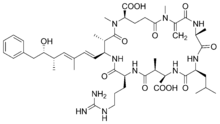
- Microcystin
-
Microcystins are cyclic nonribosomal peptides produced by cyanobacteria (e.g.Microcystis aeruginosa). They are cyanotoxins and can be very toxic for plants and animals including humans. Their hepatotoxicity may cause serious damage to the liver. Microcystins can strongly inhibit protein phosphatases type 1 (PP1) and 2A (PP2A), and are linked to pansteatitis. [1]
Microcystins consist of several uncommon non-proteinogenic amino acids such as dehydroalanine derivatives and the special β-amino acid ADDA ((all-S,all-E)-3-Amino-9-methoxy-2,6,8-trimethyl-10-phenyldeca-4,6-diene acid).
Microcystin-LR is one of over 80 known toxic variants and is the most studied by chemists, pharmacologists, biologists and ecologists. Microcystin-containing 'blooms' are a problem worldwide, including China, Brazil, Australia, the United States and much of Europe. Once ingested, microcystin travels to the liver, via the bile acid transport system, where most is stored; though some remains in the blood stream and may contaminate tissue. Microcystin binds covalently to protein phosphatases thus disrupting cellular control processes.
There appears to be inadequate information to assess carcinogenic potential of microcystins by applying EPA Guidelines for Carcinogen Risk Assessment. A few studies suggest that there may be a relationship between liver and colorectral cancers and the occurrence of cyanobacteria in drinking water in China (Yu et al., 1989; Zhou et al., 2002). Evidence is, however, limited due to limited ability to accurately assess and measure exposure.
See also
References
- National Center for Environmental Assessment. Toxicological Reviews of Cyanobacterial Toxins: Microcystins LR, RR, YR and LA (NCEA-C-1765)
- Yu, S.-Z. 1989. Drinking water and primary liver cancer. In: Primary Liver Cancer, Z.Y. Tang, M.C. Wu and S.S. Xia, Ed. China Academic Publishers, New York, NY. p. 30-37 (as cited in Ueno et al., 1996 and Health Canada, 2002).
- Zhou, L., H. Yu and K. Chen. 2002. Relationship between microcystin in drinking water and colorectal cancer. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 15(2):166-171.
External links
Categories:- Peptides
- Biomolecules
- Cyanotoxins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.