- Sejm of the Republic of Poland
-
"Sejm" redirects here. For other uses, see Sejm (disambiguation).
Sejm of the Republic of Poland
Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej
Type Type Lower house Leadership Marshal of the Sejm Ewa Kopacz, PO Deputy Marshals of the Sejm Cezary Grabarczyk, PO
Eugeniusz Grzeszczak, PSL
Marek Kuchciński, PiS
Wanda Nowicka, RP
Jerzy Wenderlich, SLDStructure Members 460 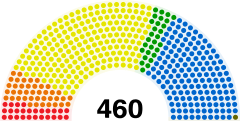
Political groups - PO (207)
- PiS (157)
- Palikot's Movement (41)
- PSL (28)
- SLD (26)
- German Minority (1)
Elections Voting system Open list proportional representation in 41 constituencies, with a 5% national election threshold (8% for coalitions) Last election 9 October 2011 Meeting place 
The Sejm Building
Śródmieście, WarsawWebsite sejm.gov.pl The Sejm [sɛjm] (
 listen) is the lower house of the Polish parliament. The Sejm is made up of 460 deputies, or Poseł in Polish (literally 'Envoy'). It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm (Marszałek Sejmu).
listen) is the lower house of the Polish parliament. The Sejm is made up of 460 deputies, or Poseł in Polish (literally 'Envoy'). It is elected by universal ballot and is presided over by a speaker called the Marshal of the Sejm (Marszałek Sejmu).In the Kingdom of Poland "Sejm" referred to the entire three-chamber parliament of Poland, comprising the lower house (Chamber of Envoys; Polish: Izba Poselska), the upper house (Senate; Polish: Senat) and the King. It was thus a three-estate parliament. Since the Second Polish Republic (1918–1939) "Sejm" has referred only to the lower house of the parliament; the upper house is called the "Senat".
Contents
- 1 History
- 2 Standing committees
- 3 Last election
- 4 See also
- 5 References
History
Sejm of the Kingdom of Poland and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
For more details on this topic, see Sejm walny. The First Sejm, which convened at Leczyca in 1182, as depicted by Jan Matejko
The First Sejm, which convened at Leczyca in 1182, as depicted by Jan Matejko
"Sejm" stems from an Old Slavic word meaning 'gathering'. Its origin were the King's Councils ('wiece'), which gained power during the time of Poland's fragmentation (1146–1295). The 1182 Sejm in Leczyca was the most notable of these councils, in that for the first time in Poland's history it established laws constraining the power of the ruler. It forbade arbitrary sequestration of supplies in the countryside and takeover of bishopric lands after the death of a bishop. However, these early Sejms were not a regular event and were formed only at the King's bequest.
After the 1493 Sejm in Piotrków, it became a regularly convening body, to which indirect elections were held every two years. The bicameral system was also established there. The Sejm now comprised two chambers: the 'Senat' (Senate) of 81 bishops and other dignitaries, and the Chamber of Envoys, made up of 54 envoys elected by small Sejms (local assemblies of landed nobility) in each of the Kingdom's provinces. At the time Poland's nobility, which accounted for around 10% of the state's population (the highest such proportion in Europe at the time) was becoming particularly influential, and with the eventual development of the 'Golden Liberty', the Sejm's powers increased dramatically.
Over time the number of envoys in the lower chamber grew in number, and power, as they pressured the king for more privileges. The Sejm eventually became even more active in supporting the goals of the privileged classes when the King ordered that the landed nobility and their estates (peasants) be drafted into military service. After the Union of Lublin in 1569, the Kingdom of Poland became, through personal union with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and thus the Sejm was supplemented with new envoys from among the Lithuanian nobility. This 'Commonwealth of Both Nations' ensured that the state of affairs surrounding the 'three estates' system' continued, with the Sejm, Senate and King each being referred to as an 'estate' and supreme deliberating body of the state. In the first few decades of the 16th century the Senate established its precedence over the Sejm, however, from the mid 1500s onwards the Sejm became a very powerful representative body of the Szlachta or 'middle nobility'. Soon the Sejm began to severely limit the king's powers. Its chambers reserved the final decisions in legislation, taxation, budget, and treasury matters (including military funding), foreign affairs, and the confirment of nobility. In 1573, in the act of the Warsaw Confederation, the nobles of the Sejm officially sanctioned, and guaranteed to each other, religious tolerance in Commonwealth territory, ensuring a refuge for those fleeing the ongoing Reformation and Counter-Reformation wars in Europe.
 In 1791, the "Great Sejm" or Four-Year Sejm of 1788–1792 adopts the May 3rd Constitution at the Royal Castle in Warsaw
In 1791, the "Great Sejm" or Four-Year Sejm of 1788–1792 adopts the May 3rd Constitution at the Royal Castle in Warsaw
Until the end of the 16th century, unanimity was not required, and the majority-voting process was the most commonly used system for voting. Later, with the rise of the Polish magnates and their increasing power, the unanimity principle was re-introduced with the institution of the nobility's right of 'liberum veto' (Latin: 'I freely forbid'). Additionally, if the envoys were unable to reach a unanimous decision within six weeks (the time limit of a single session), deliberations were declared void and all previous acts passed by that Sejm were annulled. From the mid-17th century onward, any objection to a Sejm resolution, by either an envoy or a senator, automatically caused the rejection of other, previously approved resolutions. This was because all resolutions passed by a given session of the Sejm formed a whole resolution, and, as such, was published as the annual 'constituent act' of the Sejm, e.g., Anno Domini 1667. In the 16th century, no single person or small group dared to hold up proceedings, but, from the second half of the 17th century, the liberum veto was used to virtually paralyze the Sejm, and brought the Commonwealth to the brink of collapse. The liberum veto was finally abolished with the adoption of Poland's 3rd May Constitution in 1791, a piece of legislation which was passed as 'The Government Act', and for which the Sejm required four years to propagate and adopt. The constitution's acceptance, and the possible long-term consequences it may have had, is arguably the reason for which the powers of Austria-Hungary, Russia and Prussia then decided to partition the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth; thus putting an end to over 300 years of Polish parliamentary continuity.
It is estimated that, between 1493 and 1793, sejms were held 240 times, the total debate-time sum of which was 44 years.
Poland 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
PolandForeign policySee also
Polish legislatures after the partitions
After the fall of the Duchy of Warsaw, which existed as a Napoleonic client state between 1807 and 1815, the Sejm of Congress Poland was established in the 'Kongresówka', or Congress Poland of Russia; it was composed of the king (Russian emperor), the upper house (Senate), and the lower house (Chamber of Envoys). In other
Overall, during the period from 1795 until reestablishment of Poland's sovereignty in 1918, little power was actually held by any Polish legislative body and the occupying powers of Russia, Prussia (later united Germany) and Austria-Hungary propagated legislation for their own respective formerly-Polish territories at a national level.
Sejm of Congress Poland
 Tadeusz Rejtan tries to prevent the legalisation of the first partition of Poland by preventing the members of the Sejm from entering the chamber, 1773. Jan Matejko
Tadeusz Rejtan tries to prevent the legalisation of the first partition of Poland by preventing the members of the Sejm from entering the chamber, 1773. Jan Matejko
The Chamber of Envoys, despite its name, consisted not only of 77 envoys (sent by local assemblies) from the hereditary nobility, but also of 51 deputies, elected by the non-noble population. All deputies were covered by Parliamentary immunity, with each individual serving for a term of office of six years, with half of the deputies being elected every two years. Candidates for deputy had to be able to read and write, and have a certain amount of wealth. The legal voting age was 21, except for those citizens serving in the military, the personnel of which were not allowed to vote. Parliamentary sessions were initially convened every two years, and lasted for (at least) 30 days. However, after many clashes between liberal deputies and conservative government officials, sessions were later called only four times (1818, 1820, 1826, and 1830, with the last two sessions being secret).
The Sejm had the right to call for votes on civil and administrative legal issues, and, with permission from the king, it could also vote on matters related to the fiscal policy and the military. It had the right to exercise control over government officials, and to file petitions. The 64-member Senate on the other hand, was composed of 'voivodes' and 'kasztelans' (both types of provincial governors), Russian 'princes of the blood', and nine bishops. It acted as the Parliamentary Court, had the right to control 'citizens' books', and had similar legislative rights as did the Chamber of Deputies.
In Germany and Austria-Hungary
In the Free City of Cracow (1815-1846), a unicameral Assembly of Representatives was established, and in 1827-1845, a unicameral provincial Sejm existed in the Grand Duchy of Poznań; Poles were elected to and represented the majority in both od these legislatures, however, they were largely powerless institutions and exercised only very limited power. After numerous failures in securing legislative sovereignty in the early 19th century many Poles simply gave up trying to attain a degree of independence from their foreign master-states. After this, in the mid to late 19th century, only in autonomous Galicia (1861-1914) was there a unicameral, functioning National Sejm; it is recognised today as having played a major, and overwhelming positive role in the development of Polish national institutions.
In the second half of the 19th century, Poles were able to become members of the parliaments of Austria, Prussia and Russia, where they formed Polish Clubs. Deputies of Polish nationality were elected to the Prussian Landtag from 1848, and then to the German Empire's Reichstag from 1871. Polish Deputies were members of the Austrian State Council (from 1867), and from 1906 were also elected to the Russian Imperial State Duma (lower chamber) and to the State Council (upper chamber).
Sejm of the Second Polish Republic
After the First World War and re-establishment of Polish independence, the convocation of parliament – under the democratic electoral law of 1918 became an enduring symbol of the new state's wish to demonstrate and establish continuity with the 300 year Polish parliamentary traditions established before the time of the partitions. Maciej Rataj emphatically paid tribute to this with the phrase: “There is Poland there, and so is the Sejm”.
 Józef Beck, minister of foreign affairs delivers his famous 'Honour' speech in the Sejm, 5th May 1939.
Józef Beck, minister of foreign affairs delivers his famous 'Honour' speech in the Sejm, 5th May 1939.
During the interwar period of Poland's independence, the first Legislative Sejm of 1919, a Constituent Assembly, passed the Small Constitution of 1919, which introduced a parliamentary-republic system and proclaimed the principle of the Sejm’s sovereignty. This was then strengthened, in 1921, by the March Constitution, one of the most democratic European constitutions enacted after the end of World War I. The constitution established a political system which was based on Montesquieu’s doctrine of separation of powers, and which restored the bicameral Sejm consisting of a lower house (to which the name of Sejm was from then on applied exclusively) and an upper house under the name of 'Senate'. In 1919 Roza Pomerantz-Meltzer, a member of the Zionist party, became the first woman ever elected to the Sejm.[1][2]
The legal content of the March Constitution allowed for Sejm supremacy in the system of state institutions at the expense of the executive powers, thus creating a parliamentary republic out of the Polish state. An attempt to strengthen executive powers in 1926 ( through the 'August Amendment') proved too limited and largely failed in helping avoid legislative grid-lock which had ensued as a result of too-great parliamentary power in a state which had numerus diametrically-opposed political parties sitting in its legislature. In 1935, the parliamentary republic was weakened further when, by way of, Józef Piłsudski's May Coup, the president was forced to sign the April Constitution of 1935, an act through which the head of state assumed the dominant position in legislating for the state and the Senate increased its power at the expense of the Sejm.
On 2 September 1939, the Sejm held its final pre-war session, during which it declared it declared Poland's readiness to defend itself against invading German forces. On 2 November 1939, the President dissolved the Sejm and the Senate, which were then, according to plan, to resume their activity within two months after the end of the Second World War; this, however, never happened. During wartime the National Council (1939-1945) was established to represent the legislature as part of the Polish Government in Exile. Whilst meantime, in Nazi-occupied Poland, the Council of National Unity was set up; this body functioned from 1944 to 1945 as the parliament of the Polish Underground State. With the cessation of hostilities in 1945, and subsequent rise to power of the Communist-baked Provisional Government of National Unity, the Second Polish Republic legally ceased to exist.
Sejm of the People's Republic of Poland
The Sejm in the People's Republic of Poland had 460 deputies throughout most of its history. At first, this number was declared to represent one deputy per 60,000 citizens (425 were elected in 1952), but, in 1960, as the population grew, the declaration was changed: The constitution then stated that the deputies were representative of the people and could be recalled by the people — but this article was never used, and, instead of the "five-point electoral law", a non-proportional, "four-point" version was used. Legislation was passed with majority voting.
The Sejm voted on the budget as well as on the periodic "national plans" that were a fixture of communist economies. The Sejm deliberated in sessions that were ordered to convene by the State Council.
The Sejm also chose a Prezydium ("presiding body") from among its members; the marshall of which was always a member of the United People's Party. In its preliminary session, the Sejm also nominated the Prime Minister, the Council of Ministers of Poland, and members of the State Council. It also chose many other government officials, including the head of The Supreme Chamber of Control and members of the State Tribunal and the Constitutional Tribunal, as well as the Ombudsman (the last three bodies of which were created in the 1980s).
The Senate of Poland was abolished by the Polish people's referendum, in 1946, after which the Sejm became the sole legislative body in Poland.
Sejm of the Republic of Poland
 The Sejm building in Warsaw
The Sejm building in Warsaw
After the fall of communism in 1989, the Senate was reinstated as the upper house of a bicameral national assembly, while the Sejm became the lower house. The Sejm is now composed of 460 deputies elected by proportional representation every four years.
Between 7 and 19 deputies are elected from each constituency using the d'Hondt method (with one exception, in 2001, when the Sainte-Laguë method was used) — their number being proportional to their constituency's population. Additionally, a threshold is used, so that candidates are chosen only from parties that gained at least 5% of the nationwide vote (candidates from ethnic-minority parties are exempt from this threshold).
Standing committees
- Administration and Internal Affairs Committee
- Agriculture and Rural Development Committee
- Committee on Liaison with Poles Abroad
- Constitutional Accountability Committee
- Culture and Media Committee
- Deputies' Ethics Committee
- Economic Committee
- Education, Science and Youth Committee
- Enterprise Development Committee
- Environment Protection, Natural Resources and Forestry Committee
- European Union Affairs Committee
- Family and Women Rights Committee
- Foreign Affairs Committee
- Health Committee
- Infrastructure Committee
- Justice and Human Rights Committee
- Legislative Committee
- Local Self-Government and Regional Policy Committee
- National and Ethnic Minorities Committee
- National Defence Committee
- Physical Education and Sport Committee
- Public Finances Committee
- Rules and Deputies' Affairs Committee
- Social Policy Committee
- Special Services Committee
- State Control Committee
- State Treasury Committee
- Work Committee
Last election
Summary of the 09 October 2011 Polish National Assembly election results Parties Sejm Senate Votes % Seats +/– MPs %/votes % Seats +/– Civic Platform (Platforma Obywatelska, PO) 5,629,773 39,18 207 –2 –2.33 63 +3 Law and Justice (Prawo i Sprawiedliwość, PiS) 4,295,016 29.89 157 –9 –2.22 31 –8 Palikot's Movement (Ruch Palikota, RP) 1,439,490 10.02 40 +40 — — Polish People's Party (Polskie Stronnictwo Ludowe, PSL) 1,201,628 8.36 28 –3 –0.55 2 +2 Democratic Left Alliance (Sojusz Lewicy Demokratyczne, SLD) 1,184,303 8.24 27 –26 –4.91 — — Poland Comes First (Polska jest Najważniejsza, PJN) 315,393 2.19 — —† — —† Congress of the New Right (Kongres Nowej Prawicy, KNP) 151,837 1.06 — – — – Polish Labour Party (Polska Partia Pracy, PPP) 79,147 0.55 — — — — Right of the Republic–Real Politics Union (Prawica) 35,169 0.24 — — –0.44 — — German Minority (Mniejszość Niemiecka, MN) 28,014 0.20 1 — –0.03 — — Our Home Poland (Nasz Dom Polska)[1] 9,733 0.05 — — –1.48 — — Independents (Niezależni) N/A N/A N/A N/A 4 +3 Total 14,369,503 460 100 - Registered voters: 30,762,931
- Votes counted: 15,050,027 (48,92%)
- Invalid votes: 680,524
- Valid votes: 14,369,503 (95,48%)
†PjN did not exist at the previous election, but had 15 Sejm seats and 1 Senate seat when the previous Parliament was dissolved[citation needed]See also
- Electoral districts of Poland (1935 - 1939)
Types of Sejm
- Confederated sejm (Sejm skonfederowany)
- Convocation sejm (Sejm konwokacyjny)
- Coronation sejm (Sejm koronacyjny)
- Election sejm (Sejm elekcyjny)
- National Assembly of the Republic of Poland (Zgromadzenie Narodowe)
- Sejmik
- Voivodship sejmik (Sejmik wojewódzki)
Famous Sejms
- Convocation Sejm of 1764 (Sejm konwokacyjny)
- Contract Sejm (Sejm Kontraktowy; 1989)
- Great Sejm (Sejm Wielki; 1788–1792)
- Grodno Sejm (Sejm grodzieński; 1791)
- Partition Sejm (Sejm rozbiorowy; 1773–1776)
- Repnin Sejm (Sejm Repninowski; 1767–1768)
- Silent Sejm (Sejm Niemy; 1717)
- Silesian Sejm (Sejm Śląski; 1920–1939)
References
- ^ Davies, Norman (1982). God's Playground: A History of Poland. Columbia University Press. p. 302.
- ^ Strauss, Herbert Arthur (1993). Hostages of Modernization: Studies on Modern Antisemitism, 1870-1933/39. Walter de Gruyter. p. 985.
- official website
- Description of the modern Sejm's role in the Polish political system
- CNN Election Watch
Sejms of Poland  Polish–Lithuanian
Polish–Lithuanian
Commonwealth (1569–1795)
 Republic of Poland (since 1990)General (walny) sejm · Sejmik · Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth · Sejm of the Duchy of Warsaw · Sejm of the Congress PolandCategories:
Republic of Poland (since 1990)General (walny) sejm · Sejmik · Sejm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth · Sejm of the Duchy of Warsaw · Sejm of the Congress PolandCategories:- Legislative buildings in Europe
- National lower houses
- Sejm
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Deputy Marshal of the Sejm of the Republic of Poland — (Polish: Wicemarszałek Sejmu RP) is a person elected to preside over Sejm (Polish lower chamber of parliament) sessions when the Sejm Marshal is not presiding. Throughout the course of the Third Republic, there have always been several Deputy… … Wikipedia
Vice-Marshal of the Sejm of the Republic of Poland — (Polish: Wicemarszałek Sejmu RP ) is a person elected to preside over Sejm (Polish lower chamber of parliament) sessions when the Sejm Marshal is not presiding. Throughout the course of the Third Republic, there have always been several vice… … Wikipedia
Constitution of the Republic of Poland — The Constitution of the Republic of Poland of 2 April 1997 is Poland s current constitution. It replaced the temporary amendments put into place in 1992 designed to reverse the effects of communism, establishing the nation as a democratic state… … Wikipedia
Senate of the Republic of Poland — The Senate ( Senat ) is the upper house of the Polish parliament. It consists of 100 senators elected by universal ballot and is headed by the Marshal of the Senate ( Marszałek Senatu ).HistoryThe Senate can be traced back to a council of royal… … Wikipedia
Ministries of the Republic of Poland — Poland This article is part of the series: Politics and government of Poland … Wikipedia
Prime Minister of the Republic of Poland — Infobox Political post post = Prime Minister body = the Republic of Poland insignia = Herb Polski.svg insigniasize = 100px insigniacaption = Coat of arms incumbent = Donald Tusk incumbentsince = November 16, 2007 style = residence = appointer =… … Wikipedia
Constitutional Tribunal of the Republic of Poland — Trybunał Konstytucyjny Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej Constitutional Tribunal of the Polish Rebulic Established 1990 Jurisdiction … Wikipedia
President of the Republic of Poland — Infobox Political post post = President body = the Republic of Poland insignia = Proporzec Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej.svg insigniasize = 100px insigniacaption = Presidential Jack termlength = Five years, renewable once incumbent = Lech… … Wikipedia
Supreme Chamber of Control of the Republic of Poland — Poland This article is part of the series: Politics and government of Poland … Wikipedia
Acting President of the Republic of Poland — The Acting President of the Republic of Poland ( Pełniący Obowiązki Prezydenta Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej , shorter P.o. Prezydenta RP ) is a temporary post provided for by the Polish Constitution.The constitution states that the President is an… … Wikipedia


