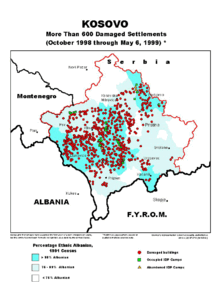
- Operation Horseshoe
-
Operation Horseshoe is a name attributed to a large-scale antiterrorism campaign which during the NATO bombing [1] escalated to ethnic cleansing of Kosovo Albanians carried out by Serbian Police and Yugoslav Army during the Kosovo War.[2][3][4]
The Yugoslav Army and the Serbian Police in early 1999 "in an organized manner, with significant use of state resources" conducted a broad campaign of violence against Albanian civilians to expel them from Kosovo and thus maintain political control of Belgrade over the province.[5][6] Serbian campaign of ethnic cleansing was cited in support of the NATO intervention. After the war, International War Crimes Tribunal sentenced some of the top Serbian political and military leaders for forcible population transfer, deportation and persecution of Kosovo civilians.[5]
Some authors dispute the existence of such a plan or some of its aspects.[7] Also, it remains unclear whether the codename "Operation Horseshoe" (Serbian: Операција Потковица, Operacija Potkovica) was ever used for a Serbian military operation.
Contents
Horseshoe plan
Horseshoe plan (German: Hufeisenplan) was the name given by the German government to a Serbian plan to expel the Albanian population of Kosovo. The operation's title suggest that Serbian military and police would squeeze the KLA and civilians in an attack launched from three sides, driving out the population as refugees fled through the open southwestern end of the horseshoe into Macedonia and Albania.[2]
The plan was detailed by German Foreign Minister Joschka Fischer in a press conference on 7 April 1999. He stated that the German government had unearthed operational plans agreed by Yugoslav commanders in late February 1999 to carry out a massive ethnic cleansing operation in Kosovo. According to Fischer, this had been put into effect as early as March 1999 — a month before the start of NATO operations — when Yugoslav President Slobodan Miloševic had told him that "he would be finished with the ethnic Albanian separatists within a week". Fischer accused Miloševic of engaging in "ethnic warfare" directed against his own people, in which a whole ethnic group had become the "victim of systematic expulsion" to "reorient the political geography" of Kosovo.
Reports from other countries supported Fischer's allegations. The Times of London reported on 8 April that:
The CIA was aware as early as last autumn of a plan, codenamed Operation Horseshoe, to kill or drive them out over several months. A village a day was the rate that Mr Miloševic calculated the West would wring its hands over without acting. In Priština, public records have been combed to identify precisely which homes, shops and businesses were Albanian-owned; Serb police and paramilitaries have emptied towns and villages neighbourhood by neighbourhood in a pattern that has been as unvaried as it has been ruthless. The packed trains, the snipers picking off those who strayed out of line on the forced marches to the borders: every detail points to the existence of a detailed blueprint, without which so many could not have been murdered or driven into exile within a fortnight. In this context, yesterday's reported sealing of the frontiers by Serb forces is a sinister development; there is no such thing as safety in Kosovo for a people marked for destruction solely because of their racial identity.[8]Further details were provided on 9 April by Rudolf Scharping, the German Defence Minister, at a press conference held in Bonn. He presented maps containing the names of towns and villages which showed arrows representing Yugoslav army and police militia units progressively encircling Kosovo in a horseshoe-shaped pincer movement. He was quoted as saying that: "Operation Horseshoe provided clear evidence that President Miloševic had long been preparing the expulsions from Kosovo and that he had simply used the time gained by the Rambouillet peace talks to organise army and police units for the campaign."
The Baltimore Sun suggested on 11 April that NATO had known about the Horseshoe plan for some time, but had underestimated its severity. The then British Foreign Secretary later supported the German reports, telling a parliamentary committee "that there was a plan developed in Belgrade known as Operation Horseshoe which was for the cleansing of Kosovo of its Kosovo population. That plan has been around for some time."[9]
Serbian military operations
Main articles: Kosovo War, War crimes in the Kosovo War, and Joint Criminal EnterpriseOperations before NATO intervention
 Ruins near Morina in the White Drin valley, at the border between Albania and Kosovo. Morina was attacked on 23/24 May 1998 by the Yugoslav Army.[10]
Ruins near Morina in the White Drin valley, at the border between Albania and Kosovo. Morina was attacked on 23/24 May 1998 by the Yugoslav Army.[10]
Serbian military response to KLA attacks culminated in Operation Horseshoe directed not only against KLA fighters but also including systematic expulsions of Kosovar civilians.[11] During the armed conflict in 1998 Yugoslav Army and Serbian police used excessive and random force, which resulted in property damage, displacement of population and death of civilians.[5] Some consider that Belgrade had already unleashed Operation Horseshoe as early as the summer of 1998, when hundreds of thousands of Kosovar Albanians were driven from their homes.[12]
Withdrawal of OSCE monitors, together with the start of NATO's bombing campaign, encouraged Milosevic to implement this "orchestrated elements to the campaign of expulsions, which could be described as a plan".[13] On 20 March 1999, the Serbian offensive, known as Operation Horseshoe, was already in motion.[14] Obviously, this operation was planned in advance.[15]
“ If it comes to the NATO bombing, if it comes to the American aggression, we Serbs will quite suffer, but the Albanians in Kosovo will be no more.[16] ” — Vojislav Šešelj, Serbian Deputy Prime MinisterOperations after NATO intervention
Since the beginning of NATO air attacks on the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (FRY) on 24 March, Yugoslav security forces have intensified their efforts to forcibly expel ethnic Albanians en masse from their homes.[17]
— Amnesty International memorandum to UN Security Council
With the beginning of NATO bombing of Yugoslavia on 24 March 1999, Serbian forces accelerated Operation Horseshoe.[4][18] In the Spring of 1999, the Yugoslav Army, Serbian police and Serb paramilitary, in an organized manner, with significant use of state resources, conducted a broad campaign of violence against Albanian civilians to expel them from Kosovo and thus maintain political control of Belgrade over the province.[5][6]
According to the legally binding verdict of the International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia, federal Army and Serbian police after the NATO bombing of Yugoslavia 24 March 1999, systematically attacked villages with Albanian population, abused, robbed and killed civilians, ordering them to go to Albania or Montenegro, burning their houses and destroying by their property.[19] Within the campaign of violence, Albanians were mass expelled from their homes, murdered, sexually assaulted, and their religious buildings destroyed. Serbian forces committed numerous war crimes during the implementation of "joint criminal enterprise" whose aim was to "through the use of violence and terror, force a significant number of Kosovo Albanians to leave their homes, across the border, the state government to retain control over Kosovo."[5] Ethnic cleansing of the Albanian population is performed by the following model: first the army surrounded a place, then followed the shelling, then the police entered the village, and often with them and the army, and then crimes occurs (murders, rapes, beatings, expulsions...).[19]
Serbian government also implemented a criminal strategy known as identity cleansing,[20] which consist of "confiscation of personal identification, passports, and other such documents to make it difficult or impossible for those driven out to return".[21] Expelled Kosovar Albanians were systematically stripped of identity and property documents including passports, land titles, automobile license plates, identity cards and other documents.[22] Physicians for Human Rights reports that nearly 60 percent of respondents to its survey observed Serbian forces removing or destroying personal identification documents.[23] This criminal practice suggesting the government was trying to block their return.[6]
In addition to confiscating the relevant documents from their holders, efforts were also made to destroy any actual birth records (and other archives) which were maintained by governmental agencies, so as to make the "cleansing" complete.[24]
Number of refugees
By early June 1999, more than 80 percent of the entire population of Kosovo and 90 percent of Kosovar Albanians were displaced from their homes.[6]
— Human Right Watch report
 Brazda/Stenkovac I Refugee Assistance Centre in Macedonia. At its height this Centre housed over 50,000 refugees.[25]
Brazda/Stenkovac I Refugee Assistance Centre in Macedonia. At its height this Centre housed over 50,000 refugees.[25]
According to the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, by March 1999 (prior to NATO bombing), more than 200,000 Albanian civilians were internally displaced, almost 70,000 Albanians had fled the province to neighboring countries and Montenegro, and a further 100,000 Yugoslav nationals, mostly Kosovar Albanians, had sought asylum in Western Europe.[26] Also, thousands of ethnic Albanian villages in Kosovo had been partially or completely destroyed by burning or shelling.[27]
Within three weeks of the start of NATO strategic bombing during the Kosovo War, there were 525,787 refugees from Kosovo in neighboring countries.[28] A month later, on 12 May, the total number of refugees had risen to 781,618.[29] By June 1999, the Yugoslav military, Serbian police and paramilitaries expelled 862,979 Albanians from Kosovo, A claim disputed by many Serbian politicians.[30] and several hundred thousand more were internally displaced, in addition to those displaced prior to March.[6] Approximately 440,000 refugees crossed the border to Albania and 320,000 to FYR Macedonia. Montenegro hosted around 70,000 refugees, while Bosnia and Herzegovina received more than 30,000.[6] Amnesty International estimated that "nearly one million people have been forced to flee Kosovo".[31]
Radio Television of Serbia never showed the columns of Albanians expelled by Serbian police and paramilitaries, except when a convoy of fleeing Albanians was killed by NATO bombs.[32] Moreover, Milosevic's propaganda trying to convince international public that huge columns of refugees fleeing Kosovo because of NATO's bombing, not Serbian military operations.[33]
War crime trials
The forces of the FRY and Serbia, have in a systematic manner, forcibly expelled and internally displaced hundreds of thousands of Kosovo Albanians from their homes across the entire province of Kosovo. To facilitate these expulsions and displacements, the forces of the FRY and Serbia have intentionally created an atmosphere of fear and oppression through the use of force, threats of force, and acts of violence.[34]
— War Crimes Indictment against Milosevic and others
International Criminal Tribunal for the Former Yugoslavia charged Slobodan Milosevic and other Serbian officials with crimes against humanity including murder, forcible population transfer, deportation and persecution of Kosovo civilians:
- Slobodan Milošević, President of Yugoslavia and Supreme Commander of the Yugoslav Army - died in 2006 during trial.
- Dragoljub Ojdanić, Chief of General Staff - sentenced to 15 years in prison.
- Nebojša Pavković, Commander of Third Army, which was responsible for Kosovo - sentenced to 22 years in prison.
- Vladimir Lazarević, Commander of the Pristina Corps of Third Army - sentenced to 15 years in prison.
- Vlajko Stojiljković, Interior Minister and Commander of the Serbian police - committed suicide in 2002, after the adoption of a law on cooperation with the Hague Tribunal.
- Sreten Lukić, Chief of Staff of the Serbian Police in Kosovo - sentenced to 22 years in prison.
- Nikola Šainović, Deputy Prime Minister of Yugoslavia - sentenced to 22 years in prison.
- Milan Milutinović, President of the Republic of Serbia - acquitted.
Presiding Judge Iain Bonomy was imposing sentence said that "deliberate actions of these forces during the campaign provoked the departure of at least 700,000 ethnic Albanians from Kosovo in the short period from late March to early June 1999."[5]
Controversy
Noam Chomsky stated that "The United Nations Commissioner for Refugees registered the first refugees outside Kosovo on 27 March ..., three days after the [NATO] bombings began".[35]
The existence of the Horseshoe plan was immediately denied by the Serbian officials. Slobodan Milošević labeled it as a "fabrication of the German Defence Ministry".[36] Milosevic denied a policy of ethnic cleansing during the NATO bombing in Kosovo, stated that "when aggression stops, when bombing stops, then it will be very easy to continue (the) political process".[37]
Ratomir Tanić, a witness at Milošević's subsequent war crimes trial, said that Horseshoe was a colloquial nickname for a "completely different" Yugoslav army plan, that should come into effect only if the ethic Albanian population take the side of the foreign aggressor in case of aggression on Yugoslavia. Then the Army would "neutralising the Albanian strongholds". Tanić stated that the army leadership didn't use this plan during the Kosovo War, "because there was no external aggression or Albanian rebellion".[38]
In April 2000, Heinz Loquai, a retired German brigadier general, published a book on the war that claimed that the German government's account had been based on a general analysis by a Bulgarian intelligence agency of Yugoslav behaviour in the war, which was turned into a specific "plan" by the German Defence Ministry.[7] According to Loquai, the Bulgarian analysis concluded that the goal of the Serbian military was to destroy the Kosovo Liberation Army, and not to expel the entire Albanian population. He also pointed to a factual flaw in the German government's presentation - it had named the plan "Potkova", which is the Croatian and Bulgarian word for horseshoe, whereas the Serbian word is potkovica.[7]
See also
- Ethnic cleansing
- Identity cleansing
- Serbian war crimes in the Yugoslav Wars
- Joint Criminal Enterprise
- War crimes in the Kosovo War
References
- ^ Did Nato miscalculate?
- ^ a b Milosevic and Operation Horseshoe, The Guardian, 18 July 1999
- ^ The Balkans in the new millennium: in the shadow of war and peace, by Tom Gallagher
- ^ a b War since 1945, by Jeremy Black
- ^ a b c d e f The verdict of the Hague Tribunal (serbian)
- ^ a b c d e f Under Orders: War Crimes in Kosovo (Human Right Watch report)
- ^ a b c Heinz Loquai: Der Kosovo-Konflikt. Wege in einen vermeidbaren Krieg. Die Zeit von Ende November 1997 bis März 1999 (in German). Nomos Verlagsgesellschaft, Baden-Baden 2000, ISBN 3789066818.
- ^ "To will the end", The Times, London, 8 April 1999
- ^ Select Committee on Foreign Affairs Fourth Report, 23 May 2000
- ^ Kosovo Chronology: From 1997 to the end of the conflict
- ^ Max Planck Yearbook of United Nations Law 2000, by Jochen Abr Frowein, Rüdiger Wolfrum
- ^ Things fall apart: containing the spillover from an Iraqi civil war, by Daniel Byman, Kenneth Michael Pollack
- ^ Report of UK Committee on Foreign Affairs
- ^ Twenty-first-century peace operations, by William J. Durch
- ^ available on Serbian
- ^ Šešelj: Karijera pretnji i uvreda
- ^ Amnesty International memorandum to UN Security Council
- ^ Collision course: NATO, Russia, and Kosovo, by John Norris
- ^ a b Presude "kosovskoj šestorki" (dobavljeno 28.12.2009.)
- ^ Erasing History: Ethnic Cleansing in Kosovo
- ^ Sustainable development in crisis conditions, by Phillip J. Cooper, Claudia María Vargas
- ^ Human geography in action, by Michael Kuby, John Harner, Patricia Gober
- ^ Ethnic Cleansing in Kosovo: An Accounting
- ^ Human Rights Practices - 2002
- ^ KFOR Pictures - Refugees
- ^ UNHCR Press Briefing Note: Kosovo, Tuesday, 2 February 1999.
- ^ UNHCR Pristina,"IDP/Shelter Survey Kosovo: Joint Assessment in 20 Municipalities," 12 November 1998.
- ^ UNHCR Press Briefing Note: Kosovo, 13 April 1999.
- ^ UNHCR Press Briefing Note: Kosovo, 13 May 1999.
- ^ Statistic from: "The Kosovo refugee crisis: an independent evaluation of UNHCR's emergency preparedness and response," UNHCR Evaluation and Policy Analysis Unit, February 2000.
- ^ Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (Kosovo): After tragedy, justice?
- ^ Laura Rozen: Serbia's culture shock
- ^ Air University - Serbian Information Operations During Operation Allied Force
- ^ Indictment against Milosevic and others
- ^ Is this really a grand NATO victory?, Noam Chomsky, New Statesman, 14 June 1999
- ^ [1]
- ^ Milosevic denies ethnic cleansing
- ^ [2]
External links
- Operation Horseshoe (Committee on Foreign Affairs Report)
- Milosevic and Operation Horseshoe, The Guardian, 18 July 1999
- Erasing History: Ethnic Cleansing in Kosovo (Report released by the U.S. Department of State)
- "Operation Horseshoe" —propaganda and reality (World Socialist Web Site)
Categories:- Military operations of the Kosovo War
- Kosovo War
- Forgery
- Propaganda
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.