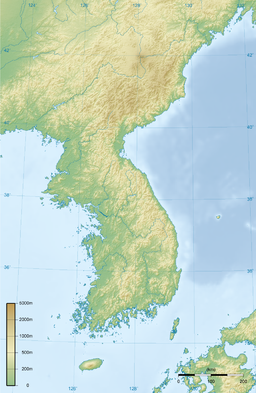
- Korean Peninsula
-
Korean Peninsula Chosŏn Pando (조선반도; 朝鮮半島) (in N. Korea), Han Bando (한반도; 韓半島) (in S. Korea) Peninsulas of Asia Countries North Korea, South Korea Borders on China, Sea of Japan, East China Sea, Yellow Sea, Korea Strait Length 1,100 km (684 mi), north to south Area 220,847 km2 (85,270 sq mi) 
The Korean Peninsula is a peninsula in East Asia. It extends southwards for about 684 miles (1,100 km) from continental Asia into the Pacific Ocean and is surrounded by the Sea of Japan to the south, and the Yellow Sea to the west, the Korea Strait connecting the first two bodies of water.
Until the end of World War II, Korea was a single political entity whose territory roughly coincided with the Korean Peninsula. Since the Armistice Agreement ended the Korean War in 1953, the northern half has been occupied by the Democratic People's Republic of Korea, while the southern half has been occupied by the Republic of Korea.
The northern boundaries for the Korean Peninsula are commonly (and tacitly) taken to coincide with today's political borders between North Korea and her northern neighbors, China (1,416 km along the provinces of Jilin and Liaoning) and Russia (19 km). These borders are formed naturally by the rivers Yalu/Amnok and Tumen/Tuman/Duman. Taking this definition, the Korean Peninsula (including its islands) has an area of 220,847 km2 (85,270 sq mi).
The peninsula is called Chosŏn Pando (조선반도; 朝鮮半島) in North Korea and Han Bando (한반도; 韓半島) in South Korea based on the respective names of the two countries. They both use "Korea" as part of their official English names.
Contents
Physical geography
Main articles: Geography of North Korea and Geography of South KoreaMountains cover 70 percent of the Korean Peninsula and arable plains are generally small and far in between the successive mountain ranges. The peninsula becomes more mountainous towards the north and the east, with the highest mountains (including Baekdu Mountain which stands at 2,744 m or 9,003 feet) found in the north.
The peninsula has 8,460 kilometres of coastline, and the south and west coasts are highly irregular in particular; most of the 3,579 islands off the peninsula are found along the south and the west coasts.
Climate
 Heavy snow fell on the eastern peninsula in February 2011.
Heavy snow fell on the eastern peninsula in February 2011.
The climate of the Korean Peninsula differs dramatically from north to south. The southern regions experience a relatively warm and wet climate similar to that of Japan, affected by warm ocean waters including the East Korea Warm Current. The northern regions experience a colder and to some extent more inland climate, in common with Manchuria. For example, the annual precipitation of the Yalu River valley (600 mm) is less than half of that on the south coast (1500 mm).[1] Likewise, there is a 20 °C difference in January temperature between the peninsula's southern and northern tips.
The entire peninsula, however, is affected by similar general patterns, including the East Asian monsoon in midsummer and the frequent incidence of typhoons in autumn. The majority of rainfall takes place during the summer months, with nearly half during the monsoon alone. Winters are cold, with January temperatures typically below freezing outside of Jeju Island. Winter precipitation is minimal, with little snow accumulation outside of mountainous areas.
Biology
Surveys of Korean flora have identified more than 3,000 species on the peninsula, of which more than 500 are endemic. The peninsula's floristic provinces are commonly divided between warm-temperate, temperate, and cold-temperate zones. The warm-temperate zone prevails over the southern coast and islands, including Jeju-do. It is largely typified by broad-leaved evergreens.
The temperate zone covers the great majority of the peninsula, away from the southern coast and high mountains. It is dominated by the Korean pine and various broad-leaved deciduous trees. Cold-temperate vegetation is found along the peninsula's northern fringe and in the high mountains, including the upper reaches of Hallasan on Jeju. Evergreens in this area include larch and juniper. Much of this vegetation is shared with Manchuria.
According to the World Wide Fund for Nature, the Korean Peninsula consists of several ecoregions. The Southern Korea evergreen forests occupy the southernmost portion of the peninsula, as well as the island of Jeju. The Central Korea deciduous forests occupy the more temperate central portion of the peninsula. The Manchurian mixed forests occupy the northern lowlands and low hills of the peninsula, and extend north into Manchuria as far as the Amur River on the Russia-China border. The Changbai Mountains mixed forests include the higher elevation mountain region along the North Korea-China border, where forests are dominated by conifers, with alpine meadows and rock slopes on the highest peaks.[2] games
Geology
The terrain of the Korean Peninsula is rumpled, covered with low mountains. Most rocks are of Precambrian origin, although isolated pockets of Paleozoic, Mesozoic, and Cenozoic rock can also be found.
There are no active volcanoes on the peninsula. However, Baekdu Mountain in the north and Hallasan in the south have crater lakes, indicating that they were active not long ago. Furthermore, hot springs indicative of low-level volcanic activity are widespread throughout the peninsula. Roughly two earthquakes are recorded per year, but few have any major impact.
See also
- Korea
- North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea)
- South Korea (Republic of Korea)
- List of Korea-related topics
- Geography of North Korea
- Geography of South Korea
- Maps of Korea at the American Geographical Society Library Digital Map Collection
Notes
References
- KOIS (Korea Overseas Information Service) (2003). Handbook of Korea, 11th ed. Seoul: Hollym. ISBN 1-56591-212-8.
- Lithuanian lake similar to the Korean Peninsula kaibab gordian
External links
- Location of The Korean Peninsula—The Official Korea Tourism Guide Site
Korea topics History - Timeline
- List of monarchs
- Military history / Gojoseon
- Jin
- Proto-Three Kingdoms
- Three Kingdoms
- North South States Period
- Later Three Kingdoms
- Goryeo
- Joseon
- Korean Empire
- Japanese rule
- Independence movements
- Provisional Government
- Division of Korea
- North Korea and South Korea
Politics - Government
- President
- Chairman
- Premier
- Supreme People's Assembly
- Presidium
- Elections
- Political parties
- Human rights
- LGBT rights
- Nuclear program
- Military
- Foreign relations
- "Juche"
Economy - List of companies
- Currency
- Communications
- Transportation
- Famine
- List of companies
- Chaebol
- "Miracle on the Han River"
- Currency
- 1997 financial crisis
- Communications
- Transportation
- Real estate
- Financial services
- International rankings
Geography GeneralDemographics Culture General- Pottery
- Painting
- Calligraphy
- Architecture
- Music
- Literature
- Cinema
North Korea- "Juche"
- Arirang Festival
- Sports
- Education
- Religion
- Tourism
South KoreaGeography of Asia Sovereign
states- Afghanistan
- Armenia
- Azerbaijan
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Bhutan
- Brunei
- Burma (Myanmar)
- Cambodia
- People's Republic of China
- Cyprus
- East Timor (Timor-Leste)
- Egypt
- Georgia
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Israel
- Japan
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- North Korea
- South Korea
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Lebanon
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mongolia
- Nepal
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Philippines
- Qatar
- Russia
- Saudi Arabia
- Singapore
- Sri Lanka
- Syria
- Tajikistan
- Thailand
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- United Arab Emirates
- Uzbekistan
- Vietnam
- Yemen
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- Palestine
- Republic of China (Taiwan)
- South Ossetia
Dependencies and
other territoriesCategories:- Peninsulas of Asia
- Geography of Korea
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.