other cities.[11] Konya was the final home of Rumi, whose tomb is in the city, and whose followers established in 1273 the Mevlevi Sufi order of Islam there and became known as the whirling dervishes.
A Turkish folk song is named "Konyalım" (making reference to a loved one from Konya).[12]
Konya produced Turkish carpets that were exported to Europe during the Renaissance.[13][14] These expensive, richly-patterned textiles were draped over tables, beds, or chests to proclaim the wealth and status of their owners, and were often included in the contemporary oil paintings as symbols of the wealth of the painter's clients.[15]
The diet of people includes a large amount of bulgur wheat and lamb meat.[citation needed]
Twin towns
Twin towns — Sister cities
Konya is twinned with:
 Multan, Pakistan[16]
Multan, Pakistan[16] Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina[17]
Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina[17] Tabriz, Iran
Tabriz, Iran Tetovo, Republic of Macedonia[18]
Tetovo, Republic of Macedonia[18] Sana'a, Yemen, (Start since October 2011)
Sana'a, Yemen, (Start since October 2011)
See also
- Anatolian Tigers
- Konya Carpets and Rugs
- Battle of Iconium (1069)
- Battle of Iconium (1190)
References and notes
- ^ a b [1] Address-based population survey 2010.
- ^ a b Encyclopædia Britannica: Konya
- ^ see William Ramsay, Cities of St. Paul, 315-384; F. F. Bruce, Paul: Apostle of the Heart Set Free Grand Rapids, MI: Eerdmans, 1977. p. 475.
- ^ Alaturka Turkey: Konya
- ^ [2][dead link]
- ^ [3][dead link]
- ^ "KTO Karatay Üniversitesi". Karatay.edu.tr. http://www.karatay.edu.tr/. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ A Fuat Mercan. "Mevlana Üniversitesi | Mevlana University". Mevlana.edu.tr. http://www.mevlana.edu.tr/. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ Programmer World: Orkut Büyükkökten
- ^ Alaaddin Hill
- ^ 'Islam problem' baffles Turkey, By Jonny Dymond - BBC
- ^ Song Lyrics
- ^ King, Donald and Sylvester, David. The Eastern Carpet in the Western World, From the 15th to the 17th century, Arts Council of Great Britain, London, 1983, ISBN 0728703629. pp. 26-27, 52-57.
- ^ Campbell, Gordon. The Grove Encyclopedia of Decorative Arts, Volume 1, "Carpet, S 2; History (pp. 187–193), Oxford University Press US, 2006, ISBN 0195189485, 9780195189483 Google books. p. 189.
- ^ Old Ottoman "Holbein" carpets in Renaissance painting
- ^ "Ministry of Foreign Affairs". Mofa.gov.pk. 2008-10-31. http://www.mofa.gov.pk/Press_Releases/2008/Oct/statement_31.html. Retrieved 2011-09-16.
- ^ daenet d.o.o.. "Sarajevo Official Web Site : Sister cities". Sarajevo.ba. http://www.sarajevo.ba/en/stream.php?kat=160. Retrieved 2009-05-06.
- ^ Тетово се збратимува со турскиот град Коња -Утрински весник
External links
- Konya travel guide from Wikitravel
- Encyclopædia Britannica: Konya
- More information about Konya
- Emporis: Database of highrises and other structures in Konya
- Detailed Pictures of Mevlana Museum
- Pictures of the city, including Mevlana Museum and several Seljuk buildings
- Konya
- 600 Pictures of the city and sights
- Extensive collection of pictures of the Mevlana museum in Konya
- Cities of St. Paul, 316-384
- Old Konya's Picture
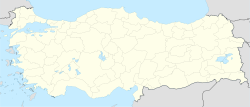
 Konya in Konya Province (in the Central Anatolia region) of Turkey
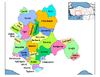
Konya in Konya Province (in the Central Anatolia region) of TurkeyUrban districts 
Rural districts Ahırlı - Akören - Akşehir - Altınekin - Beyşehir - Bozkır - Çeltik - Cihanbeyli - Çumra - Derbent - Derebucak - Doğanhisar - Emirgazi - Ereğli - Güneysınır - Hadim - Halkapınar - Hüyük - Ilgın - Kadınhanı - Karapınar - Kulu - Sarayönü - Seydişehir - Taşkent - Tuzlukçu - Yalıhüyük - Yeniceoba - YunakRegionsAegean Black Sea Central Anatolia Eastern Anatolia Marmara Mediterranean Southeastern Anatolia  Metropolitan centers in Turkey
Metropolitan centers in TurkeyFirst Journey of Paul the Apostle Categories:- Konya Province
- Cities in Turkey
- Central Anatolia Region
- Ancient Greek cities
- Konya
- Populated places along the Silk Road
- Holy cities
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.