- Ovarian reserve
-
Ovarian reserve is a term that is used to determine the capacity of the ovary to provide eggs that are capable of fertilization resulting in a healthy and successful pregnancy. While there is no known method for assessing the ovarian reserve of individual women[1], indirect determination of ovarian reserve is important in the treatment of infertility[2].
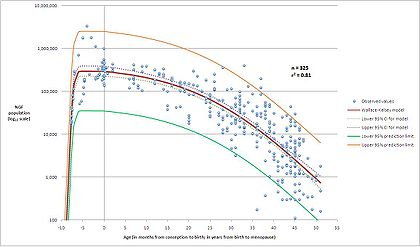
The ovary is generally thought of as an egg bank from which the woman draws during her reproductive life. The human ovary contains a population of primordial follicles. At 18–22 weeks post-conception, the female ovary contains its peak number of follicles (about 300,000 in the average case, but individual peak populations range from 35,000 to 2.5 million[3]). While each month one egg is released by ovulation the remaining follicles that were recruited towards maturation are lost by atresia. Few if any oocytes are replenished during the reproductive years. Thus with advanced maternal age the number of eggs that can be successfully recruited for a possible pregnancy declines. Attempts have been made to assess the number of potential useful oocytes in a noninvasive way.
The most commonly used test to assess this ovarian reserve is the day 3 FSH test[4]. This blood test determines the level of FSH on cycle day 3. Cycle day 3 is chosen because at this time the estrogen level is expected to be low, a critical feature, as FSH levels are subject to a negative feedback. Thus any determination of FSH needs to include the corresponding estradiol level to indicate that the FSH level was drawn, when the estrogen level was low. In a patient with infrequent menstruation, an FSH level and estrogen level could be measured at random and is valid if the estrogen level is low. Generally FSH levels are expected to be below 10 miu/ml in women with reproductive potential (levels of 10-15 miu/ml are considered borderline), however the exact numbers returned will depend on the type of assay used in a particular laboratory. Although FSH and more recently Inhibin B have been shown to have some correlation with ovarian reserve, it is now well established that Anti-Mullerian Hormone or AMH is more useful biochemical test. High levels however can be present in women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome which compromises female fertility and therefore a combination of AMH and a transvaginal ultrasound to count the number of antral follicles is probably the best way to assess ovarian reserve and future fertility. This combination is sometimes referred to as the Biological Body Clock Test.
A clomiphene challenge test is a variation on this approach[5].
Another approach is to examine the ovaries by gynecologic ultrasonography and to determine their size as ovaries depleted of eggs tend to be smaller[6] and to examine the number of antral follicles visible by sonography[7].
Women with poor ovarian reserve are unlikely to conceive with infertility therapy. Also see poor ovarian reserve and Follicle-stimulating hormone for treatment options.
References
- ^ Broekemans FJ et al. (1998) Ovarian reserve tests in infertility practice and normal fertile women. Maturitas. 30(2):205-14.
- ^ Broekemans FJ et al. (2006) A systematic review of tests predicting ovarian reserve and IVF outcome. Hum Reprod Update. 12(6):685-718.
- ^ Wallace WHB and Kelsey TW (2010) Human Ovarian Reserve from Conception to the Menopause. PLoS ONE 5(1):e8772.doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0008772
- ^ Scott RT et al. (1989) Follicle stimulating hormone levels on cycle day 3 are predictive of in vitro fertilization outcome. Fertility and Sterility. 1989; 51:651-4.
- ^ Practice Committee of the American Society for Reproductive Medicine. Use of clomiphene citrate in women. Fertil Steril 2003; 80:1302.
- ^ Wallace WHB and Kelsey TW (2004)Ovarian reserve and reproductive age may be determined from measurement of ovarian volume by transvaginal sonography. Human Reproduction; 19(7):1612-1617
- ^ Kwee et al. (2007) Ovarian volume and antral follicle count for the prediction of low and hyper responders with in vitro fertilization. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2007; 5: 9.
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.