- Superseded scientific theories
-
A superseded, or obsolete, scientific theory is a scientific theory that was once commonly accepted but that is no longer considered the most complete description of reality by a mainstream scientific consensus, or a theory which has been shown to be false. This label does not cover protoscientific or fringe science theories with limited support in the scientific community, nor does it describe theories that were never widely accepted. Some theories which were only supported under specific political authorities, such as Lysenkoism, may also be described as obsolete or superseded.
In some cases a theory or idea is found to be baseless and is simply discarded: for example, the phlogiston theory was entirely replaced by the quite different concept of energy and related laws. In other cases an existing theory is replaced by a new theory which retains elements of the earlier theory; in these cases, the older theory is often still useful because it provides a description that is "good enough" for many purposes, is more easily understood than the complete theory, and may lead to simpler calculations. An example of this is the use of Newtonian physics, which differs from the currently accepted relativistic physics by a factor which is negligibly small at velocities much lower than that of light. Newtonian physics is so satisfactory for most purposes that many secondary educational systems teach it, but not the "correct", but more complex, relativity. Another case is the theory that the earth is approximately flat; while clearly wrong for long distances, viewing a landscape as flat is still sufficient for some local maps and surveying.
Karl Popper suggested that a theory should be considered scientific if and only if it can in principle be falsified by experiment; any idea not susceptible to falsification does not belong to science.
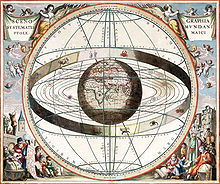 The obsolete Geocentric model of the universe places the Earth at the centre.
The obsolete Geocentric model of the universe places the Earth at the centre.
Contents
Superseded theories
Biology
- Spontaneous generation - is a principle regarding the origin of life from inanimate matter, which held that this process was a commonplace and everyday occurrence, as distinguished from univocal generation, or reproduction from parent(s). Rendered obsolete by Darwinism and abiogenesis.
- Transmutation of species, Lamarckism, Inheritance of acquired characteristics - first theories of evolution. Rendered obsolete by Darwinian evolution, Mendelian genetics and Epigenetics.
- Mendelian genetics, Classical genetics, Boveri–Sutton chromosome theory - first genetical theories. They are part of molecular genetics now.
- Maternal impression – the theory that the mother's thoughts created birth defects. Rendered obsolete by genetic theory (see also fetal origins of adult disease, genomic imprinting)
- Miasma theory of disease – the theory that diseases are caused by "bad air". Rendered obsolete by the germ theory of disease.
- Preformationism – the theory that all organisms have existed since the beginning of life, and that gametes contain a miniature but complete preformed individual. Rendered obsolete by cytology, discovery of DNA and Atomic theory.
- Recapitulation theory – the theory that "ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny". See Baer's laws of embryology.
- Telegony (pregnancy) – the theory that an offspring can inherit characteristics from a previous mate of its mother's as well as its actual parents, often associated with racism.
Chemistry
- Classical elements – discredited by Rhazes
- Caloric theory
- Phlogiston theory – replaced by Lavoisier's work on oxidation
- Part of Dalton's law[clarification needed]
- Vital essence theory, discredited by Friedrich Wöhler
Physics
- Emission theory of vision – discredited by Ibn al-Haytham (Alhacen)
- Aristotelian physics – superseded by Newtonian physics
- Luminiferous aether – failed to be detected by the sufficiently sensitive Michelson-Morley experiment, made obsolete by Einstein's work.
- Caloric theory – Lavoisier's successor to phlogiston, discredited by Rumford's and Joule's work
- Vis viva – Gottfried Leibniz's elementary and limited early formulation of the principle of conservation of energy
- "Purely electrostatic" theories of the generation of voltage differences.
- Emitter theory – another now-obsolete theory of light propagation.
- Progression of atomic theory
-
- Plum pudding model of the atom – assuming the protons and electrons were mixed together in a single mass
- Rutherford model of the atom with an impenetrable nucleus orbitted by electrons.
- Bohr model with quantized orbits
- Electron cloud model following the development of Quantum Mechanics in 1925 and the eventual atomic orbital models derived from the quantum mechanical solution to the hydrogen atom.
- All of classical physics, while useful in practice, is in principle superseded by relativistic physics and quantum physics, to which classical physics is often a close approximation.
Astronomy and cosmology
- Ptolemaic system – replaced by Nicolaus Copernicus' Heliocentric model.
- Geocentric universe – obsoleted by Copernicus
- Heliocentric universe
- Copernican system – obsoleted by Johannes Kepler and Isaac Newton
- Newtonian gravity – superseded by general relativity, to which it is an excellent approximation unless the masses involved are very large or the distances very small. The anomalous perihelion precession of Mercury was the first experimental evidence that Newtonian gravity was not totally accurate.
- Luminiferous aether theory
- Steady State Theory, a model developed by Hermann Bondi, Thomas Gold, and Fred Hoyle whereby the expanding universe was in a steady state, and had no beginning. It was a competitor of the Big Bang model until evidence supporting the Big Bang and falsifying the steady state was found.
Geography and climate
- Flat Earth theory. On length scales much smaller than the radius of the Earth, a flat map projection gives a quite accurate and practically useful approximation to true distances and sizes, but departures from flatness become increasingly significant over larger distances.
- Hollow Earth theory
- The Open Polar Sea, an ice-free sea once supposed to surround the North Pole
- Rain follows the plow – the theory that human settlement increases rainfall in arid regions (only true to the extent that crop fields evapotranspirate more than barren wilderness)
Geology
- Expanding Earth theory was superseded by subduction
- Catastrophism was largely replaced by uniformitarianism
- Geosyncline theory was superseded by plate tectonics
Psychology
- Pure behaviorist explanations for language acquisition in infancy, falsified by the study of cognitive adaptations for language.[1]
- The blank slate theory of socialization, disproven by research on cross-cultural universals[citation needed].
Medicine
- Theory of the four bodily humours
- Eclectic Medicine – Transformed into alternative medicine, and is no longer considered a scientific theory.
- Physiognomy, related to phrenology, held that inner character was strongly correlated with physical appearance.
Obsolete branches of enquiry
- Alchemy, which led to the development of chemistry
- Astrology, which led to the development of astronomy
- Phrenology, a pseudoscience
- Numerology (as distinct from number theory), a pseudoscience
Theories now considered to be incomplete
Here are theories that are no longer considered the most complete representation of reality, but are still useful in particular domains or under certain conditions. For some theories a more complete model is known, but in practical use the coarser approximation provides good results with much less calculation.
- Atomic theory initially proposed that atoms were indivisible, but now it is known that they are composed of subatomic particles.
- Atomic nuclei disintegrate at high energy.
- Newtonian mechanics was extended by the theory of relativity and by quantum mechanics. Relativistic corrections to Newtonian mechanics are unmeasurably small at velocities not approaching the speed of light, and quantum corrections are usually negligible at atomic or larger scales; Newtonian mechanics is totally satisfactory in engineering and physics under most circumstances.
- Classical electrodynamics approximates quantum electrodynamics.
- Bohr model of the atom was extended by the quantum mechanical model of the atom.
- Newton's sine-square law for the force of a fluid on a body[citation needed] is no longer considered useful at low speeds, though it has found application in hypersonic flow.
References
- ^ Crain, Stephen and Diane C. Lillo-Martin (1999). An Introduction to Linguistic Theory and Language Acquisition. Oxford: Blackwell.
See also
- Science
- Scientific theory
- Philosophy of science
- Protoscience
- Fringe science
- Pathological science
- Paradigm shift
- Timeline of cosmology
- Historical cosmologies
- History of evolutionary thought
- Creation–evolution controversy
- History of genetics
- Lists
- List of discredited substances
- List of famous discoveries
- List of famous experiments
- List of topics characterized as pseudoscience
Pseudoscience Terminology Cargo cult science · Charlatan · Crank · Fringe science · Junk science · Paranormal · Pathological science · Quackery · Snake oil · Superseded scientific theories · True-believer syndrome
Examples AIDS denialism • Astrology • Body memory • Bogdanov Affair • Creation Science • Dianetics • Faith healing • Homeopathy • Intelligent design • Japhetic theory • Lunar effect • Lysenkoism • Melanin theory • Moon landing conspiracy theories • Nibiru collision • Parapsychology • Perpetual motion • Ufology
Resources List of topics characterized as pseudoscience Categories:- Obsolete scientific theories
- History of science
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
