- Multifidus muscle
-
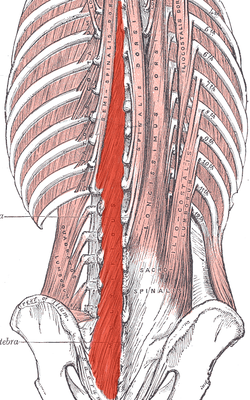
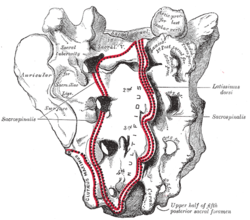
Multifidus muscle Deep muscles of the back. (Multifidus shaded in red.) Sacrum, dorsal surface. (Multifidus attachment outlined in red.) Latin musculus multifidus Gray's subject #115 400 Origin Sacrum, Erector spinae Aponeurosis, PSIS, and Iliac crest Insertion spinous process Artery Nerve Posterior branches Actions Stabilizes vertebrae in local movements of vertebral column The multifidus (multifidus spinae : pl. multifidi ) muscle consists of a number of fleshy and tendinous fasciculi, which fill up the groove on either side of the spinous processes of the vertebrae, from the sacrum to the axis. The multifidus is a very thin muscle.
Deep in the spine, it spans three joint segments, and works to stabilize the joints at each segmental level.
The stiffness and stability makes each vertebra work more effectively, and reduces the degeneration of the joint structures.
These fasciculi arise:
- in the sacral region: from the back of the sacrum, as low as the fourth sacral foramen, from the aponeurosis of origin of the Sacrospinalis, from the medial surface of the posterior superior iliac spine, and from the posterior sacroiliac ligaments.
- in the lumbar region: from all the mamillary processes.
- in the thoracic region: from all the transverse processes.
- in the cervical region: from the articular processes of the lower four vertebrae.
Each fasciculus, passing obliquely upward and medialward, is inserted into the whole length of the spinous process of one of the vertebræ above.
These fasciculi vary in length: the most superficial, the longest, pass from one vertebra to the third or fourth above; those next in order run from one vertebra to the second or third above; while the deepest connect two contiguous vertebrae.
Multifidus lies deep to the Spinal Erectors, Transverse Abdominus, and Abdominal external oblique muscle/Abdominal external oblique muscle.
Additional images
External links
- LUC mult
- multifidus+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
- Duke Orthopedics multifidus_1
- PTCentral
- Dissection at ithaca.edu
- Multifidus – Smallest Yet Most Powerful Muscle
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Back splenius (capitis, cervicis) · erector spinae (iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis) · latissimus dorsi
transversospinales: (semispinalis dorsi, semispinalis cervicis, semispinalis capitis, multifidus, rotatores) · interspinales · intertransversarii
Vertebral column: trapezius · latissimus dorsi · rhomboid (major, minor) · levator scapulae
fascia: Thoracolumbar fasciaThorax intercostales (external, internal, innermost) · subcostales · transversus thoracis · levatores costarum · serratus posterior (inferior, superior) · diaphragm
Thoracic cavity: pectoralis major · pectoralis minor · subclavius · serratus anterior
fascia: Pectoral fascia · Clavipectoral fasciaCategories:- Muscles of the torso
- Muscle stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.