- U.S. Route 50 in Maryland
-
This article is about the section of U.S. Route 50 in Maryland. For the entire length of the highway, see U.S. Route 50.
U.S. Route 50 George Washington Highway, John Hanson Highway, Blue Star Memorial Highway, Ocean Gateway, Sunburst Highway, Salisbury Bypass 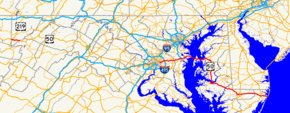
U.S. Route 50 highlighted in redRoute information Maintained by MDSHA Length: 150.06 mi[1][2][3][4][5][6][7][8] (241.50 km) Existed: 1926 – present Western section Length: 9.17 mi[1] (14.76 km) West end:  US 50 at West Virginia state line near Red House
US 50 at West Virginia state line near Red HouseMajor
junctions: US 219 in Red House
US 219 in Red HouseEast end:  US 50 at West Virginia state line in Gorman
US 50 at West Virginia state line in GormanEastern section Length: 140.49 mi[2][3][4][5][6][7][8] (226.10 km) West end:  US 50 at Washington D.C. border
US 50 at Washington D.C. borderMajor
junctions: MD 295 near Washington D.C.
MD 295 near Washington D.C.

 I-95 / I-495 near New Carrollton
I-95 / I-495 near New Carrollton

 MD 3 / US 301 in Bowie
MD 3 / US 301 in Bowie
 I-97 in Annapolis
I-97 in Annapolis
 MD 404 near Wye Mills
MD 404 near Wye Mills
 US 13 in Salisbury
US 13 in Salisbury
 MD 90 near Berlin
MD 90 near Berlin US 113 in Berlin
US 113 in BerlinEast end:  MD 528 in Ocean City (start of westbound)
MD 528 in Ocean City (start of westbound) MD 378 in Ocean City (end of eastbound)
MD 378 in Ocean City (end of eastbound)Highway system United States Numbered Highways
List • Bannered • Divided • ReplacedMaryland highway system
Interstate • US • State • Minor • Former • Turnpikes←  MD 49
MD 49MD 51  →
→U.S. Route 50 (US 50) is a major east–west route of the U.S. Highway system, stretching just over 3,000 miles (4,800 km) from Ocean City, Maryland on the Atlantic Ocean to West Sacramento, California. In the U.S. state of Maryland, US 50 exists in two sections. The longer of these serves as a major route connecting Washington, D.C. with Ocean City; the latter is the eastern terminus of the highway. The other section passes through the southern end of Garrett County for less than 10 miles (16 km) as part of the Northwestern Turnpike, entering West Virginia at both ends. One notable section of US 50 is the dual-span Chesapeake Bay Bridge across Chesapeake Bay, which links central Maryland with the Eastern Shore region, allowing motorists to reach the beaches of Ocean City and Delaware.
US 50 has received numerous upgrades during its existence in Maryland, including the building of the John Hanson Highway (which is also the unsigned Interstate 595), its extension onto the Eastern Shore and replacement of U.S. Route 213 due to the construction of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge, and the full dualization of the eastern segment of the route. Many of the older alignments of US 50 are still part of the Maryland and US highway systems, such as U.S. Route 50 Business in Salisbury, Maryland. US 50 continues to be upgraded on the Eastern Shore to better accommodate beach travelers and locals alike.
Contents
Route description
George Washington Highway
US 50 leaves Preston County in West Virginia and enters the state of Maryland in Garrett County. US 50 is routed along the old Northwestern Turnpike, presently named George Washington Highway after George Washington. This section of US 50 is a quiet, rural highway with little traffic, which stands in sharp contrast to the other, longer section. US 50 intersects only two numbered highways along this stretch: US 219 in Red House, and MD 560 east of there.
Near the West Virginia community of Gormania, US 50 crosses the Potomac River and exits Maryland. It then passes through West Virginia, Virginia, and the District of Columbia, before reentering Maryland.
John Hanson Highway
Main article: Interstate 595 (Maryland)US 50 exits the District as the John Hanson Highway, a freeway alignment extended from the east end of New York Avenue in Prince George's County. It instantly interchanges with the Baltimore-Washington Parkway at a hybrid interchange with a full cloverleaf and partial-Y elements. The B-W Parkway also allows access to Maryland Route 201. The freeway parallels the Orange Line of the Washington Metro as it weaves through the suburban area, interchanging with Maryland Route 202 and Maryland Route 410, then passes over the Orange Line and the New Carrollton Metro Station access road Maryland Route 950. It then meets a hybrid turbine interchange with Interstate 95 and 495, the Capital Beltway.
East of the interchange, US 50 enters the Interstate Highway System as the unsigned Interstate 595. The route is 10 lanes wide; beyond the MD 704 interchange, it narrows to eight lanes, with the innermost two being HOV lanes. Up to and slightly beyond the US 301/MD 3 interchange, the road surface is concrete; the roadway beyond there is asphalt. Within the US 301 interchange, the HOV lanes that began at the Capital Beltway come to an end, and US 301 joins US 50 and I-595, forming a three-route concurrency.
The central portion of the route runs through undeveloped forest and parkland, meeting Maryland Route 424 three miles (5 km) east of US 301. After meeting Interstate 97, the carriageways from I-97 straddle US 50 for a short distance before becoming MD 665, continuing toward downtown Annapolis as a direct freeway spur.
The route now runs through the Annapolis urban area, meeting MD 450 and MD 2. Continuing southeast, the route (which is now a four-route concurrency of US 50, US 301, I-595 and MD 2) eventually reaches the MD 70 interchange, where I-595 officially terminates.
Blue Star Memorial Highway
US 50 now becomes a Blue Star Memorial Highway, bearing this as its name past the MD 70 interchange. The route then passes over the Pearl Harbor Memorial Bridge over the Severn River and interchanges with the eastern end of MD 450. This interchanges also releases MD 2 from the concurrency, which travels northward to Baltimore. The US 50 and US 301 freeway pass through heavily wooded area, interchanging with few routes and offering rest stops along its final stretch through the Western Shore region. The freeway then interchanges with one last road, Oceanic Road, which passes over the toll plaza for the Chesapeake Bay Bridge.
The bridge's official name is the William Preston Lane, Jr. Memorial Bridge, and it connects Sandy Point on the Western Shore with Kent Island on the Eastern Shore. The bridge's asymmetrical dual spans are also a point of traffic congestion. The bridge raises US 50 and US 301 over two shipping channels, marked by the suspension and the through-truss spans of the structure. The bridge brings the two routes down on Kent Island, and quickly after, interchanges with Maryland Route 8 at a diamond interchange. After this interchange, the freeway portion on the Island continues, interchanging with many streets with sharp right-in/right-out ramps, until it meets the Kent Narrows Bridge, raising the routes over the Kent Narrows and bringing them down on the Eastern Shore's mainland.
Most of the interchanges along the final stretch of the freeway give access to Maryland Route 18, which parallels US 50 and 301 as a local route and a former alignment of the highway. After interchanging with Nesbit Road at another diamond interchange and the routes approach Queenstown, development ceases, and US 50 and US 301 separate at a half-trumpet interchange. US 301 continues straight along the carriageways, retaining the Blue Star Memorial Highway designation all the way to the Delaware state line. US 50, however, turns south using the ramps, and it picks up a new name: the Ocean Gateway.
Queen Anne's County
The Ocean Gateway name for US 50 is retained mostly for the remainder of its routing, changing only twice more for short distances. Continuing east from the US 50 and US 301 split, the highway becomes a four-lane, dual highway and instantly intersects Maryland Route 18 for the last time. It continues through open farmland, bearing southeast as it passes the northern terminus of Maryland Route 662 and Maryland Route 213, both former routings of the highway, which straddle Chesapeake College. US 50 then makes a curve, aiming almost perfectly south as it meets Maryland Route 404 atop the Queen Anne's/Talbot border.
Talbot County
US 50 continues to be signed as east/west, although it follows a north/south path. MD 662 weaves back and forth through open farmlands across this alignment through Talbot County as it approaches Easton, sometimes merging with it as well. North of Easton, Maryland Route 322 leaves US 50 to the west, which functions as a bypass of the town. US 50 passes east of the center of town, the speed limit dropping from 55MPH to 35MPH as it passes through the commercial sector. Outside of town, MD 322 meets US 50, and Maryland Route 565 runs concurrent with US 50 at the same intersection. MD 565 is another former alignment of US 50, possessing the residential development in the southern Talbot area. US 50 continues by Trappe, meeting the southern end of MD 565 before continuing to the Choptank River.
Dorchester County
US 50 then passes over the Senator Frederick C. Malkus Bridge and enters Cambridge and Dorchester County, the speed limit once again dropping to 35 miles per hour (56 km/h), as the route returns to an east-west alignment. The entire section of US 50 in the city of Cambridge is named Sunburst Highway; this name is carried until Woods Road at the corporate boundaries of Cambridge. Here, the route's name returns to The Ocean Gateway, and later it picks up a concurrency with Maryland Route 16 for a short while outside the city, which ends in East New Market. From here, US 50 travels through mostly rural countryside in Dorchester County with several loops of older alignments of US 50 crossing the highway. As it dodges around Vienna on the Nanticoke River, the route intersects Old Ocean Gateway as a direct spur into the town. This road, formerly US 50 and then formerly MD 731, utilized a drawbridge to cross the river before the Nanticoke Memorial Bridge and Vienna Bypass opened in 1991. US 50 then interchanges with Maryland Route 331 at a partial cloverleaf and rises onto the Nanticoke Memorial Bridge, passing over the Nanticoke River.
Wicomico County
Westbound US 50 where it joins US 13 and Salisbury Bypass east of Salisbury.
US 50 then enters Wicomico County, and soon after passes by Mardela Springs. As it does so, it intersects Maryland Route 313 and Maryland Route 54. The route continues through open farmland in a general southeastern alignment until it approaches Salisbury. Northwest of the city, US 50 diverges onto the Salisbury Bypass, a freeway bypass forming a 3/4 beltway around the city. At this junction is US 50 Business, which goes directly through Salisbury. The Salisbury Bypass soon after interchanges with Naylor Mill Road, which allows westbound Business US 50 traffic to enter the freeway eastbound. The Bypass then passes through the Northwood business park on an earthen viaduct within the city limits, interchanging partially with Northwood Drive to grant access. Soon after this, US 50 interchanges with US 13 and Business US 13, picking up a concurrency with mainline US 13.
The two routes circle around the city to the northeast and eventually meet the interchange with US 13 and US 50 Business at a partial cloverleaf. Here, US 50 leaves the Bypass, and bears east along a four-lane, divided alignment. It passes by the campus of Wor-Wic Community College and continues through open farmland once more, intersecting various routes as it parallels MD 346 and bypasses Parsonsburg, Pittsville, and Willards, to the Pocomoke River, where the route leaves the county.
Worcester County
Shortly after entering the county, Maryland Route 90 branches off to the north, bypassing the town of Berlin and bearing toward the northern part of Ocean City, Shortly after MD 90, MD 346 crosses US 50 and heads into downtown Berlin. US 50 passes through northern Berlin, and meets a full cloverleaf interchange with US 113 in the process. This interchange also features railroad tracks, which cross two of the ramps. The route meets the end of MD 346 and continues through the heavily developed West Ocean City, Maryland, weaving across older alignments, notably Maryland Route 707. Maryland Route 589 also intersects the route, which leads to Ocean Pines and the last interchange with MD 90. US 50 finally passes over the Harry W. Kelly Memorial Bridge and the Sinepuxent Bay, touching down in the town of Ocean City, and meeting its national eastern terminus.
 Nighttime view of the sign at the eastern terminus of US 50 in Ocean City, indicating the distance to the western terminus in Sacramento, California.
Nighttime view of the sign at the eastern terminus of US 50 in Ocean City, indicating the distance to the western terminus in Sacramento, California.
Although the route's ceremonial eastern terminus is at Maryland Route 528, Philadelphia Avenue, eastbound US 50 actually continues past MD 528 as North Division Street and ends at Maryland Route 378, Baltimore Avenue, a short distance from the Atlantic Ocean and Ocean City Boardwalk. From the westbound lanes as of June 2009, a sign can be seen displaying the distance to Sacramento, California as 3073 miles. This is an incorrect measure which is shared on California's end of US 50, as the route's length has been adjusted many times and shortened.
History
While the portion of U.S. 50 in Garrett County has remained largely unchanged, the eastern portion has changed significantly since the route was established in 1926.
Original 1926 plan
On the Western Shore, US 50 was on the alignment currently known as Maryland Route 450. It ended at Church Circle in Annapolis, near St. Anne's Church.[9] Beyond the end of US 50 was a ferry which connected the route to what was then Maryland Route 17 on the Eastern Shore, in Talbot County.
Extension to the Eastern Shore
Just before the Chesapeake Bay Bridge's completion, in 1948, the route was extended to Ocean City. This extension brought the route across the bay via an existing ferry service, and US 50 replaced much of U.S. Route 213 and portions of Maryland Route 404 on the Eastern Shore. As a result of US 50 being routed onto the Eastern Shore, US 213 north of what is now US 50 was removed from the U.S. Highway system, and became the current Maryland Route 213 by the late 1970s. Once the bridge was completed in 1952, it replaced the ferry, which had been in service since the 1930s.
The John Hanson Highway, named for John Hanson, was the first section of US 50 to be upgraded to a freeway in Maryland. It was completed soon after the Bay Bridge was built, and the older alignment was redesignated Maryland Route 450. A slight extension of MD 450 was then created to reconnect it with US 50 near the present-day intersection with Maryland Route 2.
Dualization of US 50
High volumes of beach traffic as a result of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge called for further upgrades to the route. A very straight alignment south through Talbot County was later created, the old routing becoming Maryland Route 662 and Maryland Route 322. In Salisbury, US 50 was moved from Main Street to Church Street. In Worcester County, its present-day alignment was created, though only dualized east of US 113 in Berlin. Following this, in the mid-1960s, a new four-lane section of US 50 was completed between Salisbury at then-US 13 and Berlin at US 113, its old alignment east of East Main Street becoming Maryland Route 346, and Church Street being returned to the city. The rest of US 50 on the Eastern Shore was in the process of being dualized. This included an adjacent span of the Chesapeake Bay Bridge being built in 1973, widening the thoroughfare to an asymmetrical five lanes.
In 1991, just as the final two-lane section of US 50 was falling into severe disrepair, Vienna was bypassed to the northeast, completing the dualization of US 50 in Maryland. The old road was turned over to Wicomico County on its side (then privatized to Delmarva Power and Light in 2007), and the Dorchester street through Vienna became Maryland Route 731. Also at this time, two extra lanes were added to the John Hanson Highway in both directions as the Interstate 595 section was designated. Some overhead signs on and near the route do include space for the Interstate 595 shield, but the shields were never installed in order to reduce motorist confusion.[10] The freeway portion was continued over to the Eastern Shore, from the Chesapeake Bay Bridge east to the US 50-301 split in Queenstown. The US 50/301 portion of the Blue Star Memorial Highway was upgraded to a freeway mostly during the late 1980s and early 1990s; prior to this it was only a divided highway with several local roads intersecting it. After being upgraded, many of these intersections became sharp right-in/right-out ramps.
The most recent upgrade to US 50 came in October 2002, when the Salisbury Bypass was extended to circle the north side of the city. US 50 was rerouted onto this, and the alignment within the city, already bypassed numerous times, became present-day US 50 Business.
Future
There are currently plans to upgrade US 50 in Queen Anne's County to a full limited access freeway, the freeway portion ending at an interchange with Maryland Route 404 atop the Queen Anne's/Talbot County border. This comes along with plans to fully dualize the latter highway in the state of Maryland.
Points of interest
- Severn River Bridge in Annapolis (rededicated as the Pearl Harbor Memorial Bridge in December, 2006)
- US Naval Academy (has its own exit off US 50)
- Chesapeake Bay Bridge
- Kent Island (site of the oldest English settlement in Maryland)
- Kent Narrows Bridge between Kent Island and Grasonville
- Frederick C. Malkus Bridge in Cambridge
- Nanticoke River Memorial Bridge in Vienna
- Harry W. Kelly Memorial Bridge in Ocean City
- Ocean City Boardwalk, near the eastern terminus
Junction list
Exits are numbered from west to east, in accordance with AASHTO guidelines.
County Location Mile Exit Destinations Notes West Virginia state line Garrett
9.17 miles (14.76 km)[1]Red House 2.1  US 219 (Garrett Highway) – Oakland
US 219 (Garrett Highway) – OaklandFormer MD 37 9.1  MD 560 (Gorman Road) – Mountain Lake Park
MD 560 (Gorman Road) – Mountain Lake ParkUS 50 exits and reenters Maryland via West Virginia, Virginia, and District of Columbia Prince George's
14.39-mile (23.16 km)[2]Cheverly 0.2  MD 295 north (Baltimore-Washington Parkway) – Baltimore
MD 295 north (Baltimore-Washington Parkway) – Baltimoreeastbound exit, westbound entrance;
B-W Parkway joins westbound and splits eastbound0.5 
 MD 201 south (Kenilworth Avenue) to DC 295/I-295 – Kenilworth, Washington, D.C.
MD 201 south (Kenilworth Avenue) to DC 295/I-295 – Kenilworth, Washington, D.C.0.5 
 MD 201 north (Kenilworth Avenue) to MD 459 – Greenbelt
MD 201 north (Kenilworth Avenue) to MD 459 – Greenbelt1.6  MD 459 west (Columbia Park Road) – Cheverly, Metro Station
MD 459 west (Columbia Park Road) – Cheverly, Metro Stationeastbound exit, westbound entrance Landover 2.8  MD 202 (Landover Road) – Upper Marlboro, Bladensburg
MD 202 (Landover Road) – Upper Marlboro, BladensburgLandover Hills 4.1 5  MD 410 (East–West Highway) – Glenarden
MD 410 (East–West Highway) – GlenardenNew Carrollton 4.5  US 50PA (Ardwick-Ardmore Road) – New Carrollton Station
US 50PA (Ardwick-Ardmore Road) – New Carrollton Stationwestbound exit;
road is unsigned spur of US 505.0 7 
 I-95 (Capital Beltway) / I-495 – Baltimore, Richmond
I-95 (Capital Beltway) / I-495 – Baltimore, RichmondSigned as exits 7A (south) and 7B (north)
Western terminus of unsigned I-5956.1 8  MD 704 (Martin Luther King Jr. Highway) – Glenarden
MD 704 (Martin Luther King Jr. Highway) – GlenardenBowie 11.7 11  MD 197 (Collington Road) – Bowie
MD 197 (Collington Road) – Bowie13.1 13 
 US 301 south / MD 3 north (Robert Crain Highway) – Upper Marlboro, Crofton
US 301 south / MD 3 north (Robert Crain Highway) – Upper Marlboro, CroftonSigned as exits 13A (US 301 south), 13B (MD 3 north) and 13C (Belair Drive)
West end of US 301 overlapAnne Arundel
19.88 miles (31.99 km)[3]16.5 16  MD 424 (Davidsonville Road) – Davidsonville, Crofton
MD 424 (Davidsonville Road) – Davidsonville, CroftonAnnapolis 21.2 21 
 I-97 north / MD 665 east – Baltimore, Downtown Annapolis
I-97 north / MD 665 east – Baltimore, Downtown Annapolis23.0 22 
 MD 450 (Defense Highway) to MD 178 – Parole, Crownsville
MD 450 (Defense Highway) to MD 178 – Parole, Crownsville23.5 23  MD 2 south (Solomons Island Road) – Edgewater
MD 2 south (Solomons Island Road) – EdgewaterWest end of MD 2 overlap 24.8 24A-B  MD 70 south (Rowe Boulevard-Bestgate Road) – Annapolis
MD 70 south (Rowe Boulevard-Bestgate Road) – AnnapolisSigned as exits 24A (MD 70 south) and 24B (Bestgate Road) westbound
Eastern terminus of unsigned I-595Pearl Harbor Memorial Bridge over Severn River Arnold 26.7 27 
 MD 2 north / MD 450 south (Governor Ritchie Highway) – Baltimore, Severna Park, Naval Academy
MD 2 north / MD 450 south (Governor Ritchie Highway) – Baltimore, Severna Park, Naval AcademySigned as exits 27A (MD 450 south) and 27B (MD 2 north) westbound;
East end of MD 2 overlap MD 648 north (Baltimore-Annapolis Boulevard)
MD 648 north (Baltimore-Annapolis Boulevard)direct turnoff from westbound carriageway 27.6 28 Bay Dale Drive – Bay Hills Golf Club 29.2 29 

 MD 179 / MD 908 / MD 931 (St. Margarets Road, Busch's Frontage Road, Cape St. Claire Road, East College Parkway)
MD 179 / MD 908 / MD 931 (St. Margarets Road, Busch's Frontage Road, Cape St. Claire Road, East College Parkway)Signed as exits 29A (MD 179) and 29B (Cape St. Claire Road) eastbound Sandy Point 30.6 31  MD 908 east (Whitehall Road)
MD 908 east (Whitehall Road)direct turnoff from eastbound carriageway 31.4 32  MD 908 north (Oceanic Drive) – Sandy Point State Park
MD 908 north (Oceanic Drive) – Sandy Point State ParkChesapeake Bay Bridge over Chesapeake Bay Queen Anne's
18.78 miles (30.22 km)[4]Stevensville 37.2 37 
 MD 8 (Romancoke Road) to MD 18 – Stevensville, Romancoke
MD 8 (Romancoke Road) to MD 18 – Stevensville, Romancoke37.9 38A  MD 835A north (Thompson Creek Road, Duke Street)
MD 835A north (Thompson Creek Road, Duke Street)Thomspon Creek Rd: roundabout on ramp, eastbound exit and entrance;
Duke Street: westbound entrance and exit (right-in/right-out)38.9 38B Shopping Center Road to Main Street westbound entrance and exit 39.0 39A  MD 18 (Castle Marina Road, Cox Neck Road)
MD 18 (Castle Marina Road, Cox Neck Road)Castle Marina Rd: westbound entrance and exit;
Cox Neck Rd: eastbound exit and entranceChester 39.5 39B 
 MD 552 (Dominion Road, Chester Station Lane) to MD 18
MD 552 (Dominion Road, Chester Station Lane) to MD 18MD 552: eastbound exit and entrance;
Chester Station Ln: westbound entrance and exit40.1 40A Piney Creek Road right-in/right-out entrance/exit 40.5 40B Dundee Avenue eastbound exit and entrance Kent Narrows 40.8 41  MD 18 (Main Street, Piney Narrows Road) – Kent Narrows West
MD 18 (Main Street, Piney Narrows Road) – Kent Narrows WestMD 18: eastbound exit and entrance;
Piney Narrows Rd: westbound entrance and exitKent Narrows Bridge over Kent Narrows 41.9 42 
 MD 18 (Main Street) / MD 835 west (Kent Narrows Road) – Kent Narrows East
MD 18 (Main Street) / MD 835 west (Kent Narrows Road) – Kent Narrows EastMD 18: eastbound entrance and exit;
MD 835: westbound entrance and exitGrasonville 42.8 43A 
 MD 18 (Main Street) / MD 835 (Long Point Road, Jackson Creek Road) – Grasonville
MD 18 (Main Street) / MD 835 (Long Point Road, Jackson Creek Road) – GrasonvilleMD 18: eastbound entrance and exit;
MD 835: westbound entrance and exit43.4 43B 
 To MD 18 to MD 835 (Chester River Beach Road)
To MD 18 to MD 835 (Chester River Beach Road)westbound entrance; eastbound entrance and exit 43.8 44A  To MD 18 (Station Lane, VFW Avenue)
To MD 18 (Station Lane, VFW Avenue)Station Ln: eastbound exit and entrance;
VFW Ave: westbound entrance and exit44.2 44B 
 MD 835 (Winchester Creek Road, Evans Avenue) to MD 18
MD 835 (Winchester Creek Road, Evans Avenue) to MD 18MD 835: westbound entrance and exit;
Evans Ave: eastbound exit and entrance44.5 45A 
 To MD 18 to MD 835 (Homeport Drive, Hess Road)
To MD 18 to MD 835 (Homeport Drive, Hess Road)Homeport Dr: westbound entrance and exit; Hess Rd: eastbound exit and entrance 44.9 45B 
 To MD 18 to MD 835 (Nesbit Road)
To MD 18 to MD 835 (Nesbit Road)Queenstown 46.1 46  US 301 north (Blue Star Memorial Highway) – Warwick, Wilmington DE
US 301 north (Blue Star Memorial Highway) – Warwick, Wilmington DEeastbound exit and westbound entrance;
East end of US 301 overlapEast end of expressway section Queenstown 46.3  MD 18 (Main Street)
MD 18 (Main Street)47.7 
 MD 456 north (Del Rhodes Avenue) to US 301
MD 456 north (Del Rhodes Avenue) to US 30149.1 Carmichael Road 50.7  MD 662 south (Wye Mills Road) – Wye Mills
MD 662 south (Wye Mills Road) – Wye MillsFormer US 50 Wye Mills 51.6  MD 213 – Centreville, Chesapeake City
MD 213 – Centreville, Chesapeake CityFormer US 213 53.1  MD 404 – Denton, Rehoboth
MD 404 – Denton, RehobothTalbot
25.45 miles (40.96 km)[5]55.4  MD 662 north (Old Wye Mills Road) – Wye Mills
MD 662 north (Old Wye Mills Road) – Wye MillsFormer US 50/US 213 55.8  MD 662 south (Wye Mills Easton Road)
MD 662 south (Wye Mills Easton Road)Former US 50/US 213 57.7  MD 662 (Wye Mills Easton Road)
MD 662 (Wye Mills Easton Road)Former US 50/US 213 Easton 61.8  MD 309 north (Cordova Road) – Cordova
MD 309 north (Cordova Road) – Cordova62.7 
 MD 322 south (Easton Parkway) to MD 33 – St. Michaels
MD 322 south (Easton Parkway) to MD 33 – St. Michaels64.2  MD 328 (Matthewstown Road, Goldsborough Road) – Denton
MD 328 (Matthewstown Road, Goldsborough Road) – Denton64.5  MD 331 (Dover Road) – Preston
MD 331 (Dover Road) – Prestonformer US 213 before construction of Choptank River bridge 65.4  To MD 565 (Dutchmans Lane)
To MD 565 (Dutchmans Lane)66.9 

 MD 322 north (Easton Parkway) to MD 565 north to MD 33 – St. Michaels
MD 322 north (Easton Parkway) to MD 565 north to MD 33 – St. Michaels67,7  MD 565 south (Old Trappe Road)
MD 565 south (Old Trappe Road)Trappe 73.02  To MD 565 (Main Street, Barber Road)
To MD 565 (Main Street, Barber Road)Frederick C. Malkus Bridge over Choptank River Dorchester
16.9 miles (27.20 km)[6]Cambridge 79.3 Maryland Avenue 80.1  MD 343 west (Washington Street) – Hudson
MD 343 west (Washington Street) – Hudson80.8  MD 16 west (Gypsy Hill Road) – Church Creek
MD 16 west (Gypsy Hill Road) – Church CreekWest end of MD 16 overlap 81.2  MD 750 east (Old Route 50)
MD 750 east (Old Route 50)frontage road 82.0  MD 750 west (Old Route 50)
MD 750 west (Old Route 50)frontage road 83.5  MD 16 east (Mt. Holly Road) – East New Market
MD 16 east (Mt. Holly Road) – East New MarketEast end of MD 16 overlap 93.5 To Marsh Road – Vienna Former US 50/MD 731 Vienna 94.5  MD 331 north (Rhodesdale-Vienna Road) – Vienna, Rhodesdale
MD 331 north (Rhodesdale-Vienna Road) – Vienna, RhodesdaleInterchange Nanticoke Memorial Bridge over Nanticoke River Wicomico
30.69 miles (49.39 km)[7]97.1  MD 731 north (Old Bradley Road)
MD 731 north (Old Bradley Road)frontage road 97.5  MD 731 west (Marsh Road)
MD 731 west (Marsh Road)Former US 50 Mardela Springs 99.9 
 MD 313 north (Delmar Road) to MD 54 – Sharptown, Delmar
MD 313 north (Delmar Road) to MD 54 – Sharptown, Delmar104.8  MD 347 south (N Main Street) – Hebron
MD 347 south (N Main Street) – Hebron105.9  MD 670 west (Lillian Street) – Hebron
MD 670 west (Lillian Street) – HebronSalisbury 107.8  US 50 Bus. east (Salisbury Parkway) – Salisbury
US 50 Bus. east (Salisbury Parkway) – SalisburyInterchange
Former US 50West end of expressway section 111.37 
 US 13 north (Ocean Highway) / US 13 Bus. south (Salisbury Boulevard) – Salisbury, Dover
US 13 north (Ocean Highway) / US 13 Bus. south (Salisbury Boulevard) – Salisbury, DoverWest end of US 13 overlap
US 13 Business is former US 13114.46 
 US 13 south (Salisbury Bypass, Ocean Highway) / US 50 Bus. west (Salisbury Parkway) – Norfolk
US 13 south (Salisbury Bypass, Ocean Highway) / US 50 Bus. west (Salisbury Parkway) – NorfolkEast end of US 13 overlap East end of expressway section 118.96  MD 992 (Eastside Road)
MD 992 (Eastside Road)frontage road 124.6 

 MD 354 (Powellville Road) to MD 12 to MD 346 – Powellville
MD 354 (Powellville Road) to MD 12 to MD 346 – PowellvilleWorcester
14.4 miles (23.17 km)[8]126.93  MD 610 north (Whaleyville Road) – Whaleyville
MD 610 north (Whaleyville Road) – Whaleyville129.23 
 MD 90 east (Ocean City Expressway) to US 113 – Ocean Pines, Ocean City
MD 90 east (Ocean City Expressway) to US 113 – Ocean Pines, Ocean CityInterchange 131.05  MD 346 (Old Ocean City Road) – Whaleyville, Berlin
MD 346 (Old Ocean City Road) – Whaleyville, BerlinFormer US 50 131.79 
 MD 992 (Caleb Road) to MD 346
MD 992 (Caleb Road) to MD 346frontage road Berlin 132.8 
 MD 818 (Main Street) to US 113
MD 818 (Main Street) to US 113Former US 113 133.13  US 113 (Worcester Highway) – Snow Hill, Dover
US 113 (Worcester Highway) – Snow Hill, DoverInterchange 133.96  MD 346 west (Old Ocean City Road)
MD 346 west (Old Ocean City Road)Former US 50 134.47 
 MD 452 north (Friendship Road, Seahawk Road) to MD 575
MD 452 north (Friendship Road, Seahawk Road) to MD 575135.73 
 MD 589 north (Racetrack Road) to MD 90
MD 589 north (Racetrack Road) to MD 90136.55  US 50WA to Holly Grove Road south
US 50WA to Holly Grove Road southfrontage road 138.2  MD 707 east (Old Bridge Road)
MD 707 east (Old Bridge Road)frontage road Ocean City 139.02  MD 611 south (Stephen Decatur Highway) – Assateague Island, Chincoteague Island
MD 611 south (Stephen Decatur Highway) – Assateague Island, Chincoteague IslandHarry W. Kelly Memorial Bridge over Isle of Wight Bay (Sinepuxent Bay) 140.42  MD 528 south (Philadelphia Avenue)
MD 528 south (Philadelphia Avenue)One-way southbound street
Beginning of US 50's westbound carriageway140.49  MD 378 north (Baltimore Avenue)
MD 378 north (Baltimore Avenue)One-way northbound street
End of US 50's eastbound carriagewayRelated routes
- Interstate 595 (Maryland)
- Maryland Route 18
- Maryland Route 213
- Maryland Route 346
- Maryland Route 404
- Maryland Route 450
- Maryland Route 662
- Maryland Route 707
References
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Garrett County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co11.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Prince George's County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co16.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Anne Arundel County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co02.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Queen Anne's County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co17.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Talbot County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co20.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Dorchester County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co09.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Wicomico County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co22.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ a b c Maryland State Highway Administration (2008). "Highway Location Reference: Worcester County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/keepingcurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2008_hlr_all/co23.pdf. Retrieved 2010-04-19.
- ^ Maryland State Highway Administration (1927). Map of Maryland (Map). http://www.mdhighwaycentennial.com/images/template/gallery/maps/1927SIDE1.jpg. Retrieved 2009-03-03.
- ^ "Interstate 595 in Maryland (US-50 from I-95/I-495 to Annapolis)". Roadstothefuture.com. http://www.roadstothefuture.com/I595_MD.html. Retrieved 2010-02-06.
External links
Roads in Prince George's County, Maryland Maryland State Highways 
U.S. Routes Interstate Highways Roads by name  U.S. Route 50
U.S. Route 50Previous state:
West VirginiaMaryland Next state:
West VirginiaPrevious state:
District of ColumbiaNext state:
TerminusCategories:- U.S. Highways in Maryland
- U.S. Route 50
- Roads in Garrett County, Maryland
- Roads in Prince George's County, Maryland
- Roads in Anne Arundel County, Maryland
- Roads in Queen Anne's County, Maryland
- Roads in Talbot County, Maryland
- Roads in Dorchester County, Maryland
- Roads in Wicomico County, Maryland
- Roads in Worcester County, Maryland
- Northwestern Turnpike
- Salisbury, Maryland
- Monuments and memorials in Maryland
- Blue Star Memorial Highways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.







