- Nucleus ambiguus
-
Brain: Nucleus ambiguus 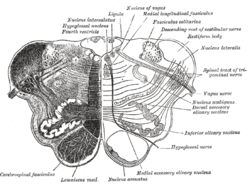
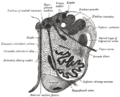
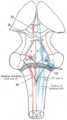
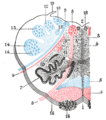
Transverse section of medulla oblongata below the middle of the olive. ("Nucleus ambiguus" labeled at center right.) Gray's subject #187 779 NeuroNames hier-762 NeuroLex ID birnlex_2650 The nucleus ambiguus (literally "ambiguous nucleus") is a region of histologically disparate cells located just dorsal (posterior) to the inferior olivary nucleus in the lateral portion of the upper (rostral) medulla. It receives upper motor neuron innervation directly via the corticobulbar tract.
This nucleus gives rise to the branchial efferent motor fibers of the vagus nerve (CN X) terminating in the laryngeal and pharyngeal muscles, as well as to the efferent motor fibers of the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) terminating in the stylopharyngeus.
Contents
Areas supplied
The muscles supplied by the vagus (included with this is the cranial part of the accessory nerve), such as levator veli palatini, are also necessary to swallow properly through integration by the nucleus of the solitary tract. The vagus also supplies the upper part of the esophagus, and other parts of the pharynx and larynx.
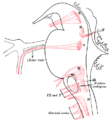
As well as motor neurons, the nucleus ambiguus in its "external formation" contains cholinergic preganglionic parasympathetic neurons for the heart.[1] These neurons are cardioinhibitory [2] This cardioinhibitory effect is one of the means by which quick changes in blood pressure are achieved by the central nervous system (the primary means being changes in sympathetic nervous system activity, which constricts arterioles and makes the heart pump faster and harder). That is, through integrated and antagonistic system with sympathetic outflow from the vasomotor center of the brainstem, the parasympathetic outflow arising from the nucleus ambiguus and dorsal motor nucleus of the vagus nerve acts to decrease cardiac activity in response to fast increases in blood pressure. The external formation of the nucleus ambiguus also sends bronchoconstrictor fibers to the bronchopulmonary system, which can produce reflexive decreases in pulmonary bronchial airflow. The pathophysiologic relevance of this system, which may act in concert with the cardioinhibitory system, is poorly understood, but likely plays a role in bronchospastic diseases like COPD/emphysema (in which inhaled anticholinergic medications such as Spiriva/tiotropium or ipratropium are standard-of-care treatment) and asthma, particularly for exercise-related asthma exacerbations, which may have a component of autonomic dysregulation.
Additional images
References
- ^ Role of the nucleus ambiguus in the regulation of heart rate and arterial pressure. BH Machado and MJ Brody. http://hyper.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/11/6/602
- ^ Localization of vagal cardioinhibitory preganglionic neurons with rat brain stem. Nosaka S et al. http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/109685993/abstract
External links
- Medical Neurosciences discuss the nucleus ambiguus.
- -1664090053 at GPnotebook
Human brain: rhombencephalon, myelencephalon: medulla (TA A14.1.04, GA 9.767) Dorsal SurfacePosterior median sulcus · Posterolateral sulcus · Area postrema · Vagal trigone · Hypoglossal trigone · Medial eminenceafferent: GVA: VII,IX,X: Solitary/tract/Dorsal respiratory group · SVA: Gustatory nucleus · GSA: VIII-v (Lateral, Medial, Inferior)
efferent: GSE: XII · GVE: IX,X,XI: Ambiguus · SVE: X: Dorsal · IX: Inferior salivatory nucleusGrey: otherWhite: Sensory/ascendingWhite: Motor/descendingVentral White: Motor/descendingVentral respiratory group · Arcuate nucleus of medulla · Inferior olivary nucleus · Rostral ventromedial medullaSurfaceGrey: Raphe/
reticularNerves of head and neck: the cranial nerves and nuclei (TA A14.2.01, GA 9.855) olfactory (AON->I) optic (LGN->II) oculomotor
(ON, EWN->III)trochlear (TN->IV) no significant branchestrigeminal
(PSN, TSN, MN, TMN->V)abducens (AN->VI) no significant branchesfacial (FMN, SN, SSN->VII) near origininside
facial canalvestibulocochlear
(VN, CN->VIII)glossopharyngeal
(NA, ISN, SN->IX)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossavagus
(NA, DNVN, SN->X)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossaaccessory (NA, SAN->XI) hypoglossal (HN->XII) Categories:- Brainstem
- Cranial nerves
- Neuroanatomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.