- Mevalonate pathway
-
The mevalonate pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway or mevalonate-dependent (MAD) route or isoprenoid pathway, is an important cellular metabolic pathway present in all higher eukaryotes and many bacteria. It is important for the production of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP) and isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP), which serve as the basis for the biosynthesis of molecules used in processes as diverse as terpenoid synthesis, protein prenylation, cell membrane maintenance, hormones, protein anchoring, and N-glycosylation. It is also a part of steroid biosynthesis.
Contents
Regulation and feedback
Several key enzymes can be activated through DNA transcriptional regulation on activation of SREBP (sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 and -2). This intracellular sensor detects low cholesterol levels and stimulates endogenous production by the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, as well as increasing lipoprotein uptake by up-regulating the LDL-receptor. Regulation of this pathway is also achieved by controlling the rate of translation of the mRNA, degradation of reductase and phosphorylation.
- For more information on regulation, see HMG-CoA reductase
Pharmacology
A number of drugs target the mevalonate pathway:
- Statins (used to decrease cholesterol levels);
- Bisphosphonates (used to treat various bone-degenerative diseases)
Alternative
Plants and apicomplexan protozoa such as malaria parasites have the ability to produce their isoprenoids (terpenoids) using an additional alternative pathway called the methylerythritol phosphate (MEP) or non-mevalonate pathway, which takes place in their plastids. In addition, most bacteria including important pathogens, such as Mycobacterium tuberculosis, synthesize IPP and DMAPP via the non-mevalonate pathway instead.
Reactions
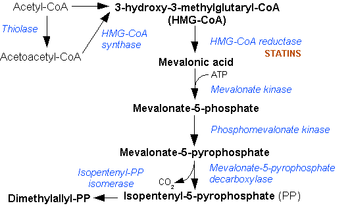
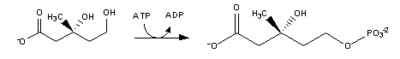
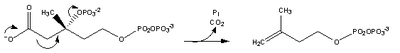
Reaction Diagram Enzyme Acetyl-CoA (citric acid cycle) undergoes condensation with another acetyl-CoA subunit via Acetyl-CoA Transferase to form acetoacetyl-CoA thiolase Acetyl-CoA condenses with acetoacetyl-CoA to form 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA (HMG-CoA). HMG-CoA synthase HMG-CoA is reduced to mevalonate by NADPH. This reaction occurs in the cytosol. It is the rate limiting step in cholesterol synthesis, which is why the enzyme catalyzing the reaction is a target of statins. HMG-CoA reductase Mevalonate to 5-phosphomevalonate. mevalonate kinase 5-phosphomevalonate to 5-pyrophosphomevalonate. phosphomevalonate kinase Mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate to 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) (see also HIDS).
mevalonate-5-pyrophosphate decarboxylase 3-isopentenyl pyrophosphate is isomerized to dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase References
- Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L. Biochemistry. 5th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman. xxxviii, 974, [976] (various pagings). ISBN 0-7167-4684-0.
- Swanson KM, Hohl RJ. Anti-cancer therapy: targeting the mevalonate pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 2006;6:15-37. PMID 16475974.
External links
- Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute page on cholesterol synthesis (including regulation)
Mevalonate pathway To HMG-CoAAcetyl-Coenzyme A acetyltransferase · HMG-CoA synthase (regulated step)To DMAPPGeranyl-To cholesterol To lanosterol7-Dehydrocholesterol pathDesmosterol pathTo Bile acids Steroidogenesis To pregnenoloneTo sex hormonesTo androgensTo estrogensOther/ungroupedCategories:- Metabolic pathways
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.