- Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
-
Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 
Parliament of the United KingdomLong title An Act to make new provision with respect to dangerous or otherwise harmful drugs and related matters, and for purposes connected therewith. Statute book chapter 1971 c. 38 Introduced by Reginald Maudling Territorial extent England and Wales; Scotland; Northern Ireland Dates Royal Assent 27 May 1971 Status: Amended Text of statute as originally enacted Official text of the statute as amended and in force today within the United Kingdom, from the UK Statute Law Database The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 is an Act of Parliament which represents UK action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs,[1] the Convention on Psychotropic Substances,[2] and the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances.[3] No such Treaty is however in any way binding on the UK Courts or Parliament and these have not been incorporated into UK law.
Offences under the Act include:[4]
- Possession of a controlled drug unlawfully
- Possession of a controlled drug with intent to supply it
- Supplying or offering to supply a controlled drug (even where no charge is made for the drug)
- Allowing premises you occupy or manage to be used unlawfully for the purpose of producing or supplying controlled drugs
It is often presented as little more than a list of prohibited drugs and of penalties linked to their possession and supply. In practice, however, the act establishes the Home Secretary as a key player in a drug licensing system. Therefore, for example, various opiates are available legally as prescription-only medicines, and cannabis (hemp)[5] may be grown under licence for 'industrial purposes'. The Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001,[6] created under the 1971 Act, are about licensing of production, possession and supply of substances classified under the act.
The act creates three classes of controlled substances, A, B, and C, and ranges of penalties for illegal or unlicensed possession and possession with intent to supply are graded differently within each class. The lists of substances within each class can be amended by order, so the Home Secretary can list new drugs and upgrade, downgrade or delist previously controlled drugs with less of the bureaucracy and delay associated with passing an act through both Houses of Parliament.
Critics of the Act say that its classification is not based on how harmful or addictive the substances are, and that it is unscientific to omit substances like tobacco and alcohol.
Contents
List of controlled drugs
Main article: Drugs controlled by the UK Misuse of Drugs ActThe Act sets out four separate categories: Class A, Class B, Class C and temporary class drugs. Substances may be removed and added to different parts of the schedule by statutory instrument, provided a report of the Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs has been commissioned and has reached a conclusion, although the Secretary of State is not bound by the council's findings.
- Class A includes heroin, cocaine, crack, ecstasy, methamphetamine, LSD and psilocybin mushrooms
- Class B includes amphetamine, codeine, cannabis, and methylphenidate
- Class C includes GHB, ketamine, diazepam, flunitrazepam and most other tranquillisers, sleeping tablets and benzodiazepines as well as anabolic steroids.
- There are currently no temporary class drugs.
Penalties
The penalties for drug offences depend on the class of drug involved. These penalties are enforced against those who do not have a valid prescription or licence to possess the drug in question. Thus it is not illegal for someone to possess heroin, a class A drug, so long as it was administered to them legally (by prescription).
Class A drugs attract the highest penalty, and imprisonment is both "proper and expedient".[7] The maximum penalties possible are as follows:[8]
Offence Court Class A Class B/Temporary class Class C Possession Magistrates 6 months / £5000 fine 3 months / £2500 fine 3 months / £500 fine Crown 7 years / unlimited fine 5 years / unlimited fine 2 years / unlimited fine Supply Magistrates 6 months / £5000 fine 6 months / £5000 fine 3 months / £2000 fine Crown Life / unlimited fine 14 years / unlimited fine 14 years / unlimited fine International cooperation
The act makes it a crime to assist in, incite, or induce, the commission of an offence, outside the UK, against another nation's corresponding law on drugs. A corresponding law is defined as another country's law "providing for the control and regulation in that country of the production, supply, use, export and import of drugs and other substances in accordance with the provisions of the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs" or another drug control treaty to which the UK and the other country are parties. An example might be lending money to a United States drug dealer for the purpose of violating that country's Controlled Substances Act.
History
The Drugs (Prevention of Misuse) Act 1964 controlled amphetamines in the United Kingdom in advance of international agreements and was later used to control LSD.
Before 1971, the UK had a relatively liberal drugs policy and it was not until United States influence had been brought to bear, particularly in United Nations circles, that controlling incidental drug activities was employed to effectively criminalise drugs use. However, it is important to note that, bar the smoking of opium and cannabis; Section 8, part d, under the 1971 Act was not an offence (relating to the prosecution of the owner of a premises/building inside of which controlled drugs were being used). However section 8 of the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 [9] was amended by Regulation 13 of Misuse of Drugs Regulations 1985 [10] and Section 38 of the Criminal Justice and Police Act 2001.[11] These amendments were however repealed in 2005 by Schedule 1 (part 6) of the Drugs Act 2005,.[12][13]
The Current Section 8 covers: people knowingly allowing premises they own, manage, or have responsibility for, to be used by any other person for:
- administration or use of any controlled drug
- supply of any controlled drug
- the production or cultivation of controlled drugs, (such as growing cannabis, making Crystal meth, preparing Magic mushrooms).[14]
Criticism and controversy
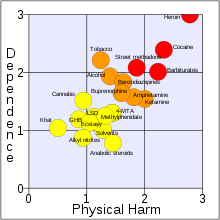 A proposed categorization of hard (red), soft (yellow) and borderline drugs (orange), following Nutt's study.[15]
A proposed categorization of hard (red), soft (yellow) and borderline drugs (orange), following Nutt's study.[15]
Notable criticism of the act includes:
- Drug classification: making a hash of it?, Fifth Report of Session 2005–06, House of Commons Science and Technology Committee, which said that the present system of drug classification is based on historical assumptions, not scientific assessment.[16]
- Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse, David Nutt, Leslie A. King, William Saulsbury, Colin Blakemore, The Lancet, 24 March 2007, said the act is "not fit for purpose" and "the exclusion of alcohol and tobacco from the Misuse of Drugs Act is, from a scientific perspective, arbitrary."[15][17]
The Transform Drug Policy Foundation offers rational criticism of the harms caused by the Government's current prohibitionist drug policy.[18] The Drug Equality Alliance (DEA) has launched legal actions against the UK Government's partial and unequal administration of the Act's discretionary powers, making particular reference to the arbitrary exclusion of alcohol and tobacco on the subjective grounds of historical and cultural precedents contrary to the Act's policy and objects.[19]
Classification of cannabis has become especially controversial. In 2004, cannabis[5] was reclassified from class B to class C,[20] in accordance with advice from the Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD). In 2009, it was returned to class B,[21] against ACMD advice.
In February 2009 the UK government was accused by its most senior expert drugs adviser Professor David Nutt of making a political decisions with regard to drug classification in rejecting the scientific advice to downgrade ecstasy from a class A drug. The Advisory Council on the Misuse of Drugs (ACMD) report on ecstasy, based on a 12-month study of 4,000 academic papers, concluded that it is nowhere near as dangerous as other class A drugs such as heroin and crack cocaine, and should be downgraded to class B. The advice was not followed.[22] Jacqui Smith, then Home Secretary, was also widely criticised by the scientific community for bullying Professor David Nutt into apologising for his comments that, in the course of a normal year, more people died from falling off horses than died from taking ecstasy.[23] Professor Nutt was later sacked by Alan Johnson (Jacqui Smith's successor as Home Secretary); Johnson saying "It is important that the government's messages on drugs are clear and as an advisor you do nothing to undermine public understanding of them. I cannot have public confusion between scientific advice and policy and have therefore lost confidence in your ability to advise me as Chair of the ACMD."[24][25]
In May 2011, a report named Taking Drugs Seriously was released by Demos. It discusses several issues with the current system, since its enactment in 1971. It states that the constant presence of new drugs will make it difficult for the government to keep up with the latest situation - over 600 drugs are now classified on the act. Comparison levels of harm previously demonstrated by David Nutt show that alcohol and tobacco were among the most lethal, while some class A drugs, such as LSD, ecstasy and magic mushrooms, were among the least harmful. [26]
See also
References
- ^ "''Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, 1961'', United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime website, accessed 6 February 2009". Unodc.org. 2007-10-24. http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/treaties/single-convention.html. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "''Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971'', United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime website, accessed 6 February 2009". Unodc.org. 2007-10-24. http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/treaties/psychotropics.html. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "''Convention against the Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988'', United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime website, accessed 6 February 2009". Unodc.org. 2007-10-24. http://www.unodc.org/unodc/en/treaties/illicit-trafficking.html. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "''Misuse of Drugs Act'', Home Office representation of the act, Home Office website, accessed 27 January 2009". Drugs.homeoffice.gov.uk. http://drugs.homeoffice.gov.uk/drugs-laws/misuse-of-drugs-act/. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ a b All varieties of cannabis, including those grown as hemp, are controlled under the act, not just drug varieties.
- ^ "''The Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001'', OPSI website, accessed 28 January 2009". Opsi.gov.uk. 2010-07-16. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/si/si2001/20013998.htm. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ R v Aramah (1982) 4 Cr App R (S) 407, per Lord Lane CJ
- ^ Class A, B and C drugs, Home Office website, accessed 27 January 2009
- ^ "Misuse of Drugs Act 1971". Opsi.gov.uk. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/RevisedStatutes/Acts/ukpga/1971/cukpga_19710038_en_1#pb4-l1g8. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ http://www.drugshelp.info/downloads/modr1985.pdf
- ^ "The Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001". Opsi.gov.uk. 2010-07-16. http://opsi.gov.uk/si/si2001/20013998. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "Drugs Act 2005". Opsi.gov.uk. 2010-07-16. http://www.opsi.gov.uk/acts/acts2005/ukpga_20050017_en_1. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "Tables of legislative effects - Statute Law Database". Statutelaw.gov.uk. http://www.statutelaw.gov.uk/Toes.aspx?autoPopulate=Y&affectingyear=2005&affectedyear=1971&affectednumber=38. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ DrugScope. "RESOURCES | What are the UK drug laws?". DrugScope. http://www.drugscope.org.uk/resources/faqs/faqpages/what-are-the-uk-drug-laws. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ a b Nutt, D.; King, L. A.; Saulsbury, W.; Blakemore, C. (2007). "Development of a rational scale to assess the harm of drugs of potential misuse". The Lancet 369 (9566): 1047–1053. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60464-4. PMID 17382831.
- ^ "Microsoft Word - HC1031.doc" (PDF). http://www.publications.parliament.uk/pa/cm200506/cmselect/cmsctech/1031/1031.pdf. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "''Scientists want new drug rankings'', BBC News website, 23 March 2007, accessed 27 January 2009". BBC News. 2007-03-23. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/health/6474053.stm?ls#drugs. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "Transform Drug Policy Foundation website, accessed 30 January 2009". Tdpf.org.uk. http://www.tdpf.org.uk/. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "Drug Equality Alliance - Mission". Drug Equality Alliance. http://www.drugequality.org. Retrieved 2009-08-28.
- ^ "''The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Modification) (No. 2) Order 2003 (No. 3201)'', OPSI website, accessed 27 January 2009". Statutelaw.gov.uk. 2004-01-29. http://www.statutelaw.gov.uk/content.aspx?ActiveTextDocId=869446. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ "''The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (Amendment) Order 2008 (No. 3130)'', OPSI website, accessed 27 January 2009". Statutelaw.gov.uk. 2008-12-10. http://www.statutelaw.gov.uk/content.aspx?LegType=All+Legislation&title=The+Misuse+of+Drugs+Act+1971&searchEnacted=0&extentMatchOnly=0&confersPower=0&blanketAmendment=0&sortAlpha=0&TYPE=QS&PageNumber=1&NavFrom=0&parentActiveTextDocId=3540710&ActiveTextDocId=3540710&filesize=8254. Retrieved 2011-01-23.
- ^ Travis, Alan (February 2009). "Government criticised over refusal to downgrade ecstasy". The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/politics/2009/feb/11/ecstasy-downgrade-drugs-class.
- ^ Kmietowicz Z (2009). "Home secretary accused of bullying drugs adviser over comments about ecstasy". BMJ 338: b612. doi:10.1136/bmj.b612. PMID 19218327.
- ^ Easton, Mark (30 October 2009) Nutt gets the sack, BBC News.
- ^ Tran, Mark (30 October 2009) Government drug adviser David Nutt sacked, The Guardian.
- ^ http://www.demos.co.uk/files/Taking_Drugs_Seriously_-_web.pdf?1305207826
External links
- UK Misuse of Drugs Act, Steve Chapman website, access 28 January 2009
- Controlled Drugs, Patient UK website, accessed 30 January 2009
- Drugs Act 2005 (c. 17), OPSI website, accessed 2 February 2009
United Kingdom legislation Pre-Parliamentary legislation Acts of Parliament by states preceding
the Kingdom of Great BritainActs of the Parliament of England to 1483 · 1485–1601 · 1603–1641 · Interregnum (1642–1660) · 1660–1699 · 1700–1706
Acts of the Parliament of Scotland
Acts of the Parliament of Ireland to 1700 · 1701–1800Acts of Parliament of the
Kingdom of Great Britain1707–1719 · 1720–1739 · 1740–1759 · 1760–1779 · 1780–1800
Acts of Parliament of the United Kingdom of
Great Britain and Ireland and the United
Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandChurch of England Measures Legislation of devolved institutions Acts of the Scottish Parliament
Acts and Measures of the Welsh Assembly
Acts of the Northern Ireland Assembly / of the Northern Ireland Parliament
Orders in Council for Northern IrelandSecondary legislation Regulation of therapeutic goods Americas Eurasia European Union · India · Netherlands · Norway · Portugal · Singapore · Soviet Union · Switzerland · Thailand · United KingdomOceania Categories:- United Kingdom Acts of Parliament 1971
- Misuse of Drugs Act 1971
- Drug control law
- English criminal law
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


