- Copper(II) nitrate
-
Copper(II) nitrate 
 Copper(II) nitrateOther namesCupric nitrate
Copper(II) nitrateOther namesCupric nitrateIdentifiers CAS number 3251-23-8 
PubChem 18616 ChemSpider 17582 
UNII 9TC879S2ZV 
RTECS number GL7875000 Jmol-3D images Image 1 - [Cu+2].[O-][N+]([O-])=O.[O-][N+]([O-])=O
Properties Molecular formula Cu(NO3)2 Molar mass 187.56 g/mol ( Appearance blue crystals
hygroscopicDensity 3.05 g/cm3 (anhydrous)
2.32 g/cm3 (trihydrate)
2.07 g/cm3 (hexahydrate)Melting point 256 °C (anhydrous, decomp)
114 °C (trihydrate)
26 °C (hexahydrate, decomposes)Boiling point 170 °C (trihydrate, decomposes)
Solubility in water 137.8 g/100 mL (0 °C) (trihydrate) Solubility hydrates very soluble in ethanol, water Structure Crystal structure orthorhombic (anhydrous)
rhombohedral (hydrates)Hazards MSDS Cu(NO3)2·3H2O EU Index Not listed Main hazards Irritant, Oxidizer NFPA 704 Related compounds Other anions Copper(II) sulfate
Copper(II) chlorideOther cations Nickel(II) nitrate
Zinc nitrate nitrate (verify) (what is:
nitrate (verify) (what is:  /
/ ?)
?)
Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa)Infobox references Copper(II) nitrate is the chemical compound with the formula Cu(NO3)2. Commonly referred to simply as copper nitrate, the anhydrous form is a blue, crystalline solid. Hydrated forms of copper nitrate, also blue, are commonly used in school laboratories to demonstrate chemical voltaic cell reactions.
Contents
Synthesis and reactions
Cu(NO3)2 forms when copper metal is treated with N2O4:[1]
- Cu + 2 N2O4 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2 NO
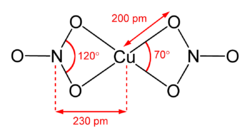
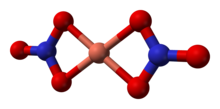
The structure of anhydrous Cu(NO3)2(gas)[2] Hydrated copper nitrate can be prepared by hydrolysis of the anhydrous material or by treating copper metal with an aqueous solution of silver nitrate or concentrated nitric acid:
- Cu + 4 HNO3 → Cu(NO3)2 + 2 H2O + 2 NO2
Copper nitrate can be used to generate nitric acid by heating it until decomposition and passing the fumes directly into water. This method is similar to the last step in the Ostwald process. The equations are as follows:
- 2 Cu(NO3)2 → 2 CuO + 4 NO2 + O2
- 3NO2 + H2O → 2HNO3 + NO
Use in organic synthesis
Copper nitrate, in combination with acetic anhydride, is an effective reagent for nitration of aromatic compounds, under what are known as "Menke conditions", in honor of the Dutch chemist who discovered that metal nitrates are effective reagents for nitration.[3] Hydrated copper nitrate absorbed onto clay affords a reagent called "Claycop". The resulting blue-colored clay is used as a slurry, for example for the oxidation of thiols to disulfides. Claycop is also used to convert dithioacetals to carbonyls.[4] A related reagent based on montmorillonite has proven useful for the nitration of aromatic compounds.[5]
References
- ^ Jolly, W. L. "The Synthesis and Characterization of Inorganic Compounds" Prentice Hall, London, 1970
- ^ Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd Edition, Oxford:Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- ^ Menke J.B. (1925). "Nitration with nitrates". Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Payes-Bas 44: 141.
- ^ Balogh, M. "Copper(II) Nitrate–K10 Bentonite Clay" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. DOI: 10.1002/047084289.
- ^ Collet, C.; Delville, A.; Laszlo, P. “Clays Direct Aromatic Nitration” Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English, 2003, Volume 29, Issue 5 , Pages 535–536. doi:10.1002/anie.199005351.
External links
Copper compounds Categories:- Copper compounds
- Nitrates
- Pyrotechnic oxidizers
- Pyrotechnic colorants
- Oxidizing agents
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


