- Aspergillosis
-
Aspergillosis Classification and external resources 
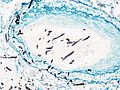
Histopathologic image of pulmonary invasive aspergillosis in a patient with interstitial pneumonia. Autopsy material. Grocott's methenamine silver stain.ICD-10 B44 ICD-9 117.3 MedlinePlus 001326 eMedicine med/174 MeSH D001228 Aspergillosis is the name given to a wide variety of diseases caused by fungi of the genus Aspergillus. The most common forms are allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, pulmonary aspergilloma and invasive aspergillosis. Most humans inhale Aspergillus spores every day. Aspergillosis develops mainly in individuals who are immunocompromised, either from disease or from immunosuppressive drugs, and is a leading cause of death in acute leukemia and hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Conversely, it may also develop as an allergic response. The most common cause is Aspergillus fumigatus.
Contents
Symptoms
A fungus ball in the lungs may cause no symptoms and may be discovered only with a chest X-ray, or it may cause repeated coughing up of blood and occasionally severe, even fatal, bleeding. A rapidly invasive Aspergillus infection in the lungs often causes cough, fever, chest pain, and difficulty breathing.
Aspergillosis affecting the deeper tissues makes a person very ill. Symptoms include fever, chills, shock, delirium, and blood clots. The person may develop kidney failure, liver failure (causing jaundice), and breathing difficulties. Death can occur quickly.
Aspergillosis of the ear canal causes itching and occasionally pain. Fluid draining overnight from the ear may leave a stain on the pillow. Aspergillosis of the sinuses causes a feeling of congestion and sometimes pain or discharge.
In addition to the symptoms, an X-ray or computerised tomography (CT) scan of the infected area provides clues for making the diagnosis. Whenever possible, a doctor sends a sample of infected material to a laboratory to confirm identification of the fungus.
Diagnosis
On chest X-ray and CT, pulmonary aspergillosis classically manifests as an air crescent sign.[1] In hematologic patients with invasive aspergillosis, the galactomannan test can make the diagnosis in a noninvasive way.
On microscopy, Aspergillus species are reliably demonstrated by silver stains, e.g., Gridley stain or Gomori methenamine-silver.[2] These give the fungal walls a gray-black colour. The hyphae of Aspergillus species range in diameter from 2.5 to 4.5 µm. They have septate hyphae,[3] but these are not always apparent, and in such cases they may be mistaken for Zygomycota.[2] Aspergillus hyphae tend to have dichotomous branching that is progressive and primarily at acute angles of about 45°.[2]
Treatment
The current treatments include voriconazole and liposomal amphotericin B. Newer findings suggest use of mild oral steroids for a longer period of time, preferably for 6-9 months in aspergillosis in pulmonary segment.
Other drugs used, such as amphotericin B, caspofungin (in combination therapy only), flucytosine (in combination therapy only) or itraconazole,[4][5] are used to treat this fungal infection. However, a growing proportion of infections are resistant to the triconazoles.[6]
Infections in animals
Albeit relatively rare in humans, aspergillosis is a common and dangerous infection in birds, particularly in pet parrots. Mallards and other ducks are particularly susceptible, as they will often resort to poor food sources during bad weather. Captive raptors, such as falcons and hawks, are susceptible to this disease if they are kept in poor conditions and especially if they are fed pigeons, which are often carriers of "asper".
Aspergillosis has been the culprit in several recent rapid die-offs among waterfowl. From 8 December until 14 December 2006, over 2,000 Mallards died in the Burley, Idaho area, an agricultural community approximately 150 miles southeast of Boise. Moldy waste grain from the farmland and feedlots in the area is the suspected source. A similar aspergillosis outbreak caused by moldy grain killed 500 Mallards in Iowa in 2005.
While there is no connection between aspergillosis and the H5N1 strain of avian influenza (commonly called "bird flu"), rapid die-offs caused by aspergillosis can spark fears of bird flu outbreaks. Laboratory analysis is the only way to distinguish bird flu from aspergillosis.
See also
- Primary cutaneous aspergillosis
- Otomycosis
References
- ^ Curtis A, Smith G, Ravin C (1 October 1979). "Air crescent sign of invasive aspergillosis.". Radiology 133 (1): 17–21. doi:10.1148/133.1.17. PMID 472287. http://radiology.rsnajnls.org/cgi/content/abstract/133/1/17?ijkey=657da61e6546d66bd27550542bc4d25be2efe638&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha.
- ^ a b c Kradin RL, Mark EJ (April 2008). "The pathology of pulmonary disorders due to Aspergillus spp". Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 132 (4): 606–14. doi:10.1043/1543-2165(2008)132[606:TPOPDD]2.0.CO;2. PMID 18384212.
- ^ "Mycology Online -- Aspergillosis". http://www.mycology.adelaide.edu.au/Mycoses/Opportunistic/Aspergillosis/. Retrieved 2008-12-10.
- ^ Herbrecht R, Denning D, Patterson T, Bennett J, Greene R, Oestmann J, Kern W, Marr K, Ribaud P, Lortholary O, Sylvester R, Rubin R, Wingard J, Stark P, Durand C, Caillot D, Thiel E, Chandrasekar P, Hodges M, Schlamm H, Troke P, de Pauw B; Invasive Fungal Infections Group of the European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer and the Global Aspergillus Study Group. (Aug 8 2002). "Voriconazole versus amphotericin B for primary therapy of invasive aspergillosis". N Engl J Med 347 (6): 408–15. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa020191. PMID 12167683.
- ^ Cornely O.A., Maertens J., Bresnik M.,Ebrahimi R., Ullman A., Bouza E., Heussel C.P., Lothorlary O., Rieger C., Boehme A., Aoun M., Horst H., Thiebaut A., Ruhnke M., Reichert D., Vianelli N., Krause S., Olavarria E., Herbrecht R., for the AmBiLoad Trial Study Group (2007). "Liposomal Amphotericin B as initial therapy for invasive mold infection: a randomized trial comparing a high-loading dose regimen with a standard dosing (AmBiLoad trial)". CID 44 (10): 1289–1297. doi:10.1086/514341.
- ^ Denning DW, Park S, Lass-Florl C, Fraczek MG, Kirwan M, Gore R, Smith J, Bueid A, Bowyer P, Perlin DS (2011). "High-frequency Triazole Resistance Found In Nonculturable Aspergillus fumigatus from Lungs of Patients with Chronic Fungal Disease". Clin Infect Dis 52 (9): 1123–9. doi:10.1093/cid/cir179. PMC 3106268. PMID 21467016. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3106268.
Additional images
External links
- USGS National Wildlife Health Center
- Aspergillus - Aspergillus website
- Aspergillosis at DoctorFungus.org
- News article in The Guardian
Infectious diseases · Mycoses and Mesomycetozoea (B35–B49, 110–118) Superficial and
cutaneous
(dermatomycosis):
Tinea=skin;
Piedra (exothrix/
endothrix)=hairBy locationTinea barbae/Tinea capitis (Kerion) · Tinea corporis (Ringworm, Dermatophytid) · Tinea cruris · Tinea manuum · Tinea pedis (Athlete's foot) · Tinea unguium/Onychomycosis (White superficial onychomycosis · Distal subungual onychomycosis · Proximal subungual onychomycosis)
Tinea corporis gladiatorum · Tinea faciei · Tinea imbricata · Tinea incognito · FavusBy organismEpidermophyton floccosum · Microsporum canis · Microsporum audouinii · Trichophyton interdigitale/mentagrophytes · Trichophyton tonsurans · Trichophyton schoenleini · Trichophyton rubrumOtherHortaea werneckii (Tinea nigra) · Piedraia hortae (Black piedra)Subcutaneous,
systemic,
and opportunisticDimorphic
(yeast+mold)Coccidioides immitis/Coccidioides posadasii (Coccidioidomycosis, Disseminated coccidioidomycosis, Primary cutaneous coccidioidomycosis. Primary pulmonary coccidioidomycosis) · Histoplasma capsulatum (Histoplasmosis, Primary cutaneous histoplasmosis, Primary pulmonary histoplasmosis, Progressive disseminated histoplasmosis) · Histoplasma duboisii (African histoplasmosis) · Lacazia loboi (Lobomycosis) · Paracoccidioides brasiliensis (Paracoccidioidomycosis)OtherBlastomyces dermatitidis (Blastomycosis, North American blastomycosis, South American blastomycosis) · Sporothrix schenckii (Sporotrichosis) · Penicillium marneffei (Penicilliosis)Yeast-likeCandida albicans (Candidiasis, Oral, Esophageal, Vulvovaginal, Chronic mucocutaneous, Antibiotic candidiasis, Candidal intertrigo, Candidal onychomycosis, Candidal paronychia, Candidid, Diaper candidiasis, Congenital cutaneous candidiasis, Perianal candidiasis, Systemic candidiasis, Erosio interdigitalis blastomycetica) · C. glabrata · C. tropicalis · C. lusitaniae · Pneumocystis jirovecii (Pneumocystosis, Pneumocystis pneumonia)Mold-likeAspergillus (Aspergillosis, Aspergilloma, Allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, Primary cutaneous aspergillosis) · Exophiala jeanselmei (Eumycetoma) · Fonsecaea pedrosoi/Fonsecaea compacta/Phialophora verrucosa (Chromoblastomycosis) · Geotrichum candidum (Geotrichosis) · Pseudallescheria boydii (Allescheriasis)Entomophthorales
(Entomophthoramycosis)Basidiobolus ranarum (Basidiobolomycosis) · Conidiobolus coronatus/Conidiobolus incongruus (Conidiobolomycosis)Enterocytozoon bieneusi/Encephalitozoon intestinalisMesomycetozoea Ungrouped Alternariosis · Fungal folliculitis · Fusarium (Fusariosis) · Granuloma gluteale infantum · Hyalohyphomycosis · Otomycosis · PhaeohyphomycosisCategories:- Fungal diseases
- Mycosis-related cutaneous conditions
- Poultry diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.