- Double harmonic scale
-
In music, the double harmonic major scale[1] is a scale whose gaps may evoke "exotic" music to Western listeners. This is also known as the Arabic and [1][2] the Byzantine scale. It is also likened to the gypsy scale because of the augmented 2 between the 2nd and 3rd degrees. Arabic scale may also refer to any Arabic mode, the simplest of which, however, to Westerners, resembles the double harmonic major scale.[3].
The sequence of steps comprising the double harmonic scale is:
- half – augmented second – half – whole – half – augmented second – half.
Or, in relation to the tonic note:
- minor 2nd, major 3rd, perfect 4th and 5th, minor 6th, major 7th.
However, this scale is commonly represented with the first and last half step each being represented as a quarter tone. The non-quarter tone form (
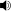 Play (help·info)) is identical to the North Indian Thaat named Bhairav and the South Indian (Carnatic) Melakarta named Mayamalavagowla.
Play (help·info)) is identical to the North Indian Thaat named Bhairav and the South Indian (Carnatic) Melakarta named Mayamalavagowla.The double harmonic scale is arrived at by either:
- raising the seventh of the Phrygian dominant scale, (a mode of the harmonic minor scale), by a semitone.
- raising the seventh and third of the Phrygian mode, (a mode of the Major Scale), by a semitone.
- lowering both the sixth and second of a major scale by a semitone.
- lowering the 2nd note of a harmonic major scale by a semitone.
- combining the lower half of phrygian dominant with the upper half of harmonic minor[1]
It is referred to as the "double harmonic" scale because it contains two augmented seconds. By contrast both the harmonic major and harmonic minor scales contain only one augmented second, located between their sixth and seventh degrees.
The double harmonic scale is uncommonly used in classical music from Western culture, as it does not closely follow any of the basic musical modes, nor is it easily derived from them. It also does not easily fit into common Western chord progressions such as the authentic cadence. The Arabic scale (in the key of E) was used in Nikolas Roubanis's "Misirlou", and Claude Debussy used the scale in "Soirée dans Grenade", "La Puerta del Vino", and "Sérénade interrompue" to evoke Spanish flamenco music or Moorish heritage[4]. A commonly known usage in western music is The Cure's "Killing An Arab"[citation needed]. The scale is also popular in India[2].
Contents
Symmetry
The double harmonic scale features radial symmetry, or symmetry around its root, or center note. Breaking up the three note chromaticism and removing this symmetry by sharpening the 2nd or flattening the 7th note respectively by one semitone yields the harmonic major and Phrygian Dominant mode of the harmonic minor scales respectively, each of which, unlike the double harmonic minor scale, has a full diminished chord backbone.
Modes
Like most heptatonic (seven pitches in the octave) scales, the double harmonic scale has a mode for each of its individual scale degrees. The most commonly known of these modes is the 4th mode, the Hungarian gypsy scale, most similar to the harmonic minor scale with a raised 4th degree.
The second mode is somewhat of a hybrid between the blues scale (contains a #4) and bebop scale (both #6 and 7).
Relationship to Phrygian major (Jewish scale)
The nearest other existing scale to the double harmonic scale is the Phrygian dominant scale. The double harmonic scale may be made from a Phrygian dominant scale by sharpening its 7th degree.
Sources
- ^ a b c Stetina, Troy (1999). The Ultimate Scale Book, p.59. ISBN 0793597889.
- ^ a b Christiansen, Mike (2003). Mel Bay Complete Guitar Scale Dictionary, p.43. ISBN 0786669942.
- ^ "R. G. Kiesewetter's 'Die Musik der Araber': A Pioneering Ethnomusicological Study of Arabic Writings on Music", p.12. Philip V. Bohlman. Asian Music, Vol. 18, No. 1. (Autumn - Winter, 1986), pp. 164-196.
- ^ Elie Robert Schmitz, Virgil Thomson (1966). The piano works of Claude Debussy, p.28. ISBN 0486215679.
See also
Musical scales Main Western Types Bebop · Diatonic · Enharmonic · Jazz · Synthetic
Name Acoustic · Alpha scale · Altered · Beta scale · Blues · Bohlen-Pierce · Double harmonic · Enigmatic · Gamma scale · Half diminished · Harmonic major · Harmonic Scale · Lydian dominant · Major locrian · Misheberak · Phrygian dominant · Whole tone
Ethnic origin Algerian · Arabic (Double harmonic • Major locrian • Quarter tone • 17 equal temperament) · Gamelan pelog · Gamelan slendro · Gypsy · Hungarian gypsy · Hungarian minor · Neapolitan minor and major · Persian · Ukrainian minor · Yo · In
Modes Modes in Western music Gregorian Other Diatonic Minor Melodic minor (I) · Dorian ♭2 (II) · Lydian Augmented (III) · Lydian Dominant (IV) · Mixolydian ♭13 (V) · Locrian ♮2 (VI) · Altered (VII)See also Properties of musical modesNumber of tones Pentatonic · Hexatonic · Heptatonic · Octatonic · Chromatic
Categories:- Modes
- Scales with unusual key signatures
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.



