- Ramus of the mandible
-
Bone: Ramus of the mandible Mandible. Outer surface. Side view Mandible. Inner surface. Side view Latin ramus mandibulae Gray's subject #44 173 The ramus of the mandible (perpendicular portion) is quadrilateral in shape, and has two surfaces, four borders, and two processes.
Contents
Surfaces
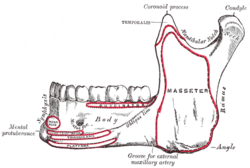
The lateral surface is flat and marked by oblique ridges at its lower part; it gives attachment throughout nearly the whole of its extent to the masseter.
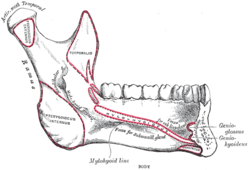
The medial surface presents about its center the oblique mandibular foramen, for the entrance of the inferior alveolar vessels and nerve.
The margin of this opening is irregular; it presents in front a prominent ridge, surmounted by a sharp spine, the lingula mandibulae, which gives attachment to the sphenomandibular ligament; at its lower and back part is a notch from which the mylohyoid groove runs obliquely downward and forward, and lodges the mylohyoid vessels and nerve.
Behind this groove is a rough surface, for the insertion of the internal pterygoid muscle (Pterygoideus internus). The mandibular canal runs obliquely downward and forward in the ramus, and then horizontally forward in the body, where it is placed under the alveoli and communicates with them by small openings.
On arriving at the incisor teeth, it turns back to communicate with the mental foramen, giving off two small canals which run to the cavities containing the incisor teeth.
In the posterior two-thirds of the bone the canal is situated nearer the internal surface of the mandible; and in the anterior third, nearer its external surface.
It contains the inferior alveolar vessels and nerve, from which branches are distributed to the teeth.
Borders
The lower border of the ramus is thick, straight, and continuous with the inferior border of the body of the bone. At its junction with the posterior border is the angle of the mandible, which may be either inverted or everted and is marked by rough, oblique ridges on each side, for the attachment of the Masseter laterally, and the Pterygoideus internus medially; the stylomandibular ligament is attached to the angle between these muscles. The anterior border is thin above, thicker below, and continuous with the oblique line.
The posterior border is thick, smooth, rounded, and covered by the parotid gland. The upper border is thin, and is surmounted by two processes, the coronoid in front and the condyloid behind, separated by a deep concavity, the mandibular notch.
Processes
The coronoid process is a thin, triangular eminence, which is flattened from side to side and varies in shape and size.
The condyloid process is thicker than the coronoid, and consists of two portions: the condyle, and the constricted portion which supports it, the neck.
The mandibular notch, separating the two processes, is a deep semilunar depression, and is crossed by the masseteric vessels and nerve.
Additional images
External links
- lesson1 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 25420.000-1
- Anatomy at PSU skel/mandible2
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 34256.000-1
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of head and neck: the facial skeleton of the skull (TA A02.1.08–15, GA 2.156–177) Maxilla SurfacesProcessesOtherZygomatic Palatine FossaePlatesProcessesMandible external surface (Symphysis menti, Lingual foramen, Mental protuberance, Mental foramen, Mandibular incisive canal) · internal surface (Mental spine, Mylohyoid line, Sublingual fovea, Submandibular fovea) · Alveolar part of mandibleRamusMinor/
noseNasal bone: Internasal suture · Nasal foramina
Inferior nasal concha: Ethmoidal process · Maxillary process
Vomer: Vomer anterior · Synostosis vomerina · Vomer posterior (Wing)
Lacrimal: Posterior lacrimal crest · Lacrimal groove · Lacrimal hamulusCategories:- Bones of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.