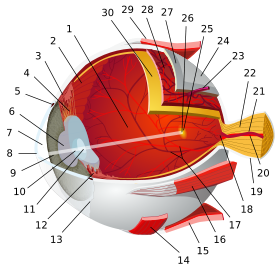
- Nerve fiber layer
-
Nerve fiber layer 
Section of retina. (Stratum opticum labeled at right, second from the top.) 
Plan of retinal neurons. (Stratum opticum labeled at left, second from the top.) Latin stratum neurofibrum retinae Gray's subject #225 1015 The retinal nerve fiber layer (nerve fiber layer, stratum opticum, RNFL) is formed by the expansion of the fibers of the optic nerve; it is thickest near the porus opticus, gradually diminishing toward the ora serrata.
As the nerve fibers pass through the lamina cribrosa sclerae they lose their medullary sheaths and are continued onward through the choroid and retina as simple axis-cylinders.
When they reach the internal surface of the retina they radiate from their point of entrance over this surface grouped in bundles, and in many places arranged in plexuses.
Most of the fibers are centripetal, and are the direct continuations of the axis-cylinder processes of the cells of the ganglionic layer, but a few of them are centrifugal and ramify in the inner plexiform and inner nuclear layers, where they end in enlarged extremities.
Patients with retinitis pigmentosa have abnormal thinning of the RNFL which correlates with the severity of the disease.[1] However the thickness of the RNFL also decreases with age and not visual acuity.[2] The sparing of this layer is important in the treatment of the disease as it is the basis for connecting retinal prostheses to the optic nerve, or implanting stem cells that could regenerate the lost photoreceptors.
RNFL is a sensitive structure. Some process can excites its natural apoptosis. Harmful situation can make some damage on RNFL such as high intraocular pressure, high fluctuation on phase of intraocular pressure, inflammation, vascular disease and any kind of hypoxia. Gede Pardianto (2009) reported 6 cases of RNFL thickness change after the procedures of phacoemulsification.[3]
References
- ^ Walia S, Fishman GA, Edward DP, Lindeman M. Retinal nerve fiber layer defects in RP patients. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007 Oct;48(10):4748-52. PMID: 17898300
- ^ Oishi A, Otani A, Sasahara M, Kurimoto M, Nakamura H, Kojima H, Yoshimura N. Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in patients with retinitis pigmentosa. Eye. 2008 Mar 14, online advance publication. PMID: 18344951
- ^ Pardianto G, Mastering phacoemulsification in Mimbar Ilmiah Oftalmologi Indonesia.2009;10:26.
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Sensory system – visual system – globe of eye (TA A15.2.1–6, TH 3.11.08.0-5, GA 10.1005) Fibrous tunic (outer) Episcleral layer • Schlemm's canal • Trabecular meshworkUvea/vascular tunic (middle) Retina (inner) LayersCellsPhotoreceptor cells (Cone cell, Rod cell) → (Horizontal cell) → Bipolar cell → (Amacrine cell) → Retina ganglion cell (Midget cell, Parasol cell, Bistratified cell, Giant retina ganglion cells, Photosensitive ganglion cell) → Diencephalon: P cell, M cell, K cell
Muller gliaOtherAnterior segment Posterior segment Other M: EYE
anat(g/a/p)/phys/devp/prot
noco/cong/tumr, epon
proc, drug(S1A/1E/1F/1L)
Categories:- Eye anatomy
- Neuroscience stubs
- Eye stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.