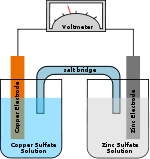
- Concentration cell
-
A concentration cell is a limited form of a galvanic cell that has two equivalent half-cells of the same material differing only in concentrations. One can calculate the potential developed by such a cell using the Nernst Equation. A concentration cell produces a voltage as it attempts to reach equilibrium. This equilibrium occurs when the concentration of reactant in both cells are equal.
Concentration cells generate electricity from the free energy that can be extracted from the difference in chemical concentrations of reactants, in the same reaction. This energy is generated from thermal energy that the cells absorb as heat, as the electricity flows. This generation of electricity from ambient thermal energy, without a temperature gradient, is possible because the convergence of chemical concentrations in the two cells increases entropy, and this increase more than compensates for the entropy decreased when heat is converted into electrical energy.
Concentration cell methods of chemical analysis compare a solution of known concentration with an unknown, determining the concentration of the unknown via the Nernst Equation or comparison tables against a group of standards.
Concentration cell corrosion occurs when two or more areas of a metal surface are in contact with different concentrations of the same solution. There are three general types of concentration cells:
Contents
Metal ion concentration cells
In the presence of water, a high concentration of metal ions will exist under faying surfaces and a low concentration of metal ions will exist adjacent to the crevice created by the faying surfaces. An electrical potential will exist between the two points. The area of the metal in contact with the high concentration of metal ions will be cathodic and will be protected, and the area of metal in contact with the low metal ion concentration will be anodic and corroded.[citation needed]
Oxygen concentration cells
Water in contact with the metal surface will normally contain dissolved oxygen. An oxygen cell can develop at any point where the oxygen in the air is not allowed to diffuse uniformly into the solution, thereby creating a difference in oxygen concentration between two points. Corrosion will occur at the area of low-oxygen concentration which are anodic.
Active-passive cells
For metals that depend on a tightly adhering passive film (usually an oxide) for corrosion protection, salt that deposits on the metal surface in the presence of water, in areas where the passive film is broken, the active metal beneath the film will be exposed to corrosive attack. An electrical potential will develop between the large area of the cathode (passive film) and the small area of the anode (active metal). Rapid pitting of the active metal will result.
See also
- Liquid junction potential
- Electrochemical potential
- Membrane potential
Categories:- Battery (electricity)
- Chemistry stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.