- Belgian Chamber of Representatives
-
Belgian Chamber of Representatives
Dutch: Kamer van Volksvertegenwoordigers
French: Chambre des Représentants
German: Abgeordnetenkammer53nd legislature, ordinary session 2010-2011 Type Type Lower house Leadership President André Flahaut, Parti Socialiste
since July 20, 2010First
Vice-PresidentBen Weyts, N-VA
since July 20, 2010Second
Vice-PresidentCorinne De Permentier, MR
since July 20, 2010Vice-President Sonja Becq, CD&V
since July 20, 2010Vice-President Siegfried Bracke, N-VA
since July 20, 2010Vice-President André Frédéric, PS
since July 20, 2010Structure Members 150 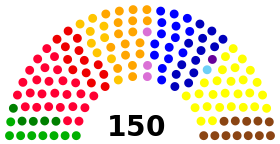
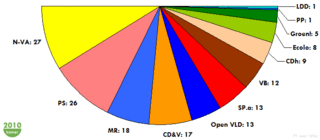
Political groups New Flemish Alliance (27)
Parti Socialiate (27)
Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams (17)
Mouvement Réformateur (15)
Socialistische Partij Anders (13)
Ecolo/Groen! (13)
Open VLD (13)
Vlaams Belang (12)
Centre démocrate humaniste (9)Elections Voting system Open list proportional representation within eleven constituencies, with 5% constituency electoral thresholds (except BHV) Last election 13 June 2010 Meeting place 
Palace of the Nation, Brussels Website dekamer.be
lachambre.beBelgium 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
BelgiumFederal JudiciarySubdivisionsRelated subjects
The Belgian Chamber of Representatives (Dutch:
 Kamer van Volksvertegenwoordigers (help·info), French: la Chambre des Représentants, German: Abgeordnetenkammer) is one of the two chambers in the bicameral Federal Parliament of Belgium, the other being the Senate. It is considered to be the "lower house" of the Federal Parliament.
Kamer van Volksvertegenwoordigers (help·info), French: la Chambre des Représentants, German: Abgeordnetenkammer) is one of the two chambers in the bicameral Federal Parliament of Belgium, the other being the Senate. It is considered to be the "lower house" of the Federal Parliament.Contents
Members and elections
Article 62 of the Belgian Constitution fixes the number of seats in the Chamber of Representatives at 150. There are 11 electoral districts, which correspond with the Provinces, except in Flemish Brabant, which is divided into two electoral districts: Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde and Leuven. The number of seats for each electoral district is proportional to its population. All electoral districts have an electoral threshold of 5%, except for the electoral districts of Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde, Leuven and Walloon Brabant. The Court of Arbitration annulled the electoral threshold in those constituencies after a complaint by theChristian Democratic and Flemish, New Flemish Alliance and Flemish Interest parties.[1]
There are 10 monolingual (5 Dutch and 5 French-speaking) electoral districts. Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde is the only bilingual electoral district as it encompasses both the 19 bilingual municipalities from the Brussels-Capital Region and the 35 Dutch-speaking municipalities of Halle-Vilvoorde in Flemish Brabant, including 7 municipalities with linguistic facilities for French-speaking inhabitants.
The seats are divided among the political parties]] using the D'Hondt method of proportional representation, which slightly favours large parties and coalitions.
The Representatives are divided into two so-called "language groups". Of the total of 150 Representatives, 88 are part of the Dutch language group, which consists of the Representatives from the Dutch language area, and 62 are part of the French language group, which consists of the Representatives from the French language area and the German language area. For the Representatives from Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde the language in which they take their oath as a Representative determines which language group they belong to. Following the 2007 federal election, the Chamber has a German-speaking member for the first time since 1999, Kattrin Jadin.[2]
Nevertheless, because of the Belgian Constitution, both linguistic communities are granted equal powers in the Parliament. Although in general bills can be passed without a majority in both linguistic groups, bills relating to specific issues (so called 'community laws') can not and need the consent of both language groups.[3]
The following table shows current distribution of seats between the language groups and the electoral districts. It is probably going to change, with Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde and Leuven being rearranged to Brussels and Flemish Brabant. This change is still heavily contested in Wallonia, but is obliged by Arbitration Court, since the present situation was deemed illegal in 2002 as unconstitutional.
 The Palace of the Nation in Brussels, home to both Chambers of the Federal Parliament of Belgium
The Palace of the Nation in Brussels, home to both Chambers of the Federal Parliament of Belgium
Dutch language group French language group Electoral district Seats Electoral district Seats Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde 9 Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde 13 Antwerp 24 Hainaut 19 East Flanders 20 Liège 15 Leuven 7 Luxembourg 4 Limburg 12 Namur 6 West Flanders 16 Walloon Brabant 5 Total 88 Total 62 Qualifications
Article 64 of the Belgian Constitution sets forth four qualifications for representatives: each representative must be at least 21 years old, possess the Belgian nationality, have the full enjoyment of civil and political rights, and be resident in Belgium. A representative can only enter into office after having taken the oath of office, in either of the three official languages in Belgium: Dutch, French or German. He or she can also choose to take the oath in more than one language. The oath of office is as follows: "I swear to observe the Constitution". (Dutch: Ik zweer de Grondwet na te leven, French: Je jure d'observer la Constitution, German: Ich schwöre, die Verfassung zu befolgen)
Certain offices are incompatible with the office of representative.[4] Members of a regional or community parliament who take the oath of office as a representative automatically cease to sit in the regional or community parliament, in accordance with the Belgian Electoral Code. The same applies the other way around as well, a representative who takes the oath of office in a regional or community parliament automatically ceases to be a representative. A member of the Chamber of Representatives may not also be a member of the Senate at the same time and senators must give up their seats in the Senate in order to join the Chamber of Representatives.
Another important incompatibility is based on the separation of powers. A representative who is appointed as a minister ceases to sit in the Chamber of Representatives and is replaced for as long as he or she is a minister, but if that individual resigns as a minister, he or she can return to the Chamber, in accordance with Article 50 of the Belgian Constitution. A representative cannot be a civil servant or a member of the judiciary at the same time, however, a civil servant who is elected to the Chamber is entitled to political leave and doesn't have to resign as a civil servant. It is also not possible to be a member of the Federal Parliament and a Member of the European Parliament at the same time.
The Chamber of Representatives does not systematically check whether any of these (or other) incompatibilities apply to its members, however, newly-elected members are informed of the most important incompatibilities at the start of their mandate and it is up to them to verify whether they are in compliance with the regulations regarding incompatibilities and, if not, to determine which office they will abandon.
Officers
The Chamber of Representatives elects a presiding officer, known as the President, at the beginning of each parliamentary term, which starts on the second Tuesday of October each year. The President is assisted by up to five Vice-Presidents, two of which are known respectively as the First Vice-President and the Second Vice-President, who are also elected at the beginning of each parliamentary term. The President is customarily a member of one of the parties forming the government coalition, only thrice in the history of the Chamber has the President been a member of the opposition. The First Vice-President is usually a member of the other language group than that of the President. The current President of the Belgian Chamber of Representatives is André Flahaut of Parti Socialiste.
The President presides over the plenary assembly of the Chamber of Representatives, guides and controls debates in the assembly, and is responsible for ensuring the democratic functioning of the Chamber, for the maintenance of order and security in the assembly and for enforcing the Rules of the Chamber of Representatives. To this end, he or she is given considerable powers. He or she also represents the Chamber at both the national (to the other institutions) and the international level. The President also assesses the admissibility of bills and proposals.
The President of the Chamber or Representatives, together with the President of the Belgian Senate, ranks immediately behind the King in the order of precedence. The elder of the two takes the second place in the order of precedence. The Presidents of the Chamber of Representatives and the Senate rank above the Prime Minister.
The Bureau of the Chamber of Representatives is composed of the President, the Vice-Presidents, the Secretaries and the floor leaders of the fractions with at least 5 members. The fractions that have at least 12 members and have no President, Vice-President or Secretary sitting on the Bureau can appoint an additional member. The Bureau is elected for the duration of one parliamentary term, but in practice the composition of the Bureau remains the same for the entire duration of the legislature, which is 4 years unless the Federal Parliament is dissolved early. The Bureau is responsible for the management of the Chamber of Representatives. In addition, the Bureau also appoints and dismisses the staff of the Chamber of Representatives. The Bureau usually meets once every three months.
There is also a Conference of Presidents, which is one of the most important bodies of the Chamber of Representatives. It consists of the President and the Vice-Presidents of the Chamber, former Presidents of the Chamber who are still members of the Chamber and the floor leader and a member of each fraction. A member of the Federal Government responsible for the relations with the Chamber attends the meetings of the Conference as well. The Conference meets weekly to discuss the day-to-day business and the work of the Chamber.
The Chamber of the Representatives has, just like the Senate, a College of Quaestors, which consists of five Representatives who are elected by the plenary assembly for a duration of two years. The Quaestors are in charge of the housekeeping of the Chamber of Representatives, they are also responsible for matters such as human resources and computers. The Colleges of Quaestors of the Senate and the Chamber of Representatives meet regularly to settle common problems concerning the library, buildings, security, catering, etc.
Procedure
Like the Senate, the Chamber of Representatives meets in the Palace of the Nation in Brussels. The hemicycle of the Chamber of Representatives is decorated in green. In contrast, the hemicycle of the Senate is decorated in red. These colours were inspired on the colours used by the House of Commons and the House of Lords of the Parliament of the United Kingdom.[5]
The Belgian Constitution provides that the Federal Parliament meets by right on the second Tuesday of October every year for a parliamentary session of at least 40 days. This means that the parliamentary session is opened automatically without being convened by the King. The Constitution also provides that the Senate cannot meet when the Chamber of Representatives is not in session. Although the Constitution provides that the Federal Parliament must remain in session for at least 40 days, in practice it remains in session throughout the year. In principle, an ordinary session lasts from the second Tuesday of October until the day before the second Tuesday of October the following year, however, the Federal Parliament goes into recess three times a year, for the Christmas holidays, the Easter holidays and for the summer holidays from 20 July until the end of September. In the event that the Federal Parliament is dissolved and new elections are held before the end of the parliamentary term, the newly-elected Chamber meets in extraordinary session until the start of the next ordinary session.[6]
The committees of the Chamber of Representatives usually meet on Tuesday and Wednesday. On Wednesday, the Conference of President meets to set the agenda for the plenary session. On Thursday morning the fractions meet. The Chamber of Representatives usually meets for a plenary session on Thursday afternoon and every two weeks it meets in plenary session on Wednesday as well. Every Thursday afternoon between 2:00 p.m. and 3:00 p.m. is question time. There are usually no parliamentary activities on Friday.[6]
Article 53 of the Belgian Constitution provides that at least a majority of its members must be present in order for the Chamber to make decisions. It is noteworthy that this does not apply to all business of the Chamber, such as debates or questions to members of the Federal Government, but that a quorum must only be present in order to make decisions. If not enough members are present, the decision is invalid. In order to make a decision, at least 50% plus 1 of the members present and voting must vote in the affirmative. If a vote is tied, the President does not have a casting vote and the proposal is rejected. The procedure outlined in Article 53 of the Constitution applies to all most decisions, however, the Constitution establishes two exceptions: in order to amend the Constitution, a two-thirds majority of the members must be present and at least two-thirds of the votes cast must be in the affirmative, and in order to adopt a so-called special law, a qualified majority of 50% plus 1 of each language group must be present and at least 50% plus 1 must be present and at least 50% plus 1 of the votes cast in each language group, as well as two-thirds of the votes cast of the two language groups together, must be in the affirmative.[7]
The Chamber may vote in three manners. Firstly, the Chamber may vote by roll call. In the past, the names of the members were read in alphabetical order and each member had to announce his or her vote when his name was called, however, since 1995, voting by roll call has been done electronically. Voting by roll call is the most frequently used method and is compulsory in three cases: at the end of debates on a government statement, the vote on bills as a whole and when requested by at least 8 members. Secondly, the Chamber may vote by sitting and standing. This method is used in less important cases requiring quick treatment and in which there is a clear majority. In the event of doubt, the vote is taken again or done electronically. Voting by sitting and standing is anonymous and is used for votes on amendments and individual articles of a bill. Finally, the Chamber may conduct a secret vote. In principle, the votes are public and votes on legislation are never secret, only the appointments and nominations the Chamber has to make take place by secret vote.[7]
Committees
The Chamber of Representatives uses committees for a variety of purposes. The Chamber has several standing committees, each of which has responsibility for a particular area of government (for example justice or social affairs). These standing committees examine and consider bills and legislative proposals, and may for this purpose hold hearings. A standing committee comprises 17 Representatives, members are appointed using proportional representation. The chairpersons of the standing committees are also divided among the parties in accordance with the same principle of proportional representation. As a result, some standing committees are chaired by members of the opposition.
List of standing committees
- Defence
- Social Affairs
- Justice
- Foreign Relations
- Revision of the Constitution and Reform of the Institutions
- Problems regarding Commercial and Economic Law
- Interior, General Affairs and the Civil Service
- Economy, Science Policy, Education, National Scientific and Cultural Institutions, Middle Classes and Agriculture
- Finances and Budget
- Infrastructure, Communications and Public Enterprises
- Public Health, Environment and Social Renewal
Legislative functions
Since the elections of 21 May 1995, there has been a breakdown of powers[8] between the Chamber of Representatives and the Senate, which resulted in the Senate having fewer competences than the Chamber of Representatives. Prior to that, the Chamber of Representatives and the Senate did the same legislative work on an equal footing. This means that the both chambers had to pass exactly the same version of a bill.
In certain matters both the Chamber and the Senate still have equal power, which means that both Chambers must pass exactly the same version of the bill. These include constitutional revisions, laws requiring a qualified majority (the so-called "community laws"), laws on the basic structure of the Belgian State, laws approving agreements of cooperation between the Federal State, the Communities and the Regions, laws on the approval of international treaties, and laws on the organisation of the judiciary, the Council of State, and the Constitutional Court of Belgium. However, bills concerning international treaties are introduced in the Senate first before moving on to the Chamber.
For almost all other legislation, the Chamber of Representatives takes precedence over the Senate. However, the Senate may still intervene as a chamber of consideration and reflection as it has the opportunity to, within specific time limits, examine the texts adopted by the Chamber and, if there is a reason to do so, make amendments. The Chamber can subsequently adopt or reject the amendments proposed by the Senate or make new proposals. Whatever the case, the Chamber has the final word on all "ordinary legislation". The Senate may also submit a bill it has adopted to the Chamber which can approve, reject or amend it, in this case the Chamber also has the final word.
There are also certain matters for which the Chamber of Representatives is exclusively responsible. These matters include the granting of naturalisations, passing legislation with regard to the civil and criminal liability of the ministers of the Federal Government, the government budget and the State's accounts, appointing parliamentary ombudsmen and examine their activities, and determining military quotas.
Relationship with the Government
The members of the Federal Government are answerable to the Chamber of Representatives, in accordance with Article 101 of the Belgian Constitution. Upon taking office, the Federal Government must have the confidence of the majority of the Representatives. The Chamber of Representatives is also exclusively responsible for the political control of the Federal Government. The confidence in the Federal Government may be revoked by the Chamber at any time by the adoption of a motion of no confidence or by the rejection of a motion of confidence.[9]
Latest election
Main article: Belgian general election, 2010Summary of the 13 June 2010 Belgian Chamber of Representatives election results Parties Chamber Votes +/− % +/− Seats +/− New Flemish Alliance (Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie) 1,135,617 * 17.40% * 27 * Socialist Party (Parti Socialiste) 894,543  169,756
169,75613.70%  2.85%
2.85%26  6
6Christian Democratic and Flemish (Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams) 707,986 * 10.85% * 17 * Reformist Movement (Mouvement Réformateur) 605,617  229,456
229,4569.28%  3.23%
3.23%18  5
5Socialist Party – Differently (Socialistische Partij – Anders) 602,867  81,523
81,5239.24%  1.02%
1.02%13  1
1Open Flemish Liberals and Democrats (Vlaamse Liberalen en Democraten) 563,873  225,572
225,5728.64%  3.19%
3.19%13  5
5Flemish Interest (Vlaams Belang) 506,697  293,147
293,1477.76%  4.23%
4.23%12  5
5Humanist Democratic Centre (Centre Démocrate Humaniste) 360,441  43,636
43,6365.52%  0.53%
0.53%9  1
1Ecolo 313,047  27,331
27,3314.80%  0.30%
0.30%8  0
0Green! (Groen!) 285,989  20,161
20,1614.38%  0.40%
0.40%5  1
1List Dedecker (Lijst Dedecker) 150,577  118,071
118,0712.31%  1.72%
1.72%1  4
4Popular Party (Parti Populaire) 84,005 — 1.29% — 1 — Others 316,108 — 4.84% — — — Total 6,527,367 100% 150 Source: Federal Portal − Chamber Elections 2010.
Notes: * Christian Democratic and Flemish and the New Flemish Alliance contested the 2007 elections together, receiving 18.51% of the votes and 30 seats.
Current composition
See also: List of Belgian RepresentativesCurrent party standings, as of July 3rd, 2010:
Affiliation Members Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie 27 Parti Socialiste 26 Mouvement Réformateur 18 Christen-Democratisch en Vlaams 17 Open Vlaamse Liberalen en Democraten 13 Socialistische Partij Anders 13 Vlaams Belang 12 Centre Démocrate Humaniste 9 Ecolo 8 Groen! 5 Lijst Dedecker 1 Parti Populaire 1 Total 150 See also
- List of Presidents of the Belgian Chamber of Representatives
- Belgian Federal Parliament
- Belgian Senate
- Politics of Belgium
References
- ^ "Factsheet on electoral legislation" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives. 2007-05-01. Archived from the original on 2007-12-03. http://web.archive.org/web/20071203124705/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/09_01E.pdf. Retrieved 2007-11-14.
- ^ "Les 23 députés MR ont prêté serment à la Chambre – Prestation de Serment aussi au Sénat pour les 6 sénateurs MR" (in French). Mouvement Réformateur. 2007-06-29. http://www.mr.be/News/news.php?id=2958. Retrieved 2007-07-04.
- ^ "Fact Sheet on the composition of the Chamber" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives. Archived from the original on 2005-11-12. http://web.archive.org/web/20051112001201/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/10E.pdf. Retrieved 2006-03-13.
- ^ "Incompatibilities and disqualifications". The Belgian Senate. http://www.senate.be/english/federal_parliament_en.html#T.4.1. Retrieved 2007-06-29.
- ^ "Visitor's Guide to the Belgian Federal Parliament" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives and Senate. Archived from the original on 2007-12-03. http://web.archive.org/web/20071203124701/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/13E.pdf. Retrieved 2007-09-16.
- ^ a b "Factsheet on the workings of the Chamber of Representatives" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives. Archived from the original on 2007-12-03. http://web.archive.org/web/20071203124701/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/13E.pdf. Retrieved 2007-09-16.
- ^ a b "Factsheet on the workings of the Chamber of Representatives: Votes" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives. Archived from the original on 2007-12-03. http://web.archive.org/web/20071203124713/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/13_02E.pdf. Retrieved 2007-09-16.
- ^ "Factsheet on the Senate" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives. Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. http://web.archive.org/web/20070930043252/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/15E.pdf. Retrieved 2007-09-01.
- ^ "Factsheet on the Chamber of Representatives" (PDF). The Belgian Chamber of Representatives. Archived from the original on 2007-09-30. http://web.archive.org/web/20070930042904/http://www.dekamer.be/kvvcr/pdf_sections/pri/fiche/11E.pdf. Retrieved 2007-09-01.
External links
Governments of Belgium Federal Belgium Government (Prime Ministers) — Parliament consisting of the Chamber of Representatives (representatives) and Senate (senators)
Brussels-Capital Region Brussels Government (Minister-President) — Brussels Parliament (members)Flemish Region and Community
(merged institutions)Walloon Region French Community German-speaking Community See also: Politics of Belgium · Political parties in Belgium · Elections in BelgiumCategories:- National lower houses
- Belgian Chamber of Representatives
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.