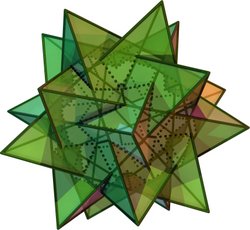
- Compound of five tetrahedra
-
Compound of five tetrahedra 
Type Regular compound Index UC5, W24 Elements
(As a compound)5 tetrahedra:
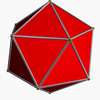
F = 20, E = 30, V = 20Dual compound Self-dual Symmetry group chiral icosahedral (I) Subgroup restricting to one constituent chiral tetrahedral (T) Stellation diagram Stellation core Convex hull 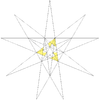
Icosahedron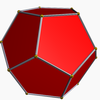
DodecahedronThis compound polyhedron is also a stellation of the regular icosahedron. It was first described by Edmund Hess in 1876.
Contents
As a compound
It can be constructed by arranging five tetrahedra in rotational icosahedral symmetry (I), as colored in the upper right model. It is one of five regular compounds which can be constructed from identical Platonic solids.
It shares the same vertex arrangement as a regular dodecahedron.
There are two enantiomorphous forms (the same figure but having opposite chirality) of this compound polyhedron. Both forms together create the reflection symmetric compound of ten tetrahedra.
- Transparent Models (Animation)
As a stellation
It can also be obtained by stellating the icosahedron, and is given as Wenninger model index 24.
As a facetting
It is a facetting of a dodecahedron, as shown at left.
Group theory
The compound of five tetrahedra is a geometric illustration of the notion of orbits and stabilizers, as follows.
The symmetry group of the compound is the (rotational) icosahedral group I of order 60, while the stabilizer of a single chosen tetrahedron is the (rotational) tetrahedral group T of order 12, and the orbit space I/T (of order 60/12 = 5) is naturally identified with the 5 tetrahedra – the coset gT corresponds to which tetrahedron g sends the chosen tetrahedron to.
An unusual dual property
This compound is unusual, in that the dual figure is the enantiomorph of the original. This property seems to have led to a widespread idea that the dual of any chiral figure has the opposite chirality. The idea is generally quite false: a chiral dual nearly always has the same chirality as its twin. For example if a polyhedron has a right hand twist, then its dual will also have a right hand twist.
In the case of the compound of five tetrahedra, if the faces are twisted to the right then the vertices are twisted to the left. When we dualise, the faces dualise to right-twisted vertices and the vertices dualise to left-twisted faces, giving the chiral twin. Figures with this property are extremely rare.
See also
References
- Wenninger, Magnus (1974). Polyhedron Models. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-09859-9.
- Coxeter, HSM, Regular Polytopes, 3rd Edn., Dover 1973.
- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald; Du Val, P.; Flather, H. T.; Petrie, J. F. (1999). The fifty-nine icosahedra (3rd ed.). Tarquin. ISBN 978-1-899618-32-3. MR676126 (1st Edn University of Toronto (1938))
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Tetrahedron 5-Compound" from MathWorld.
- Metal Sculpture of Five Tetrahedra Compound
- VRML model: [1]
- Compounds of 5 and 10 Tetrahedra by Sándor Kabai, The Wolfram Demonstrations Project.
Notable stellations of the icosahedron Regular Uniform duals Regular compounds Regular star Others Icosahedron Small triambic icosahedron Great triambic icosahedron Compound of five octahedra Compound of five tetrahedra Compound of ten tetrahedra Great icosahedron Excavated dodecahedron Final stellation 








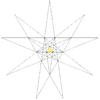
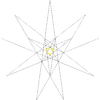
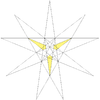
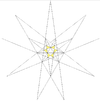


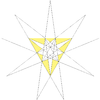
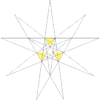

The stellation process on the icosahedron creates a number of related polyhedra and compounds with icosahedral symmetry. Categories:- Polyhedral stellation
- Polyhedral compounds
- Chiral polyhedra
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.