- Movement proteins
-
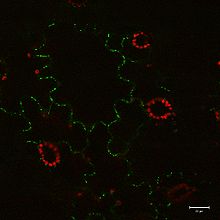 TMV MP30 localizes to plasmodesmata when fused to GFP. This image was captured using confocal laser scanning microscopy
TMV MP30 localizes to plasmodesmata when fused to GFP. This image was captured using confocal laser scanning microscopy
Successful infection of a plant by a plant virus depends on its ability to move from the cell initially infected to neighbouring cells in order to spread infection. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have robust cell walls, which viruses cannot easily penetrate. Movement proteins are non-structural proteins encoded by many, if not all, plant viruses to enable their movement from one infected cell to neighbouring cells. Some plant viruses express more than one movement protein. The movement protein of Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) has been most extensively studied. Plant viruses can also be transported over longer distances through the host plant in the vascular system via the phloem.
Plant virus movement between cells
Most plant viruses move between plant cells via plasmodesmata, pores between plant cell walls that allow the plant cells to communicate with each other. Plasmodesmata usually only allow the passage of small diffusible molecules, such as various metabolites. Neither virus particles nor viral genomic nucleic acid can pass through plasmodesmata unaided.
Function of movement proteins
Movement proteins modify the plasmodesmata by one of two well understood molecular mechanisms. The movement proteins of many plant viruses form a transport tubule within the pore of the plasmodesmata that allow the transport of mature virus particles. Examples of viruses that use this mechanism are Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV) and Tomato spotted wilt virus (TSWV). The second mechanism by which movement proteins work is by associating with and coating the genome of the virus, causing the ribonucleoprotein complexes to be transported through plasmodesmata into neighbouring cells. TMV's 30KDa movement protein acts via this mechanism, although it may also have other roles in infection.
References
- Plant viruses Microbiology @ Leicester
- Lucas WJ (January 2006). "Plant viral movement proteins: agents for cell-to-cell trafficking of viral genomes". Virology 344 (1): 169–84. doi:10.1016/j.virol.2005.09.026. PMID 16364748. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0042-6822(05)00578-7.
- Boevink P, Oparka KJ (August 2005). "Virus-host interactions during movement processes". Plant Physiol. 138 (4): 1815–21. doi:10.1104/pp.105.066761. PMC 1183373. PMID 16172094. http://www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=16172094.
- Beachy RN, Heinlein M (July 2000). "Role of P30 in replication and spread of TMV". Traffic 1 (7): 540–4. doi:10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010703.x. PMID 11208141. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/resolve/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=1398-9219&date=2000&volume=1&issue=7&spage=540.

This protein-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
