- Oxime
-
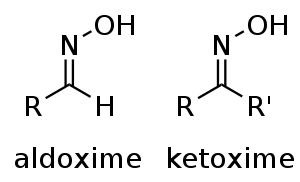
An oxime is a chemical compound belonging to the imines, with the general formula R1R2C=NOH, where R1 is an organic side chain and R2 may be hydrogen, forming an aldoxime, or another organic group, forming a ketoxime. O-substituted oximes form a closely related family of compounds. Amidoximes are oximes of hemiaminals with general structure RC(=NOH)(NRR'). Certain amidoximes react with benzenesulfonyl chloride to substituted ureas in the Tiemann rearrangement [1][2]
Oximes are usually generated by the reaction of hydroxylamine and aldehydes or ketones. The term oxime dates back to the 19th century, a portmanteau of the words oxygen and imide[citation needed].
Contents
Structure and properties
Oximes exist as two geometric stereoisomers: a syn isomer and an anti isomer. Aldoximes, except for aromatic aldoximes, exist only as a syn isomer, while ketoximes can be separated almost completely and obtained as a syn isomer and an anti isomer.
Oximes have three characteristic bands in the infrared spectrum, at wavenumbers 3600 (O-H), 1665 (C=N) and 945 (N-O).[3]
Preparation
Oximes can be synthesized by condensation of an aldehyde or a ketone with hydroxylamine. The condensation of aldehydes with hydroxylamine gives aldoxime, and ketoxime is produced from ketones and hydroxylamine. Generally, oximes exist as colorless crystals and are poorly soluble in water. Therefore, oximes can be used for the identification of ketone or aldehyde.
Oximes can also be obtained from reaction of nitrites such as isoamyl nitrite with compounds containing an acidic hydrogen atom. Examples are the reaction of ethyl acetoacetate and sodium nitrite in acetic acid,[4][5] the reaction of methyl ethyl ketone with ethyl nitrite in hydrochloric acid.[6] and a similar reaction with propiophenone,[7] the reaction of phenacyl chloride,[8] the reaction of malononitrile with sodium nitrite in acetic acid[9]
A conceptually related reaction is the Japp-Klingemann reaction.
Reactions
The hydrolysis of oximes proceeds easily by heating in the presence of various inorganic acids, and the oximes decompose into the corresponding ketones or aldehydes, and hydroxylamines. The reduction of oximes by sodium amalgam or hydrogenation produces amines. The reduction of aldoximes gives both primary amines and secondary amines.
Generally oximes can be changed to the corresponding amide derivatives by treatment with various acids. This reaction is called Beckmann rearrangement. In this reaction, a hydroxyl group is exchanged with the group that is in the anti position of the hydroxyl group. The amide derivatives that are obtained by Beckmann rearrangement can be transformed into a carboxylic acid by means of hydrolysis (base or acid catalyzed).And an amine by hoffman degradation of the amide in the presence of alkali hypoclorites at 80 degrees Celsius, the degradation is itself prone to side reactions namely, the formation of biurets or, cyanate polymers, To avoid this side reaction strict temperature control is necessary, the reaction must be conducted at sufficient temperature to isomerise the cyanate to the isocyante. also, good solvation is also crucial to be successful. Beckmann rearrangement is used for the industrial synthesis of caprolactam (see applications below).
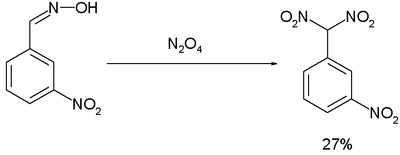
The Ponzio reaction (1906) [10] concerning the conversion of m-nitrobenzaldoxime to m-nitrophenyldinitromethane with dinitrogen tetroxide, was the result of research into TNT-like high explosives:[11]
In the Neber rearrangement certain oximes are converted to the corresponding alpha-amino ketones.
Uses
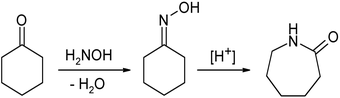
In their largest application, an oxime is an intermediate in the industrial production of caprolactam, a precursor to Nylon 6. About half of the world's supply of cyclohexanone, more than a billion kilograms annually, is converted to the oxime. In the presence of sulfuric acid catalyst, the oxime undergoes the Beckmann rearrangement to give the cyclic amide caprolactam:
Other applications
Dimethylglyoxime (dmgH2) is a reagent for the analysis of nickel and a popular ligand in its own right. Typically a metal reacts with two equivalents of dmgH2 concomitant with ionization of one proton.
Oxime compounds are used as antidotes for nerve agents. A nerve agent inactivates acetylcholinesterase molecules by phosphorylation of the molecule. Oxime compounds can reactivate acetylcholinesterate by attaching to the phosphorus atom and forming an oxime-phosphonate which then splits away from the acetylcholinesterase molecule. The most effective oxime nerve-agent antidotes are pralidoxime (also known as 2-PAM), obidoxime, methoxime, HI-6, Hlo-7, and TMB-4.[12] The effectiveness of the oxime treatment depends on the particular nerve agent used.[13] Perillartine, the oxime of perillaldehyde is used as an artificial sweetener in Japan, as it is 2000 times sweeter than sucrose. Salicylaldoxime is a chelator. Glyoxime, produced via the condensation of glyoxal with hydroxylamine,[14] forms highly energetic copper, lead and silver salts (copper, lead and silver glyoximate respectively).[15] However these compounds are too unstable to be of any commercial value. Diaminoglyoxime, a glyoxime derivative, is a key synthetic precursor, used to prepare various compounds, containing the highly reactive furazan ring.
Methyl Ethyl Ketoxime is a skin-preventing additive in many oil-based paints.
References
- ^ Ferdinand Tiemann (1891). "Ueber die Einwirkung von Benzolsulfonsäurechlorid auf Amidoxime". Chemische Berichte 24: 4162–4167. doi:10.1002/cber.189102402316.
- ^ Robert Plapinger, Omer Owens (1956). "Notes - The Reaction of Phosphorus-Containing Enzyme Inhibitors with Some Hydroxylamine Derivatives". J. Org. Chem. 21: 1186. doi:10.1021/jo01116a610.
- ^ W. Reusch. "Infrared Spectroscopy". Virtual Textbook of Organic Chemistry. Michigan State University. http://www.cem.msu.edu/~reusch/VirtTxtJml/Spectrpy/InfraRed/infrared.htm.
- ^ Hans Fischer (1943), "2,4-Dimethyl-3,5-dicarbethoxypyrrole", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv2p0202; Coll. Vol. 2: 202
- ^ Hans Fischer (1955), "Kryptopyrrole", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv3p0513; Coll. Vol. 3: 513
- ^ W. L. Semon and V. R. Damerell (1943), "Dimethoxyglyoxime", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv2p0204; Coll. Vol. 2: 204
- ^ Walter H. Hartung and Frank Crossley (1943), "Isonitrosopropiophenone", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv2p0363; Coll. Vol. 2: 363
- ^ Nathan Levin and Walter H. Hartung (1955), "ω-chloroisonitrosoacetophenone", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv3p0191; Coll. Vol. 3: 191
- ^ J. P. Ferris, R. A. Sanchez, and R. W. Mancuso (1973), "p-toluenesulfonate", Org. Synth., http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv5p0032; Coll. Vol. 5: 32
- ^ Giacomo Ponzio (1906). "Einwirkung von Stickstofftetroxyd auf Benzaldoxim". J. Prakt. Chem. 73: 494. doi:10.1002/prac.19060730133.
- ^ Louis F. Fieser and William von E. Doering (1946). "Aromatic-Aliphatic Nitro Compounds. III. The Ponzio Reaction; 2,4,6-Trinitrobenzyl Nitrate". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 68: 2252. doi:10.1021/ja01215a040.
- ^ Aaron Rowe (2007-11-27), New Nerve Gas Antidotes, Wired (magazine), http://blog.wired.com/wiredscience/2007/11/building-a-bett.html
- ^ Kassa, J. (2002). "Review of oximes in the antidotal treatment of poisoning by organophosphorus nerve agents". Journal of Toxicology — Clinical Toxicology 40: 803. doi:10.1081/CLT-120015840.
- ^ Michelman, J; Michelman, J. S. (1965). "Furazan". Journal of Organic Chemistry 30: 1854–1859. doi:10.1021/jo01017a034.
- ^ Urben, Peter (1999). Bretherick's Handobook of Reactive Chemical Hazards. 1 (5 ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 799.
Antidotes (V03AB) Nervous system Barbiturate overdoseBemegride • EthamivanBenzodiazepine overdoseGHB overdoseReversal of neuromuscular blockadeCardiovascular Other Paracetamol toxicity (Acetaminophen)OtherPrednisolone/promethazine • oxidizing agent (potassium permanganate) • iodine-131 (Potassium iodide) • Methylthioninium chloride#Emetic Ipecacuanha (Syrup of ipecac) • Copper sulfateFunctional groups Acetyl · Acetoxy · Acryloyl · Acyl · Alcohol · Aldehyde · Alkane · Alkene · Alkyne · Alkoxy group · Amide · Amine · Azo compound · Benzene derivative · Carboxylic acid · Cyanate · Disulfide · Ester · Ether · Epoxide · Haloalkane · Hydrazone · Hydroxyl · Imine · Isocyanate · Isonitrile · Isothiocyanate · Ketone · Methine · Nitrile · Nitro compound · Nitroso compound · Organophosphorus · Oxime · Peroxide · Phosphonous and Phosphonic acid · Pyridine derivative · Sulfone · Sulfonic acid · Sulfoxide · Thiocyanate · Thioester · Thioether · Thiol · Urea
See also Chemical classificationCategories:- Functional groups
- Organic compounds
- Oximes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.