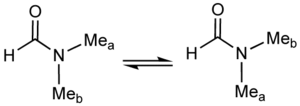- Fluxional molecule
-
Fluxional molecules are molecules that undergo dynamics such that some or all of their atoms interchange between symmetry-equivalent positions. Because virtually all molecules are fluxional in some respects, e.g. bond rotations in most organic compounds, the term fluxional depends on the context and the method used to assess the dynamics. Often, a molecule is considered fluxional if its spectroscopic signature exhibits line-broadening (beyond that dictated by the Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle) due to chemical exchange. In some cases, where the rates are slow, fluxionality is not detected spectroscopically, but by isotopic labeling.
Contents
Carbonium ion
The prototypical fluxional molecule is the carbonium ion, which is protonated methane, CH5+.[1][2][3] In this unusual species, whose IR spectrum was recently experimentally observed[4][5] and more recently understood,[6] the barriers to proton exchange are lower than the zero point energy. Thus, even at absolute zero there is no rigid molecular structure, the H atoms are always in motion. More precisely, the spatial distribution of protons in CH5+ is many times broader than its parent molecule CH4, methane.[7][8]
NMR spectroscopy
A classic example of a fluxional molecule is dimethylformamide.[9]
At temperatures near 100 °C, the 500 MHz NMR spectrum of this compound shows only one signal for the methyl groups. Near room temperature however, separate signals are seen for the non-equivalent methyl groups. The rate of exchange can be readily calculated at the temperature where the two signals are just merged. This "coalescence temperature" depends on the measuring field. The relevant equation is:
- k = πΔνo/21/2 ~ 2 Δνo
where Δνo is the difference in Hz between the frequencies of the exchanging sites. These frequencies are obtained from the limiting low-temperature NMR spectrum. At these lower temperatures, the dynamics continue, of course, but the contribution of the dynamics to line broadening is negligible.
For example, if Δνo = 1ppm @ 500 MHz
- k ~ 2(500) = 1000 s-1 (ca. 0.5 millisecond half-life)
Many molecular processes exhibit fluxionality that can be probed on the NMR time scale. Well-known examples include:
- Cope rearrangement in bullvalene and other 1,5-dienes.
- Berry pseudorotation in iron pentacarbonyl and phosphorus pentafluoride.
- chair inversion in cyclohexane.
IR spectroscopy
Although less common, some dynamics are also observable on the time-scale of IR spectroscopy. One example is electron transfer in a mixed valence dimer of metal clusters. Application of above equation for coalescence of two signals separated by 10 cm−1 gives the following result:[10]
- k ~ 2 Δνo ~ 2(10 cm-1)(300 x 108 cm/s) ~ 6 x 1011 s-1
Clearly, processes that induce line-broadening on the IR time-scale must be extremely rapid.
References
- ^ Kramer, G. M. (1999). Science 286: 1051.
- ^ Oka, T.; White, E. T. (1999). Science 286: 1051.
- ^ Marx, D.; Parrinello, M. (1999). Science 286: 1051.
- ^ D. W. Boo, Z. F. Liu, A. G. Suits, J. S. Tse, Y. T. Lee (1995). "Dynamics of Carbonium Ions Solvated by Molecular Hydrogen: CH5+(H2)n (n = 1, 2, 3)". Science 269 (5220): 57–9. doi:10.1126/science.269.5220.57. PMID 17787703.
- ^ E. T. White, J. Tang, T. Oka (1999). "CH5+: The infrared spectrum observed". Science 284 (5411): 135–7. doi:10.1126/science.284.5411.135. PMID 10102811.
- ^ Asvany, O.; Kumar P, P.; Redlich, B.; Hegemann, I.; Schlemmer, S.; Marx, D. (2005). "Understanding the Infrared Spectrum of Bare CH5+". Science 309 (5738): 1219–1222. doi:10.1126/science.1113729. PMID 15994376.
- ^ Thompson, KC; Crittenden, DL; Jordan, MJ (2005). "CH5+: Chemistry's chameleon unmasked". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127 (13): 4954–4958. doi:10.1021/ja0482280. PMID 15796561.
- ^ For an animation of the dynamics of CH5+, see http://www.theochem.ruhr-uni-bochum.de/research/marx/topic4b.en.html
- ^ H. S. Gutowsky; C. H. Holm (1956). "Rate Processes and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectra. II. Hindered Internal Rotation of Amides". J. Chem. Phys. 25 (6): 1228–1234. doi:10.1063/1.1743184.
- ^ Casey H. Londergan author2 = Clifford P. Kubiak; Kubiak, Clifford P. (2003). "Electron Transfer and Dynamic Infrared-Band Coalescence: It Looks Like Dynamic NMR Spectroscopy, but a Billion Times Faster". Chemistry, a European Journal 9 (24): 5969ff. doi:10.1002/chem.200305028.
Categories:- Chemical compounds
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.