- Deep Space 2
-
Deep Space 2 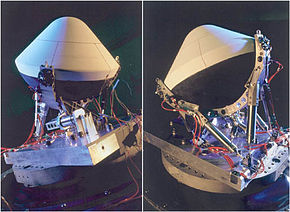
DS2 probe with heatshield and mountingOperator NASA/JPL Major contractors Lockheed Martin Mission type Lander / impactor Launch date 1999-01-03 20:21:10 UTC Launch vehicle Delta II 7425 Launch site Space Launch Complex 17
Cape Canaveral Air Force StationMission duration (failure in transit)
Last contact on day 334
1999-12-03 20:00:00 UTC [1]Landing site 73°S 210°W / 73°S 210°W (Projected) COSPAR ID DEEPSP2 Homepage nmp.jpl.nasa.gov/ds2/ Mass 2.4 kg (5.3 lb) each Power 300mW (Li-SOCl2 batteries) Instruments Main instruments Impact accelerometer
Water detection apparatus
Soil conductivity probe
Descent accelerometerSpectral band S-band Deep Space 2 was a NASA probe which was part of the New Millennium Program. It included two highly advanced miniature space probes which were sent to Mars aboard the Mars Polar Lander in January 1999.[2] The probes were named "Scott" and "Amundsen", in honor of Robert Falcon Scott and Roald Amundsen, the first explorers to reach the Earth's South Pole. Intended to be the first spacecraft to penetrate below the surface of another planet, after entering the Mars atmosphere DS2 was to detach from the Mars Polar Lander mother ship and plummet to the surface using only an aeroshell impactor, with no parachute. The mission was declared a failure on March 13, 2000, after all attempts to reestablish communications following the descent went unanswered.[3]
Contents
Background
Each probe weighed just 2.4 kg (5.3 lb) and was encased in a protective aeroshell. They rode to Mars aboard another spacecraft, the Mars Polar Lander. Upon arrival just above the south polar region of Mars on December 3, 1999,[2] the basketball-sized shells were released from the main spacecraft, plummeting through the atmosphere and hitting the planet's surface at over 179 m/s (590 ft/s). On impact, each shell was designed to shatter, and its grapefruit-sized probe was to punch through the soil and separate into two parts. The lower part, called the forebody, was designed to penetrate as far as 0.6 meters (2 ft 0 in) into the soil. The upper part of the probe, or aftbody, was designed to remain on the surface in order to radio data to the Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft in orbit around Mars. The Mars Global Surveyor would act as a relay in order to send the data collected back to Earth. The two sections of the probe were designed to remain connected via a data cable.[3]
Mission failure
The probes reached Mars apparently without incident, but communication was never established after landing. It is not known what the cause of failure was. The crash review board[4] suggests several possible causes for failure:
- the probe radio equipment had a low chance of surviving the impact.
- the probes may simply have hit ground which was too rocky for survival.
- The batteries on the probes, which had been charged prior to launch almost a year earlier, might not have retained sufficient power.[5]
Deep Space 2 penetratorDS2 functional animationDS2 probe componentsSee also
Notes
- ^ Phil Davis; Kirk Munsell (23 January 2009). "Missions to Mars: Mars Polar Lander - Key Dates". Solar System Exploration. NASA. http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?MCode=MPL. Retrieved 2009-04-22.
- ^ a b Davis, Phil; Munsell, Kirk (January 23, 2009). "Missions to Mars: Deep Space 2 - Key Dates". Solar System Exploration. NASA. http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?Sort=Target&Target=Mars&MCode=DS2. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
- ^ a b "Deep Space 2 (DEEPSP2)". NSSDC Master Catalog. NASA - National Space Science Data Center. 2000. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/masterCatalog.do?sc=DEEPSP2. Retrieved July 8, 2009.
- ^ "Report on the Loss of the Mars Polar Lander and Deep Space 2 Missions". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 22 March 2000. ftp://ftp.hq.nasa.gov/pub/pao/reports/2000/2000_mpl_report_1.pdf.
- ^ Young, Thomas (March 14, 2000). Mars Program Independent Assessment Team Summary Report. Draft #7 3/13/00. House Science and Technology Committee. http://www.spaceref.com/news/viewpr.html?pid=1444. Retrieved April 22, 2009.
References
- Michael C. Malin (July 2005). "Hidden in Plain Sight: Finding Martian Landers". Sky and Telescope 110 (7): 42–46. ISSN 00376604.
- "Press Kit: 1998 Mars Missions" (.PDF) (Press release). National Aeronautics and Space Administration. December 8, 1998. http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/files/misc/mars98launch.pdf. Retrieved April 22, 2009.
External links
- Deep Space 2 website at JPL
Failed and cancelled Mars missions Failed at launch 
Failed en route Mars 1 · Zond 2 · Mars 6 · Mars 7 · Phobos 1 · Mars Observer · Nozomi · Mars Climate Orbiter · Mars Polar Lander · Deep Space 2 · Beagle 2Cancelled (year cancelled) Voyager · Marsokhod (Mars 4NM) · Mars sample return (Mars 5NM) · Mars Surveyor 2001 Lander · NetLander · Mars Telecommunications Orbiter · Beagle 3 · Mars Astrobiology Explorer-Cacher (2011)New Millennium Program Launched Deep Space 1 · Deep Space 2 · Earth Observing-1 · Space Technology 5
Cancelled Champollion · Deep Space 4 · Earth Observing-2 · Earth Observing-3 · Space Technology 4 · Space Technology 6 · Space Technology 7 · Space Technology 8
Categories:- 1999 in spaceflight
- Inactive extraterrestrial land probes
- Mars missions
- NASA probes
- New Millennium Program
- Spacecraft launched by Delta II rockets
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




