- Carbon trioxide
-
"CO3" redirects here. For the polyatomic ion CO2−
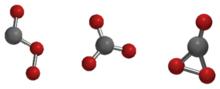
3, see Carbonate. For the postal district, see CO postcode area.Carbon trioxide (CO3) is an unstable oxide of carbon (an oxocarbon). Three possible isomers of carbon trioxide, denoted Cs, D3h, and C2v, have been most studied by theoretical methods, and the C2v state has been shown to be the ground state of the molecule.[1][2]
Carbon trioxide should not be confused with the stable carbonate ion (CO32−).
Carbon trioxide can be produced, for example, in the drift zone of a negative corona discharge by reactions between carbon dioxide (CO2) and the atomic oxygen (O) created from molecular oxygen by free electrons in the plasma.[3]
Another reported method is photolysis of ozone O3 dissolved in liquid CO2, or in CO2/SF6 mixtures at -45°C, irradiated with light of 2537 Å. The formation of CO3 is inferred but it appears to decay spontaneously by the route 2CO3 → 2CO2 + O2 with a lifetime much shorter than 1 minute.[4]
Carbon trioxide can be made by blowing ozone at dry ice (solid CO2), and it has also been detected in reactions between carbon monoxide (CO) and molecular oxygen (O2).
References
- ^ Tim Kowalczyk, Electronic structure and spectroscopy of carbon trioxide
- ^ Kowalczyk, T; Krylov, AI (Aug 2007). "Electronic structure of carbon trioxide and vibronic interactions involving Jahn-Teller states". J. Phys. Chem. A 111 (33): 8271–8276. doi:10.1021/jp073627d. ISSN 1089-5639. PMID 17661455.
- ^ Sabin, J. R; Kim, H (1971). "A theoretical study of the structure and properties of carbon trioxide". Chemical Physics Letters 11 (5,): 593–597. Bibcode 1971CPL....11..593S. doi:10.1016/0009-2614(71)87010-0.
- ^ DeMore W. B., Jacobsen C. W. (1969). "Formation of carbon trioxide in the photolysis of ozone in liquid carbon dioxide". Journal of Physical Chemistry 73 (9): 2935–2938. doi:10.1021/j100843a026.
Further reading
- Electronic structure and spectroscopy of carbon trioxide
- Sobek V., Skalný J. D. (1993). "A simple model of processes in the drift region of negative corona discharge in a mixture of air with halocarbons". Czechoslovak Journal of Physics 43 (8): 807. doi:10.1007/BF01589802. http://springerlink.com/content/n8qq2t7q21711481/.
- Pople J. A. , Seeger U., Seeger R., Schleyer P. v. R. (2004). "The structure of carbonate". Journal of Computational Chemistry 1 (2): 199–203. doi:10.1002/jcc.540010215.
- Moll N. G., Clutter D. R., Thompson W. E. (1966). "Carbonate: Its Production, Infrared Spectrum, and Structure Studied in a Matrix of Solid CO2". The Journal of Chemical Physics 45 (12): 4469–4481. doi:10.1063/1.1727526.
- Gimarc B. M., Chou T. S. (1968). "Geometry and Electronic Structure of Carbon Trioxide". The Journal of Chemical Physics 49 (9): 4043–4047. doi:10.1063/1.1670715.
- DeMore W. B., Dede C. (1970). "Pressure dependence of carbon trioxide formation in the gas-phase reaction of O(1D) with carbon dioxide". Journal of Physical Chemistry 74 (13): 2621–2625. doi:10.1021/j100707a006.
- Francisco J. S., Williams I. H. (1985). "A theoretical study of the force field for carbon trioxide". Chemical Physics 95 (3): 373. doi:10.1016/0301-0104(85)80160-9.
Oxocarbons Common oxides Exotic oxides Compounds derived from oxides Categories:- Oxocarbons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.