- Bilberry
-
For other uses, see Bilberry (disambiguation).
Bilberry is any of several species of low-growing shrubs in the genus Vaccinium (family Ericaceae), bearing edible berries. The species most often referred to is Vaccinium myrtillus L., but there are several other closely related species.
Contents
Vernacular names
Bilberry (especially Vaccinium myrtillus) is known in English by a very wide range of local names. As well as "bilberry", these include blaeberry (
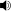 /ˈbleɪbɛri/, whortleberry (/ˈhɜrtəlbɛri/), (ground) hurts, whinberry, winberry, windberry, wimberry, myrtle blueberry and fraughan. The berries were called black-hearts in 19th century south-western England, according to Thomas Hardy's 1878 novel The Return of the Native.[1] In several other languages its name translates as "blueberry", and this may cause confusion with the related plants more usually known as "blueberry" in English, which are in the separate section Cyanococcus of the Vaccinium genus.
/ˈbleɪbɛri/, whortleberry (/ˈhɜrtəlbɛri/), (ground) hurts, whinberry, winberry, windberry, wimberry, myrtle blueberry and fraughan. The berries were called black-hearts in 19th century south-western England, according to Thomas Hardy's 1878 novel The Return of the Native.[1] In several other languages its name translates as "blueberry", and this may cause confusion with the related plants more usually known as "blueberry" in English, which are in the separate section Cyanococcus of the Vaccinium genus.Species
Bilberries include several closely related species of the Vaccinium genus, including:
- Vaccinium myrtillus L. (bilberry)
- Vaccinium uliginosum L. (bog bilberry, bog blueberry, bog whortleberry, bog huckleberry, northern bilberry, ground hurts)
- Vaccinium caespitosum Michx. (dwarf bilberry)
- Vaccinium deliciosum Piper (cascade bilberry)
- Vaccinium membranaceum (mountain bilberry, black mountain huckleberry, black huckleberry, twin-leaved huckleberry)
- Vaccinium ovalifolium (oval-leafed blueberry, oval-leaved bilberry, mountain blueberry, high-bush blueberry).
Diseases
Bilberry plants can suffer from Bilberry Blight,[2] caused by Phytophthora kernoviae. There have been severe outbreaks in Staffordshire, England.[3]
Wild and cultivated harvesting
Bilberries are found in very acidic, nutrient-poor soils throughout the temperate and subarctic regions of the world. They are closely related to North American wild and cultivated blueberries and huckleberries in the genus Vaccinium. One characteristic of bilberries is that they produce single or paired berries on the bush instead of clusters, as the blueberry does. Blueberries have more evergreen leaves.
The fruit is smaller than that of the blueberry but with a fuller taste. Bilberries are darker in colour, and usually appear near black with a slight shade of purple. While the blueberry's fruit pulp is light green, the bilberry's is red or purple, heavily staining the fingers and lips of consumers eating the raw fruit. The red juice is used by European dentists to show children how to brush their teeth correctly, as any improperly brushed areas will be heavily stained.
Bilberries are extremely difficult to grow and are thus seldom cultivated. Fruits are mostly collected from wild plants growing on publicly accessible lands, notably Finland, Sweden, Norway, Iceland, Scotland, Wales, Ireland, parts of England, Alpine countries, Carpathian Mountains in Ukraine, Belarus, Romania, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Poland and northern parts of Turkey and Russia. Note that in Austria, Finland, Norway, Sweden and Switzerland, it is an everyman's right to collect bilberries, irrespective of land ownership, with the exception of private gardens and nature reserves. Bilberries can be picked by a berry-picking rake like lingonberries, but are more susceptible to damage. Bilberries are softer and juicier than blueberries, making them difficult to transport. Because of these factors, the bilberry is only available fresh on markets and in gourmet stores, where in the latter they can cost up to 25 Euro per pound. Frozen bilberries however are available all year round in most of Europe.
In Finland, bilberries are collected from forests. They are eaten fresh or can be made in different jams and dishes. The famous one is the bilberry pie (Finnish: mustikkapiirakka, Swedish blåbärspaj).
In Ireland, the fruit is known as fraughan, from the Irish fraochán, and is traditionally gathered on the last Sunday in July, known as Fraughan Sunday.
Bilberries were also collected at Lughnasadh in August, the first traditional harvest festival of the year, as celebrated by Gaelic people. The crop of bilberries was said to indicate how well the rest of the crops would fare in their harvests later in the year.
The fruits can be eaten fresh or made into jams, fools, juices or pies. In France and in Italy, they are used as a base for liqueurs and are a popular flavoring for sorbets and other desserts. In Brittany, they are often used as a flavoring for crêpes, and in the Vosges and the Massif Central bilberry tart (tarte aux myrtilles) is a traditional dessert.
Bilberry is used as a food plant by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species - see list of Lepidoptera that feed on Vaccinium
Possible medicinal uses
Often associated with improvement of night vision, bilberries are mentioned in a popular story of World War II RAF pilots consuming bilberry jam to sharpen vision for night missions. However, a recent study[4] by the U.S. Navy found no such effect and origins of the RAF story cannot be found.[5]
Although the effect of bilberry on night vision is unfounded, laboratory studies in rats have provided preliminary evidence that bilberry consumption may inhibit or reverse eye disorders such as macular degeneration.[6]
Bilberries are recognized as a good source of flavonoids, some of which have antioxidant activity.[7]
As a deep purple fruit, bilberries contain anthocyanin pigments.
 Wild bilberries collected in Norway.
Wild bilberries collected in Norway.
Standardization of its food products
- ISO 6664
See also
- Blåbärssoppa, a soup made from bilberries
- Blueberry
- List of fruits
- List of vegetables
- Vaccinium myrtillus
References
- ^ Hardy, Thomas, The Return of the Native (p. 311, Oxford World's Classics edition)
- ^ "Phytophthora". Natural England. http://www.naturalengland.org.uk/ourwork/conservation/biodiversity/threats/phytophthora.aspx. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ^ "Disease of Bilberry (Phytophthora)". Staffordshire County Council. http://www.staffordshire.gov.uk/environment/eLand/phytophthora/ChannelHome.aspx. Retrieved 26 June 2011.
- ^ Muth ER, Laurent JM, Jasper P (April 2000). "The effect of bilberry nutritional supplementation on night visual acuity and contrast sensitivity". Alternative Medicine Review 5 (2): 164–73. PMID 10767671. http://www.thorne.com/altmedrev/.fulltext/5/2/164.pdf.
- ^ [1] Bilberry Bombs, WebMD, October 2000
- ^ Fursova AZh, Gesarevich OG, Gonchar AM, Trofimova NA, Kolosova NG (2005). "Dietary supplementation with bilberry extract prevents macular degeneration and cataracts in senesce-accelerated OXYS rats [Dietary supplementation with bilberry extract prevents macular degeneration and cataracts in senesce-accelerated OXYS rats]" (in Russian). Advances in Gerontology 16: 76–9. PMID 16075680.
- ^ Lovro Žiberna,corresponding author Mojca Lunder, Špela Može, Andreja Vanzo, and Gorazd Drevenšek (2009). Cardioprotective effects of bilberry extract on ischemia-reperfusion-induced injury in isolated rat heart. 9. PMC 2778928. PMID 0. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2778928.
External links
Categories:- Vaccinium
- Medicinal plants
- Berries
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


