- Neural groove
-
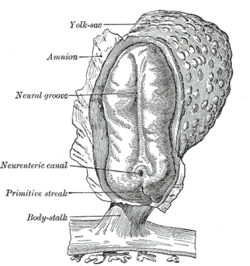
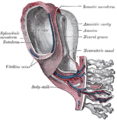
Neural groove Human embryo—length, 2 mm. Dorsal view, with the amnion laid open. X 30. Latin sulcus neuralis Gray's subject #7 50 Carnegie stage 9 Precursor neural plate Gives rise to neural tube Code TE E5.13.1.0.1.0.3 The neural groove is a shallow median groove between the neural folds of an embryo. The neural folds are two longitudinal ridges that are caused by a folding up of the ectoderm in front of the primitive streak of the developing embryo. [1]
The groove gradually deepens as the neural folds become elevated, and ultimately the folds meet and coalesce in the middle line and convert the groove into a closed tube, the neural tube or canal, the ectodermal wall of which forms the rudiment of the nervous system.
After the coalescence of the neural folds over the anterior end of the primitive streak, the blastopore no longer opens on the surface but into the closed canal of the neural tube, and thus a transitory communication, the neurenteric canal, is established between the neural tube and the primitive digestive tube. The coalescence of the neural folds occurs first in the region of the hind-brain, and from there extends forward and backward; toward the end of the third week the front opening (anterior neuropore) of the tube finally closes at the anterior end of the future brain, and forms a recess which is in contact, for a time, with the overlying ectoderm; the hinder part of the neural groove presents for a time a rhomboidal shape, and to this expanded portion the term sinus rhomboidalis has been applied. Before the neural groove is closed a ridge of ectodermal cells appears along the prominent margin of each neural fold; this is termed the neural crest or ganglion ridge, and from it the spinal and cranial nerve ganglia and the ganglia of the sympathetic nervous system are developed. By the upward growth of the mesoderm the neural tube is ultimately separated from the overlying ectoderm.
The cephalic end of the neural groove exhibits several dilatations, which, when the tube is closed, assume the form of three vesicles; these constitute the three primary cerebral vesicles, and correspond respectively to the future fore-brain (prosencephalon), mid-brain (mesencephalon), and hind-brain (rhombencephalon). The walls of the vesicles are developed into the nervous tissue and neuroglia of the brain, and their cavities are modified to form its ventricles. The remainder of the tube forms the medulla spinalis or spinal cord; from its ectodermal wall the nervous and neuroglial elements of the medulla spinalis are developed while the cavity persists as the central canal.[2]
References
Additional images
External links
- Swiss embryology (from UL, UB, and UF) iperiodembry/carnegie03
- Embryology at UNSW Notes/week3_5
- Diagram at embryology.med.unsw.edu.au
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.Prenatal development/Mammalian development of nervous system (GA 9.733 and GA 10.1002, TE E5.13-16) Neurogenesis Cranial neural crest (Cardiac neural crest complex) · Truncal neural crestRostral neuropore
Cephalic flexure · Pontine flexure
Alar plate (sensory) · Basal plate (motor)
Germinal matrixEye development Auditory development M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
M: EAR
anat(e/p)/phys/devp
noco/cong, epon
proc, drug(S2)
Categories:- Embryology of nervous system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.