- Sarracenia purpurea
-
Purple pitcher plant 
Flowering Sarracenia purpurea, Newfoundland Scientific classification Kingdom: Plantae (unranked): Angiosperms (unranked): Eudicots (unranked): Asterids Order: Ericales Family: Sarraceniaceae Genus: Sarracenia Species: S. purpurea Binomial name Sarracenia purpurea
L.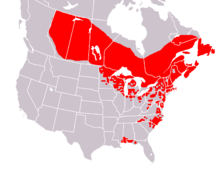
Sarracenia purpurea range Sarracenia purpurea, commonly known as the purple pitcher plant, northern pitcher plant, or side-saddle flower, is a carnivorous plant in the family Sarraceniaceae. Its range includes almost the entire eastern seaboard of the United States, the Great Lakes, and south eastern Canada, making it the most common and broadly distributed pitcher plant, as well as the only member of the genus that inhabits cold temperate climates. The species is the floral emblem of the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador.
Contents
Description
 S. purpurea, Temagami, Ontario
S. purpurea, Temagami, Ontario
Like other species of Sarracenia, S. purpurea obtains most of its nutrients through prey capture.[1] However, prey acquisition is said to be inefficient, with less than 1% of the visiting prey captured within the pitcher.[2] Even so, anecdotal evidence by growers often shows that pitchers quickly fill up with prey during the warm summer months. Prey fall into the pitcher and drown in the rainwater that collects in the base of each leaf. Prey items such as flies, ants, spiders, and even moths, are then digested by an invertebrate community, made up mostly by the mosquito Wyeomyia smithii and the midge Metriocnemus knabi. Protists, rotifers (including Habrotrocha rosa), and bacteria form the base of inquiline food web that shreds and mineralizes available prey, making nutrients available to the plant.[3][4][5] New pitcher leaves do produce digestive enzymes such as hydrolases and proteases, but as the individual leaves get older into their second year, digestion of prey material is aided by the community of bacteria that live within the pitchers.[6][7]
Taxonomy
The species is further divided into two subspecies, S. purpurea subsp. purpurea and S. purpurea subsp. venosa. The former is found from New Jersey north and requires a winter dormancy, while the latter is found from New Jersey south and tolerates warmer temperatures.
In 1999, Sarracenia purpurea subsp. venosa var. burkii was described as a species of its own: Sarracenia rosea. This re-ranking has been debated among carnivorous plant enthusiasts since then, but further morphological evidence has supported the split.[8] The following species and infraspecific taxa are usually recognized:
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. purpurea
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. purpurea f. heterophylla
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. purpurea f. ruplicola (invalid)
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. venosa
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. venosa var. burkii [=S. rosea]
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. venosa var. burkii f. luteola[9]
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. venosa var. montana
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. venosa var. burkii [=S. rosea]
Gallery
-
With sign showing Ojibway name of Pitcher Plant from the bog at Lake Bemidji State Park
References
- ^ Wakefield AE, Gotelli NJ, Wittman SE, Ellison AM (2005). "Prey addition alters nutrient stoichiometry of the carnivorous plant Sarracenia purpurea" (abstract). Ecology 86 (7): 1737–1743. doi:10.1890/04-1673. http://www.esajournals.org/esaonline/?request=get-abstract&issn=0012-9658&volume=086&issue=07&page=1737.
- ^ Newell SJ, Nastase AJ (1998). "Efficiency of nutrient capture by Sarracenia purpurea (Sarraceniaceae), the Northern Pitcher Plant". American Journal of Botany 85 (1): 88–91. doi:10.2307/2446558. JSTOR 2446558.
- ^ Heard SB (1994). "Pitcher plant midges and mosquitoes: a processing chain commensalism" (abstract). Ecology 75 (6): 1647–1660. doi:10.2307/1939625. JSTOR 1939625.
- ^ Mouquet N., Daufresne T., Gray S. M., Miller T. E. (2008). "Modelling the relationship between a pitcher plant (Sarracenia purpurea) and its phytotelma community: mutualism or parasitism?". Functional Ecology 22 (4): 728–737. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01421.x.
- ^ Peterson C. N., Day S., Wolfe B. E., Ellison A. M., Kolter R., Pringle A. (2008). "A keystone predator controls bacterial diversity in the pitcher-plant (Sarracenia purpurea) microecosystem". Environmental Microbiology 10 (9): 2257–2266. doi:10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01648.x. PMID 18479443.
- ^ Rice, Barry. (2007). About Sarracenia purpurea, the purple pitcher plant. The Carnivorous Plant FAQ. Accessed online: 21 June 2008.
- ^ Gallie D. R., Chang S.-C. (1997). "Signal transduction in the carnivorous plant Sarracenia purpurea. Regulation of secretory hydrolase expression during development and in response to resources". Plant Physiology 115 (4): 1461–1471. doi:10.1104/pp.115.4.1461. PMC 158611. PMID 9414556. http://www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/reprint/115/4/1461.
- ^ Ellison A. M., Buckley H. L., Miller T. E., Gotelli N. J. (2004). "Morphological variation in Sarracenia purpurea (Sarraceniaceae): geographic, environmental, and taxonomic correlates" (PDF). American Journal of Botany 91 (11): 1930–1935. doi:10.3732/ajb.91.11.1930. PMID 21652339. http://www.amjbot.org/cgi/reprint/91/11/1930.pdf.
- ^ Hanrahan B., Miller J. (1998). "History of Discovery: Yellow Flowered Sarracenia purpurea L. subsp. venosa (Raf.) Wherry var. burkii". Carnivorous Plant Newsletter 27 (1): 14–17. http://www.carnivorousplants.org/cpn/Species/v27n1p14_17.html.
External links
- Sarracenia purpurea at Barry Rice's carnivorous plant FAQ.
- Botanical Society of America, Sarracenia - the Pitcher Plants
Sarracenia S. alabamensis · S. alata · S. flava · S. jonesii · S. leucophylla · S. minor · S. oreophila · S. psittacina · S. purpurea · S. rosea · S. rubraCategories:- Flora of New Brunswick
- Flora of Newfoundland and Labrador
- Flora of Nova Scotia
- Flora of Ontario
- Flora of Prince Edward Island
- Flora of Quebec
- Flora of Manitoba
- Flora of Saskatchewan
- Flora of Connecticut
- Flora of Indiana
- Flora of Maine
- Flora of Massachusetts
- Flora of Michigan
- Flora of New Hampshire
- Flora of New Jersey
- Flora of New York
- Flora of Ohio
- Flora of Pennsylvania
- Flora of Rhode Island
- Flora of Vermont
- Flora of West Virginia
- Flora of Illinois
- Flora of Minnesota
- Flora of Wisconsin
- Flora of Delaware
- Flora of Georgia (U.S. state)
- Flora of Maryland
- Flora of North Carolina
- Flora of South Carolina
- Flora of Virginia
- Medicinal plants
- Sarracenia
- Sarracenia purpurea subsp. purpurea
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





