- Geography of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
-
Saint-Pierre and Miquelon Capital Saint-Pierre
46°47′N 56°11′W / 46.783°N 56.183°WLargest city Saint-Pierre Area - Total 242 km2
93.4 sq miPopulation - July 2007 census 7,036 - Density 25/km2 (176th)
66/sq miSaint Pierre and Miquelon is a French overseas collectivity in the Western Hemisphere and the Northern Hemisphere. It consists of an island archipelago off the coast of Newfoundland near North America. The collectivity shares a maritime boundary with Canada.
Contents
Location
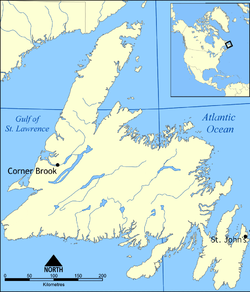
Saint Pierre and Miquelon are situated south of Newfoundland in the North Atlantic Ocean. Their distance north-south from Newfoundland is 60 kilometres (32 nmi). The islands are even closer to the long Burin Peninsula, which is situated just 25 kilometres (13 nmi) to the east. In addition, Green Island, which belongs to Newfoundland, is located about halfway between the southern part of Miquelon-Langlade and Newfoundland at 46°52′44″N 56°05′21″W / 46.87889°N 56.08917°W, only 10 kilometres (6 mi) from both Langlade and St. Pierre.[1]
Physical geography
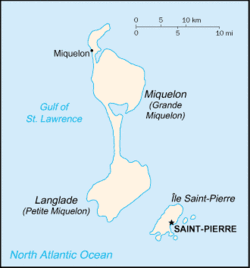
Saint Pierre and Miquelon is an archipelago of eight islands, Saint-Pierre (25 km²) and Miquelon-Langlade (216 km²) being the major ones. Collectively the area of the islands is 242 km², which is about the size of Brooklyn in New York City. The total coastline is 120 km. The territory also include the surrounding fishing areas in the North Atlantic Ocean.
Saint-Pierre
The island of Saint-Pierre is surrounded to the south-east by smaller dependencies, Petit Colombier, Île aux Marins, Île aux Pigeons and Île aux Vainqueurs, and Grand Colombier to the north. These islands have all been inhabited at one time or another.[2] The settlement of Saint Pierre on Saint Pierre Island is the largest settlement in Saint Pierre and Miquelon.
St. Pierre is separated from Miquelon-Langlade by a 6 kilometres (3.2 nmi) strait with very fierce currents. Fishermen call this section of ocean "The Mouth of Hell". The waters around these islands are very treacherous, and there have been over 600 shipwrecks along the coasts of the islands.
Miquelon-Langlade
The island(s) of Miquelon-Langlade consists of three formerly separate islands Miquelon (110 km²), Langlade (91 km²) and Le Cap. In the 18th century an isthmus of sand called La Dune was formed naturally between Miquelon and Langlade. The isthmus was reinforced by hand with sand and Quaternary deposits to what is now an 13 kilometres (8.1 mi) sand dune. Along the isthmus there are over 500 wrecked ships.[2]
What was originally the island Miquelon is now also called Grande Miquelon while Petite Miquelon refers to Langlade.[1] The settlement of Miquelon lies at the junction of the northwest corner of Miquelon Island and Le Cap.
Climate
The climate is very damp and windy and winters are harsh and long. The spring and early summer are foggy and cool. Late summer and early fall are sunny.
Environment
Seals and other wildlife can be found in the Grand Barachois lagoon of Miquelon. Every spring, whales migrating to Greenland are visible off the coasts of Miquelon and St Pierre.
Trilobite fossils have been found on Langlade. There were a number of stone pillars off the island coasts called "L'anse aux Soldats" that have been eroded away and disappeared in the 1970s.[3]
Maritime claims:
exclusive economic zone: 200 nautical miles (370.4 km; 230.2 mi)
territorial sea: 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)Climate: cold and wet, with much mist and fog; spring and autumn are windy
Terrain: mostly barren rock
Elevation extremes:
lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Morne de la Grande Montagne 240 mNatural resources: fish, deepwater ports
Land use:
arable land: 13%
permanent crops: 0%
permanent pastures: 0%
forests and woodland: 4%
other: 83% (1993 est.)Natural hazards: persistent fog throughout the year can be a maritime hazard
Environment - current issues: The fishing beds have been overfished, and may or may not recover.
Geography - note: vegetation scanty
See also
- Canada–France Maritime Boundary Case
- List of airports in Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- List of cities in Saint-Pierre and Miquelon
- List of islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- List of rivers of Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
Notes
- ^ a b Janzen, Olaf Uwe (2001). "St. Pierre et Miquelon". Memorial University of Newfoundland. http://www.heritage.nf.ca/exploration/pierre_miquelon.html. Retrieved 2007-08-29.
- ^ a b "Saint-Pierre and Miquelon". http://www.st-pierre-et-miquelon.com/english/index.php. Retrieved 2010-06-12.
- ^ "La Géologie des îles Saint-Pierre et Miquelon" (in French). Encyclopédie des îles Saint-Pierre & Miquelon. Miquelon Conseil. Archived from the original on 2006-01-11. http://web.archive.org/web/20060111105117/http://www.grandcolombier.com/2003-geographie/geologie/index.html.
External links
Sovereign states Antigua and Barbuda · Bahamas · Barbados · Belize · Canada · Costa Rica · Cuba · Dominica · Dominican Republic · El Salvador · Grenada · Guatemala · Haiti · Honduras · Jamaica · Mexico · Nicaragua · Panama · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Trinidad and Tobago · United States
Dependencies and
other territoriesAnguilla · Aruba · Bermuda · Bonaire · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Curaçao · Greenland · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Montserrat · Navassa Island · Puerto Rico · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States Virgin Islands
Climate of North America Sovereign states Antigua and Barbuda · Bahamas · Barbados · Belize · Canada · Costa Rica · Cuba · Dominica · Dominican Republic · El Salvador · Grenada · Guatemala · Haiti · Honduras · Jamaica · Mexico · Nicaragua · Panama · Saint Kitts and Nevis · Saint Lucia · Saint Vincent and the Grenadines · Trinidad and Tobago · United States
Dependencies and
other territoriesAnguilla · Aruba · Bermuda · Bonaire · British Virgin Islands · Cayman Islands · Curaçao · Greenland · Guadeloupe · Martinique · Montserrat · Puerto Rico · Saint Barthélemy · Saint Martin · Saint Pierre and Miquelon · Saba · Sint Eustatius · Sint Maarten · Turks and Caicos Islands · United States Virgin Islands
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.