- Monnet Plan
-
- This article deals with the 1945-47 plan of the immediate post-war period. For the Monnet plan of 1950, see European Coal and Steel Community.
The Monnet plan was proposed by French civil servant Jean Monnet after the end of World War II. It was a reconstruction plan for France that proposed giving France control over the German coal and steel areas of the Ruhr area and Saar and using these resources to bring France to 150% of pre-war industrial production. The plan was adopted by Charles de Gaulle in early 1946. The plan would permanently limit Germany's industrial capacity. It would also ensure the use of Germany's resources for European reconstruction.
Contents
Background
The early French plans were concerned with keeping Germany weak and strengthening the French economy at the expense of that of Germany. French foreign policy aimed to dismantle German heavy industry, place the coal rich Ruhr area and Rhineland under French control or at a minimum internationalize them, and also to join the coal-rich Saarland with the iron-rich province of Lorraine (which had been handed over from Germany to France again in 1944).[1] When American diplomats reminded the French of what a devastating effect this would have on the German economy, France's response was to suggest the Germans would just have to "make [the] necessary adjustments" to deal with the inevitable foreign exchange deficit.[1]
Five Year plans
The "Monnet plan" was in effect the first five-year plan for modernization and equipment, a plan for national economic reconstruction which drew heavily on earlier French plans to make France the largest steel producer in Europe. Monnet's aim was to modernize the French economy so as to make it internationally competitive, especially versus German exports. To carry out his plans he shaped the Planning Commissariat and entrenched it in the French bureaucracy. Germany was seen as a necessary tool for carrying out the plans. The planned steel production increases to 15 million tonnes of steel a year could only be achieved by replacing former German steel exports and increasing the imports of German coal and coke, making control of this German resource vital.[2]
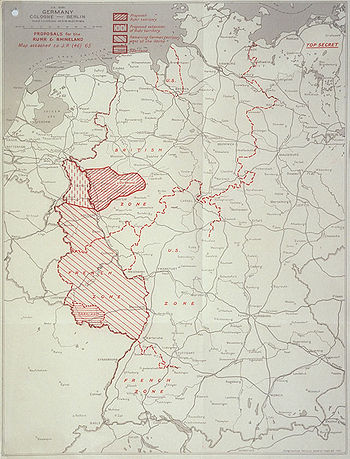
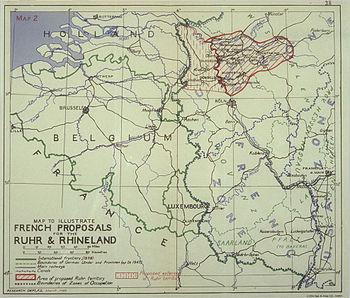
French proposals for the area spanned by the German coalfields east of the Rhine had since late 1945, therefore, been to turn it into an International State with its own currency and customs and supervised by an International Authority which would include the US and France. Part of the reason for these proposals was in 1946 explained to the US by a French Foreign Office official: "With the aim of military security we prefer to increase French steel production and output to the detriment of the Ruhr."[2]
The UK and the US were generally reluctant to acquiesce to the French demands, since they feared it would lead to increased Russian influence.[2]
Monnet's memoirs show no hard evidence of an interest in European unity before April 1948, when he realized it was a central US objective.[3] He then wrote to Schumann that to ward off the current dangers there was only one solution; it would "only be possible through the creation of a federation of the west".[3]
The Saar Area
In 1947 France detached the coal-rich Saar area from Germany and turned it into the Saar protectorate under French economic control. The area returned to German administration on January 1, 1957, but France retained the right to mine from its coal mines until 1981.
As a protectorate, the Saar area was economically integrated with France and nominally politically independent although security and foreign policy was dictated from France. In addition, France maintained a High Commissioner in the Saar with wide-ranging powers. Parties advocating a return of the Saar to Germany were banned, with the consequence that West Germany did not recognize the democratic legality of the Saar government. In view of continued conflict between Germany and France over the future of the Saarland, efforts were made by the other Western European nations to find a solution to the potentially dangerous problem. Placed under increasing international pressure France finally agreed to a compromise. The Saar territory was to be Europeanised under the context of the Western European Union. France and Germany agreed in the Paris Agreements that until a peace treaty was signed with Germany, the Saar area would be governed under a "statute" that was to be supervised by a European Commissioner who in turn would be responsible to the Council of Ministers of the Western European Union. The Saarland would however have to remain in economic union with France.[4][5]
Despite the endorsement of the statute by West Germany, in the 1955 referendum amongst the Saarlanders that was needed for it to come into effect the statute was rejected by 67.7% of the population. Despite French pre-referendum assertions that a "no" to the statute would simply result in the Saarland remaining in its previous status as a French-controlled territory, the claim of the campaign group for a "no" to the statute that it would lead to unification with West Germany turned out to be correct. The Saarland was politically reintegrated with West Germany in 1 January 1957, but economic reintegration took many additional years. In return for agreeing to return the Saar, France demanded and gained the following concessions:
- France was permitted to extract coal from the Warndt coal deposit until 1981.
- Germany had to agree to the channelisation of the Moselle. This reduced French freight costs in the Lorraine steel industry.
- Germany had to agree to the teaching of French as the first foreign language in schools in the Saarland. Although no longer binding, the agreement is still in the main followed.[5][6]
As one minor consequence of French efforts to Frenchify the territory, it was alone in the western occupied territories not to accept any refugees from the expulsions of Germans in the Eastern provinces and German settlements elsewhere in Eastern Europe. France did not wish to increase the German-speaking population in the territory.
The Ruhr Area
In September 1946 the US government stated in the Stuttgart speech Restatement of Policy on Germany that it would accept the French claims on the Saarland, but that: "the United States will not support any encroachment on territory which is indisputably German or any division of Germany which is not genuinely desired by the people concerned. So far as the United States is aware the people of the Ruhr area and the Rhineland desire to remain united with the rest of Germany. And the United States is not going to oppose their desire."
The U.S. was at this point in time becoming more concerned by the risk of Western Germany slipping into the communist camp, and a detachment of the Ruhr from Germany was seen as dangerous from that standpoint.
However, in 1949 the Ruhr Agreement was imposed on the (West) Germans as a pre-condition for permitting them to establish the Federal Republic of Germany.[7] By controlling the production and distribution of coal and steel (i.e., how much coal and steel the Germans themselves would get), the International Authority for the Ruhr (IAR) in effect controlled the entire West German economy, much to the dismay of the Germans. They were however permitted to send their delegations to the authority after the Petersberg agreement.
With the 1951 West German agreement to in 1952 join the European Coal and Steel Community in order to lift the restrictions imposed by the IAR,[8] thus also ensuring French security by perpetuating French access to Ruhr coal,[9] the role of the IAR was taken over by the European Coal and Steel Community.[10]
See also
References and notes
- ^ a b http://www.collectionscanada.ca/obj/s4/f2/dsk2/ftp03/MQ54257.pdf
- ^ a b c Alan S. Milward, "The Reconstruction of Western Europe, 1945-51" pp. 97-98
- ^ a b Alan S. Milward, George Brennan, Federico Romero "The European Rescue of the Nation-state: Second Edition" p.335
- ^ Yes or No, Time Magazine Monday, Oct. 17, 1955
- ^ a b Bverfg No. 7 E 4, 157 1 BvF 1/55 "Saar Statute" Institute of Global Law, University College London (Google Caché)
- ^ The issue of the Saar European NAvigator
- ^ Amos Yoder, "The Ruhr Authority and the German Problem", "The Review of Politics", Vol. 17, No. 3 (Jul., 1955), pp. 345-358
- ^ No more guns from the Ruhr!
- ^ France Restored: Cold War Diplomacy and the Quest for Leadership in Europe, 1944-1954 H-Net Reviews June 2001
- ^ Information bulletin Frankfurt, Germany: Office of the US High Commissioner for Germany Office of Public Affairs, Public Relations Division, APO 757, US Army, January 1952 "Plans for terminating international authority for the Ruhr" , pp. 61-62] (main URL)
External links
- French proposal regarding the detachment of German industrial regions September 8, 1945
- Ruhr Delegation of the United States of America, Council of Foreign Ministers American Embassy Moscow, March 24, 1947
- The Marshall Plan, 1948-1951 Albrecht Ritschl, Humboldt Universitaet – Berlin
- William I. Hitchcock. France Restored: Cold War Diplomacy and the Quest for Leadership in Europe, 1944-1954 Reviewed by Sean Kennedy, University of New Brunswick.
- Challenging the United States: French Foreign Policy 1944 - 1948 Good overview, but very large file.
- France, Germany and the Struggle for the War-making Natural Resources of the Rhineland Describes the contest over the centuries.
Categories:- Aftermath of World War II
- France–Germany relations
- 20th century in Germany
- 20th century in France
- Economic planning
- 1940s in France
- 1940s in Germany
- 1945 in France
- 1945 in Germany
- 1946 in France
- 1946 in Germany
- 1947 in France
- 1947 in Germany
- 1940s economic history
- 1945 in international relations
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.