- Dilophosaurus
-
Dilophosaurus
Temporal range: Early Jurassic, 193 Ma
Replica skull and neck, Royal Tyrrell Museum Scientific classification 
Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Reptilia Superorder: Dinosauria Order: Saurischia Suborder: Theropoda Family: †Dilophosauridae Genus: †Dilophosaurus
Welles, 1970Species - †D. wetherilli (Welles, 1954) [originally Megalosaurus] (type)
- †D. sinensis? Hu, 1993
Dilophosaurus (
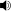 /daɪˌlɒfɵˈsɔrəs/ dy-lof-o-sawr-əs or /daɪˌloʊfɵˈsɔrəs/; Greek: di for "two", lophos "crest", and sauros "lizard") was a theropod dinosaur from the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic Period, about 193 million years ago. The first specimens were described in 1954, but it was not until over a decade later that the genus received its current name. It is one of the earliest known Jurassic theropods and one of the least understood.[1]
/daɪˌlɒfɵˈsɔrəs/ dy-lof-o-sawr-əs or /daɪˌloʊfɵˈsɔrəs/; Greek: di for "two", lophos "crest", and sauros "lizard") was a theropod dinosaur from the Sinemurian stage of the Early Jurassic Period, about 193 million years ago. The first specimens were described in 1954, but it was not until over a decade later that the genus received its current name. It is one of the earliest known Jurassic theropods and one of the least understood.[1]Dilophosaurus has appeared several times in popular culture, such as in the 1993 film Jurassic Park.
Contents
Description
Dilophosaurus measured around six meters (20 ft) long and may have weighed half a ton.
The most distinctive characteristic of Dilophosaurus is the pair of rounded crests on its skull, possibly used for display.[2][3] Studies by Robert Gay show no indication that sexual dimorphism was present in the skeleton of Dilophosaurus, but says nothing about crest variation.[1] The teeth of Dilophosaurus are long, but have a fairly small base and expand basally.[4] Another skull feature was a notch behind the first row of teeth, giving Dilophosaurus an almost crocodile-like appearance, similar to the putatively piscivorous spinosaurid dinosaurs. This "notch" existed by virtue of a weak connection between the premaxillary and maxillary bones of the skull. This conformation led to the early hypothesis that Dilophosaurus scavenged off dead carcasses, with the front teeth being too weak to bring down and hold large prey.[5]
Classification
Dilophosaurus may be a primitive member of the clade containing both ceratosaurian and tetanuran theropods. Alternatively, some paleontologists classify this genus as a large coelophysoid.
Discovery and species
 Depiction of Early Jurassic environment preserved at the SGDS, with Dilophosaurus wetherilli in bird-like resting pose[6]
Depiction of Early Jurassic environment preserved at the SGDS, with Dilophosaurus wetherilli in bird-like resting pose[6]
The first Dilophosaurus specimens were discovered by Sam Welles in the summer of 1942 in Arizona.[7] The specimen was brought back to Berkeley for cleaning and mounting, where it was given the name Megalosaurus wetherilli.[8] Returning to the same formation a decade later to determine from which time period the bones dated, Welles found a new specimen not far from the location of the previous discovery. The specimens were later renamed Dilophosaurus, based on the double crest clearly visible in the new skeleton.[4][8]
There is another species of Dilophosaurus (D. sinensis),[9] which may or may not belong to this genus. It is possibly closer to the Antarctic theropod Cryolophosaurus, based on the fact that the anterior end of the jugal does not participate in the internal antorbital fenestra and that the maxillary tooth row is completely in front of the orbit and ends anterior to the vertical strut of the lacrimal. This species was recovered from the Yunnan Province of China in 1987, with the prosauropod Yunnanosaurus and later described and named in 1993 by Shaojin Hu.[10]
A third species, D. breedorum, was coined by Samuel Welles through Welles and Pickering (1999). This species was based upon crested specimen UCMP 77270. Welles' original material lacked well-preserved crests, and he suggested that the crested specimens pertained to a different species.[2] He was unable to complete a manuscript describing this during his lifetime, and the name eventually came out in a private publication distributed by Pickering.[11] This species has not been accepted as valid in other reviews of the genus.[4][12]
Paleobiology
Paleopathology
One Dilophosaurus wetherilli specimen shows potential damage "due to injury or crushing" to a vertebra, and a potential abscess on a humerus. A Dilophosaurus wetherilli is also known with an unusually small left humerus compared to a very robust right arm, a possible example of "fluctuating asymmetry". Fluctuating asymmetry results from developmental disturbances and is more common in populations under stress and can therefore be informative about the quality of conditions a dinosaur lived under.[13]
In a 2001 study conducted by Bruce Rothschild and other paleontologists, 60 foot bones referred to Dilophosaurus were examined for signs of stress fracture, but none were found.[14]
In popular culture
Dilophosaurus appears in the novel Carnosaur, in which a member of the genus kills a member of Parliament.
Dilophosaurus is prominently featured in both Michael Crichton's 1990 novel Jurassic Park and its 1993 movie adaptation. It is depicted spitting blinding poison, aiming for the eyes to blind and paralyze its prey (much like a spitting cobra); in the film, it also has a retractable neck frill around its neck (much like a frill-necked lizard). There is no evidence to support either the frill or the venom spitting,[15] which was acknowledged by Crichton as creative license.[16] In the film, Steven Spielberg also reduced the size of Dilophosaurus to 3 feet (0.91 m) tall and 5 feet (1.5 m) long in order to avoid confusion with the Velociraptors.[17] Jurassic Park merchandise, including toys and video games (such as Jurassic Park: Operation Genesis, Telltale's Jurassic Park: The Game and the arcade games The Lost World: Jurassic Park and Jurassic Park III), often include Dilophosaurus.
Despite its inaccuracies, the Jurassic Park depiction of Dilophosaurus has been taken up by others. Several other video games, such as ParaWorld, Jurassic: The Hunted, Nanosaur and Ice Age: Dawn of the Dinosaurs, feature Dilophosaurus modeled after the representations in Jurassic Park, and The Whitest Kids U'Know sketch "Dinosaur Rap" (a music video for Trevor Moore's "Gettin' High With Dinosaurs") features a Dilophosaurus, complete with a short frill. A more accurately restored Dilophosaurus was featured in the documentary When Dinosaurs Roamed America, killing an Anchisaurus and scaring off a pack of Syntarsus (now known as Megapnosaurus). More accurately-sized, yet slightly larger Dilophosaurus wetherilli also make an appearance in the 2008 video game Turok.
See also
References
- ^ a b Gay, Robert (2005). "Evidence for sexual dimorphism in the Early Jurassic theropod dinosaur, Dilophosaurus and a comparison with other related forms In: Carpenter, Ken, ed. The Carnivorous Dinosaurs". The Carnivorous Dinosaurs. Indiana University Press. pp. 277–283. ISBN 0-253-34539-1.
- ^ a b Welles, S. P. (1984). "Dilophosaurus wetherilli (Dinosauria, Theropoda), osteology and comparisons". Palaeontogr. Abt. A 185: 85–180.
- ^ Welles, S. P. (1954). "New Jurassic dinosaur from the Kayenta formation of Arizona". Bulletin of the Geological Society of America 65 (6): 591–598. doi:10.1130/0016-7606(1954)65[591:NJDFTK]2.0.CO;2.
- ^ a b c Gay, Robert (2001). "New specimens of Dilophosaurus wetherilli (Dinosauria: Theropoda) from the early Jurassic Kayenta Formation of northern Arizona". Western Association of Vertebrate Paleontologists annual meeting volume Mesa, Arizona 1: 1.
- ^ Norman, David (1985). The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Dinosaurs. New York: Crescent Books. pp. 62–67. ISBN 0-517-468905.
- ^ http://www.plosone.org/article/info:doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0004591
- ^ Welles, Sam (2007). "Dilophosaurus Discovered". ucmp.berkeley.edu. University of California, Berkeley. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/dilophosaur/discovery.html. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
- ^ a b Welles, Sam (2007). "Dilophosaurus Details". ucmp.berkeley.edu. University of California, Berkeley. http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/dilophosaur/details.html. Retrieved 2007-11-17.
- ^ Irmis, Randall (2004-12-22). "First Report of Megapnosaurus from China" (PDF). PaleoBios 24 (3): 11–18. http://ist-socrates.berkeley.edu/~irmisr/megapno.pdf.
- ^ Hu, Shaojin (1993). "A Short Report On the Occurrence of Dilophosaurus from Jinning County, Yunnan Province". Vertebr. PalAsiatica 31: 65–69.
- ^ Olshevsky, George (1999-12-05). "Dinosaur Genera List corrections #126". Dinosaur Mailing List Archives. Cleveland Museum of Natural History. http://dml.cmnh.org/1999Dec/msg00097.html. Retrieved 2008-06-25.
- ^ Tykoski, R.S. & Rowe, T. (2004). "Ceratosauria". In: Weishampel, D.B., Dodson, P., & Osmolska, H. (Eds.) The Dinosauria (2nd edition). Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 47–70 ISBN 0-520-24209-2
- ^ Molnar, R. E., 2001, Theropod paleopathology: a literature survey: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 337-363.
- ^ Rothschild, B., Tanke, D. H., and Ford, T. L., 2001, Theropod stress fractures and tendon avulsions as a clue to activity: In: Mesozoic Vertebrate Life, edited by Tanke, D. H., and Carpenter, K., Indiana University Press, p. 331-336.
- ^ Bennington, J Bret (1996). "Errors in the Movie "Jurassic Park"". American Paleontologist 4 (2): 4–7.
- ^ Crichton, Michael (1990). Jurassic Park. Alfred A. Knopf. ISBN 0-394-58816-9.
- ^ The Making of Jurassic Park by Don Shay & Jody Duncan, Boxtree Ltd; 1st Edition. edition (30 Jun 1993), ISBN 1852837748
External links
Categories:- Coelophysoids
- Dinosaurs of Asia
- Dinosaurs of North America
- Jurassic dinosaurs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.




